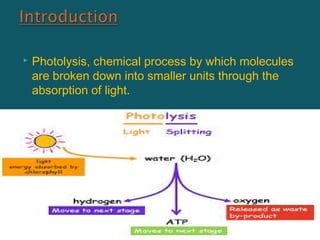
Photolysis is a chemical process where molecules are broken down by light absorption. Flash photolysis is commonly used to study short-lived intermediates in photochemical reactions, employing a photolysis flash to initiate reactions followed by a monitoring flash to measure absorption spectra. To study processes in the nanosecond time range, lasers can be used to generate photolysis pulses less than 20 nanoseconds, allowing observation of excited singlet state lifetimes and other fast reactions. Laser flash photolysis systems employ a laser pulse to synchronize a photolysis spark and provide pulses to initiate reactions and monitor absorption on nanosecond timescales, enabling identification of transient intermediates and insight into fast reaction mechanisms.