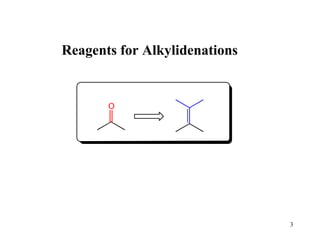
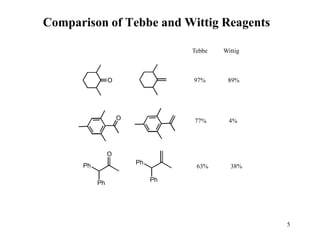
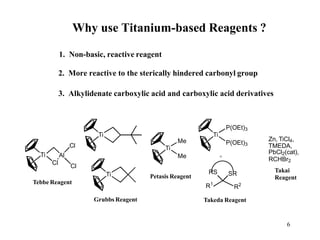
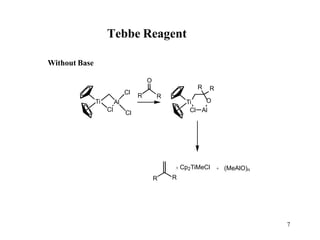
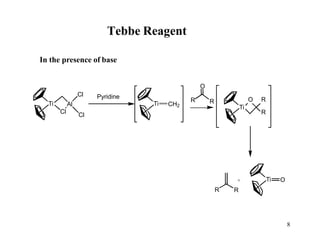
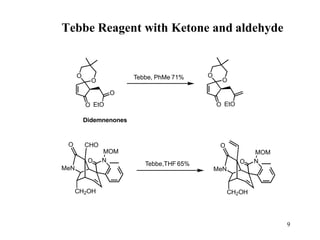
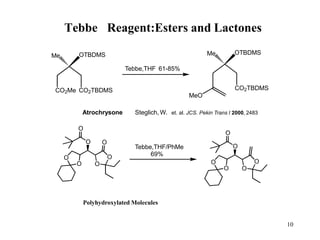
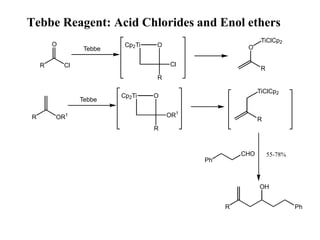
The Tebbe reagent is an organometallic compound used to convert carbonyl compounds to the related alkene derivative through methylenation. It contains titanium and is more reactive than Wittig reagents, especially for sterically hindered carbonyl groups. The Tebbe reagent can methylenate a wide range of functional groups and generates the reactive titanium methylidene at low temperature, though it is highly sensitive to moisture and air.