This document presents a study on assessing water quality in Chandrapur City, India using a Water Quality Index (WQI). Water samples were collected from 6 locations in the city during rainy and winter seasons. The samples were analyzed for 10 parameters and the WQI was calculated using a weighted arithmetic index method. The results found that most locations had WQI values indicating water quality from poor to unsuitable for drinking, and quality deteriorated from rainy to winter season due to increased microbial activity. The study demonstrated that WQI is useful for evaluating overall water quality and comparing different locations.


![K. Ansari, N. M. Hemke / International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications
(IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 3, Issue 3, May-Jun 2013, pp.233-237
235 | P a g e
5.0 PHYSICO-CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF WATER SAMPLES :
Table 2 shows the values of various physico-chemical parameters for different locations.
Samples
Parameters
WHO/
BIS
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6
R W R W R W R W R W R W
PH 6.5-8.5 7.0 7.5 6.9
5
7.5 6.9
6
7.5 7.0
4
7.6 7.01 7.2 7.0
Total Hardness(mg
/l)
500 268 540 144 292 160 576 284 224 240 30
0
212
Chlorides (mg/l) 200 40 275.9
1
25 55.9
8
28 93.9
7
65 155.9
5
66 50 97.66
Alkalinity (mg/l) 200 300 170 220 204 440 212 450 250 280 20
0
78
D.O. (mg/l) 4-6 4.2 8 6.0 6.5 8.0 8.2 6.8 8.2 7.0 7.8 9.0
B.O.D. (mg/l) 6 60 80 87 110 80 100 98 100 100 90 110
M.P.N.(per 100 ml) 10 900 920 7.2 16 20 17 180 210 430 92
0
540
Turbidity(NTU) 5-10 3.8 0.5 2.0 0.4 4.2 0.4 3.0 0.6 2.0 3.0 3.7
Fluoride(mg/l) 1.5 1.1 0.7 1.0 0.3 0.6 0.8 0.9 0.6 0.18 0.4 1.4
Iron (mg/l) 0.3 0.1 0.1 0.1
2
0.12 0.1 0.18 0.1
6
0.2 0.18 0.2 0.16
