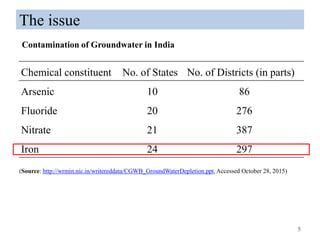
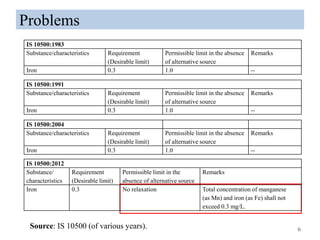
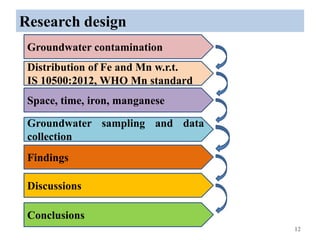
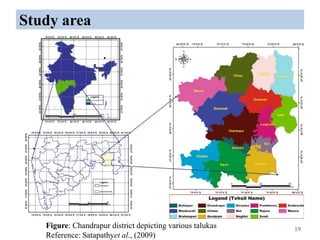
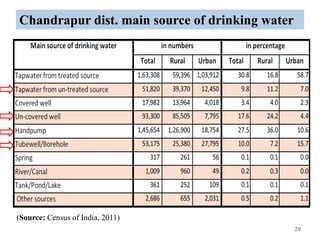
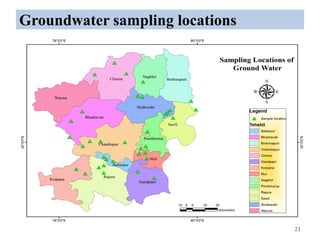
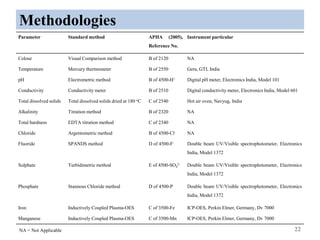
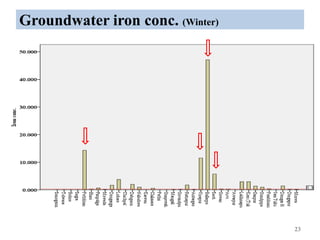
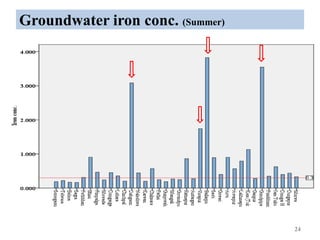
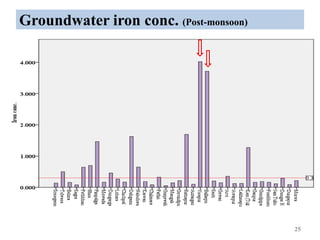
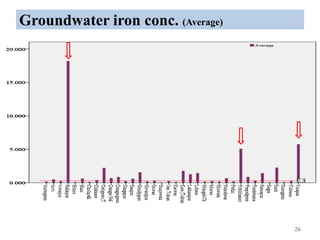
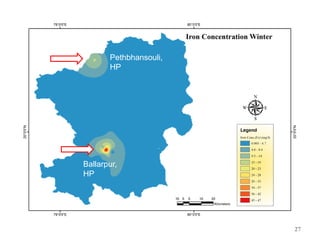
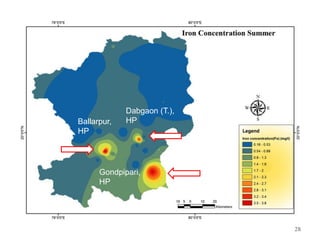
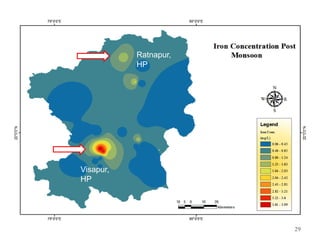
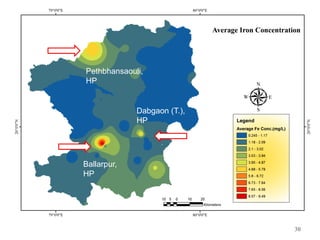
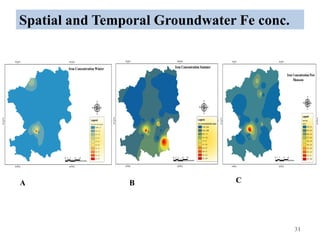
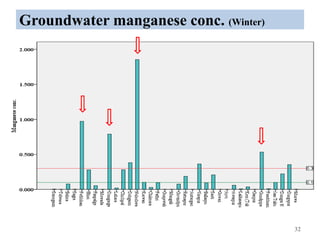
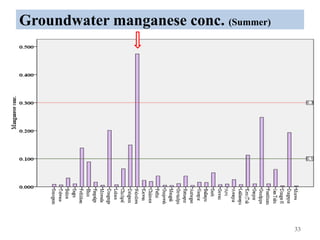
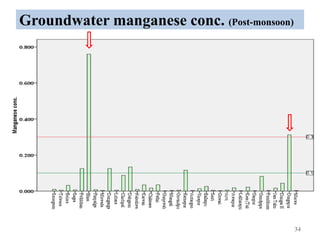
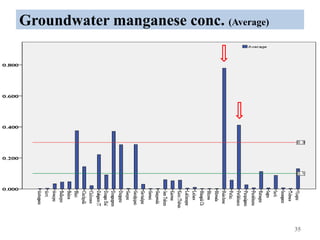
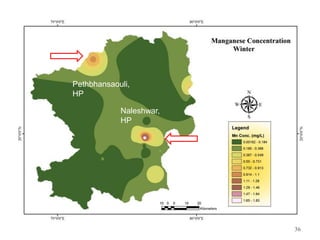
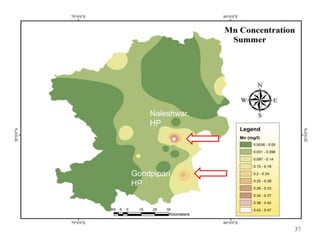
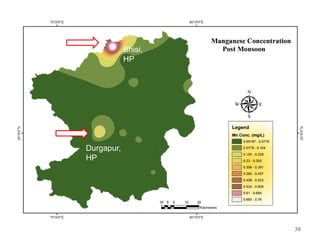
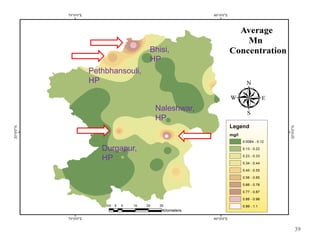
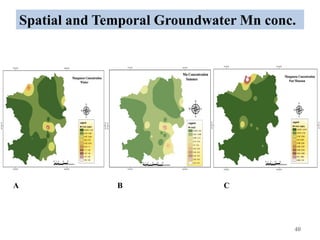
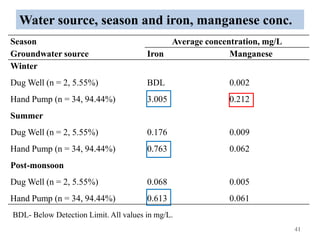
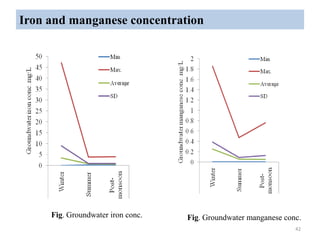
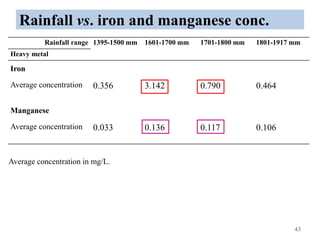
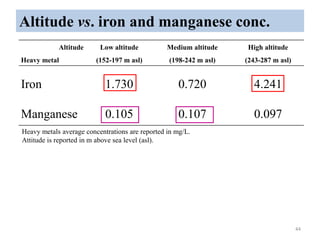
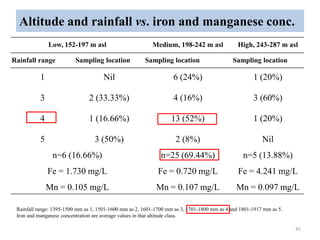
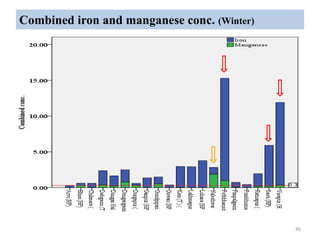
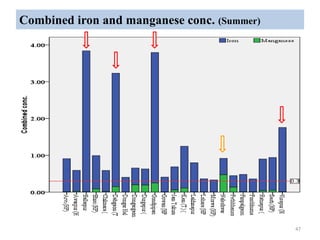
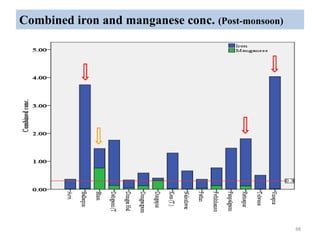
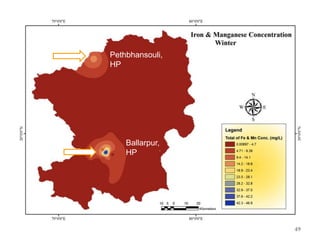
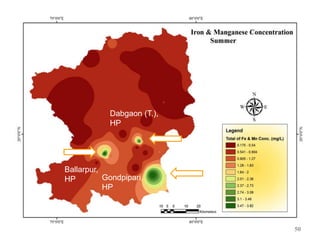
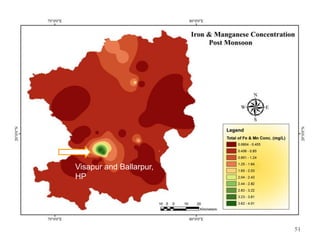
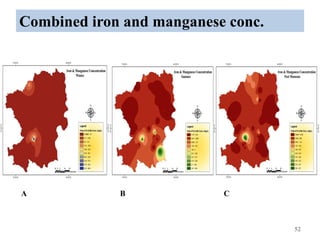
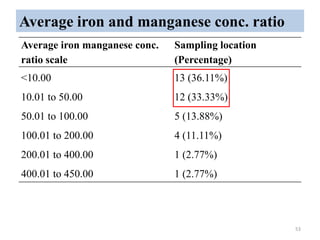
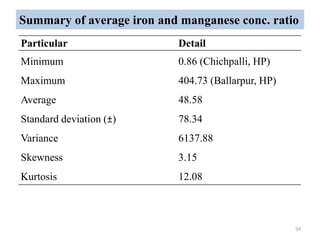
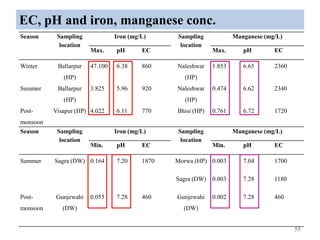
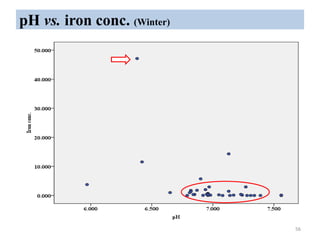
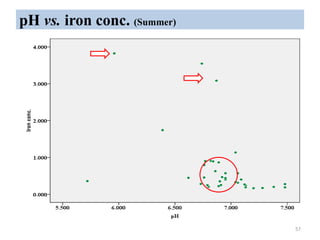
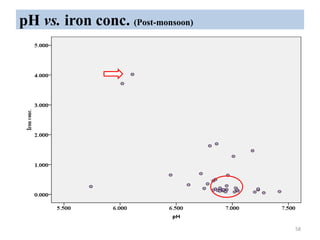
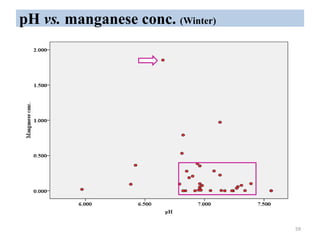
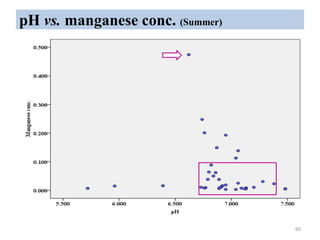
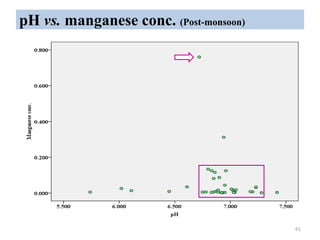
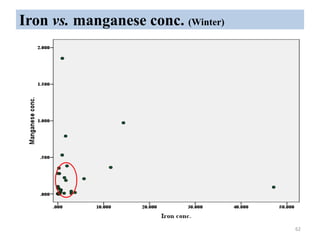
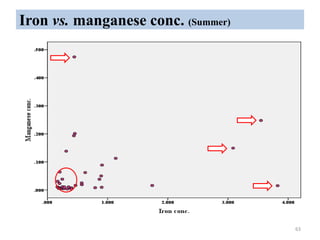
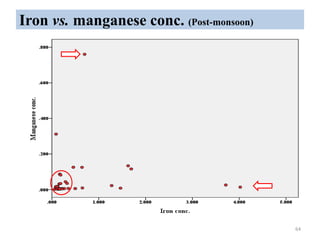
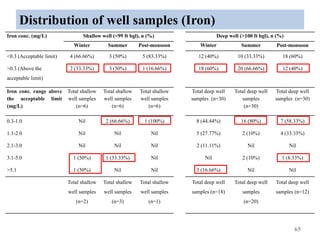
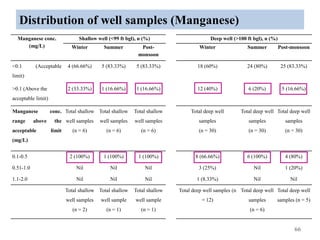
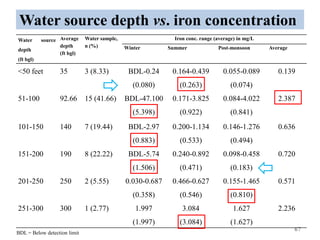
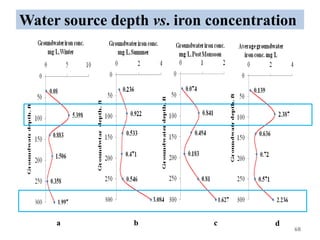
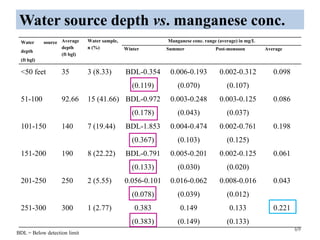
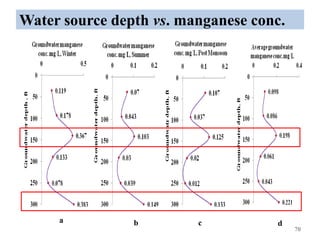
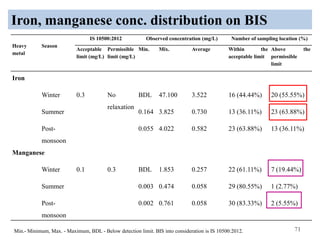
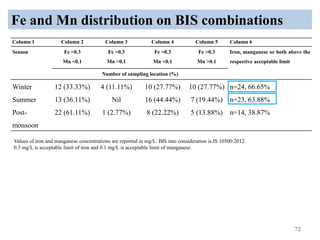
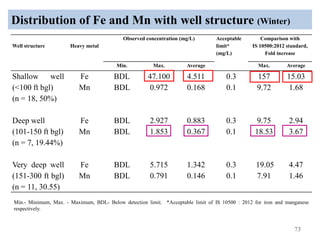
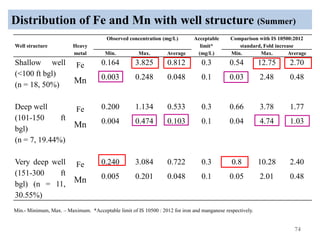
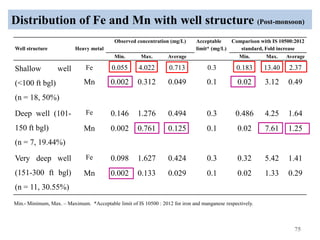
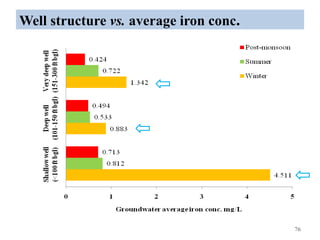
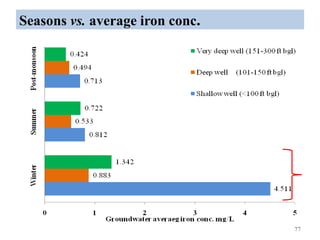
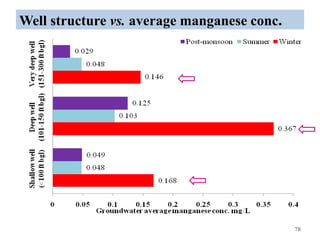
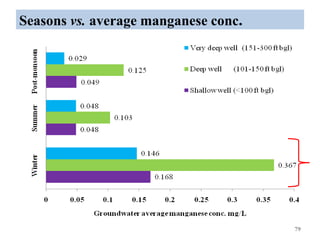
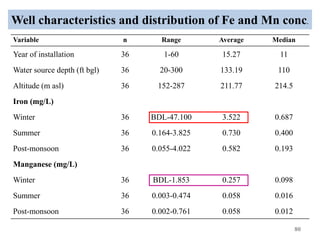
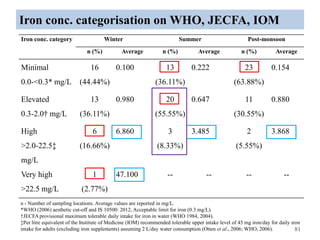
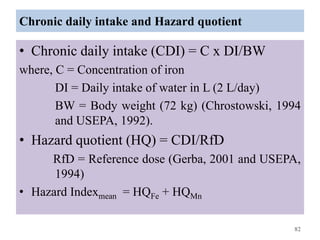
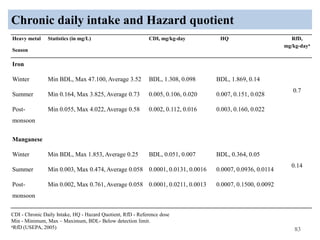
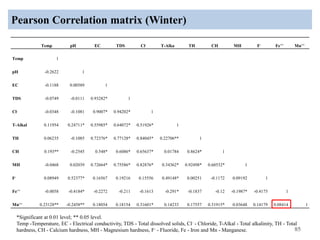
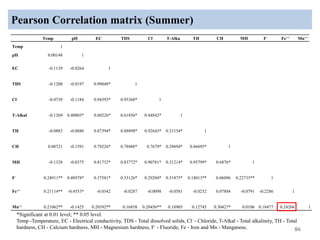
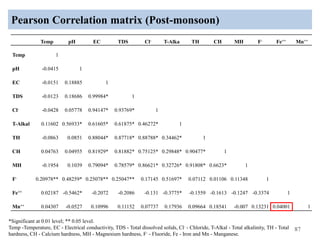
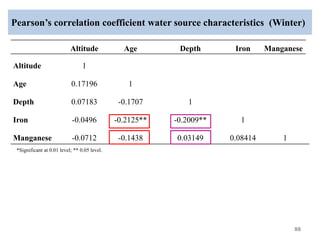
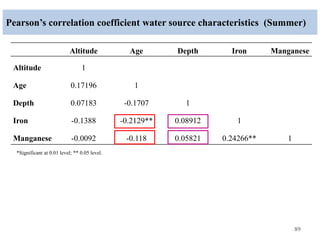
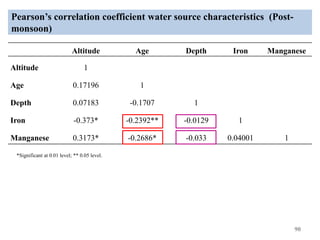
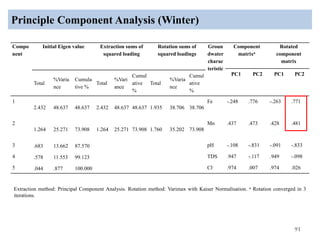
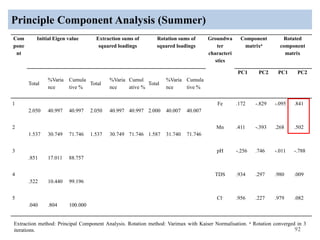
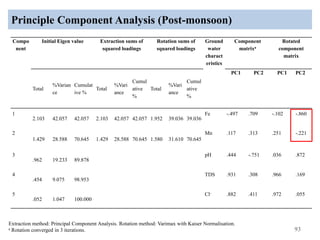
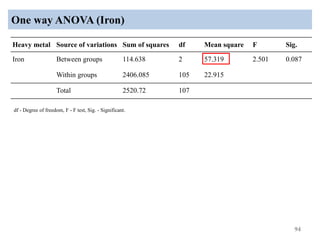
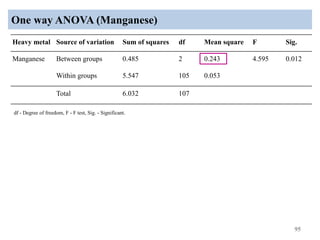
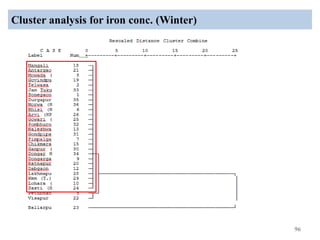
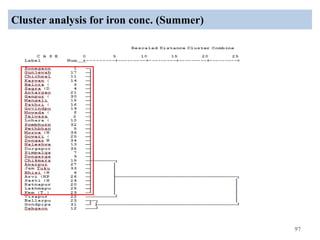
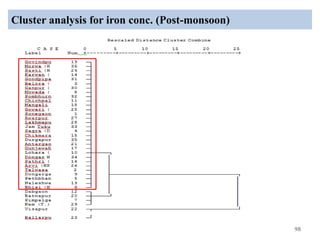
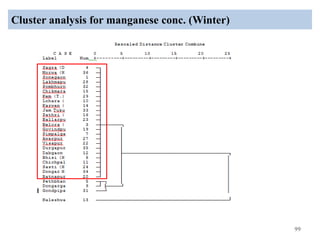
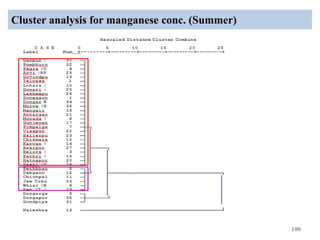
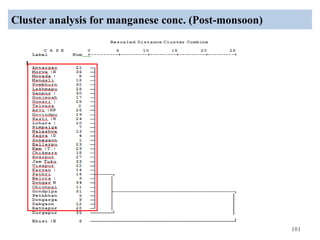
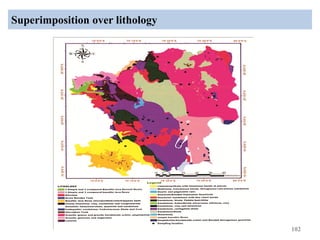
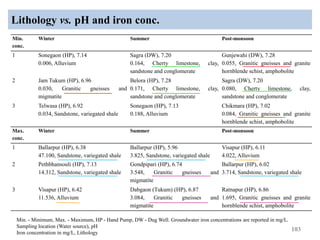
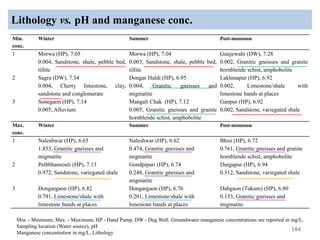
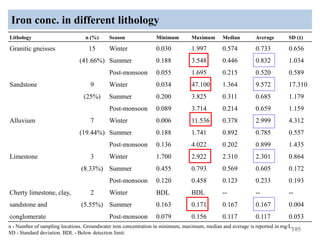
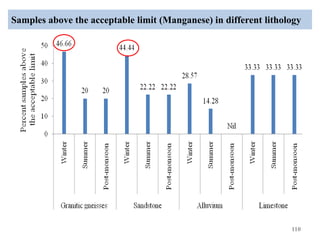
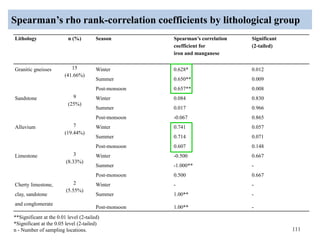
The thesis examines the spatial and temporal distribution of iron and manganese in groundwater in Chandrapur District, Maharashtra. The study aims to understand the distribution of iron and manganese with respect to source type, depth, season and other factors. It also aims to identify plausible sources of iron and manganese in groundwater. The methodology involves literature review, sampling groundwater from identified locations, analyzing iron and manganese concentrations, and interpreting the data. Key findings show seasonal and spatial variations in iron and manganese levels, with some sources exceeding Indian drinking water standards. Depth, rainfall, and altitude also influence concentration levels. The study helps characterize groundwater quality in the district and identify sources of contamination.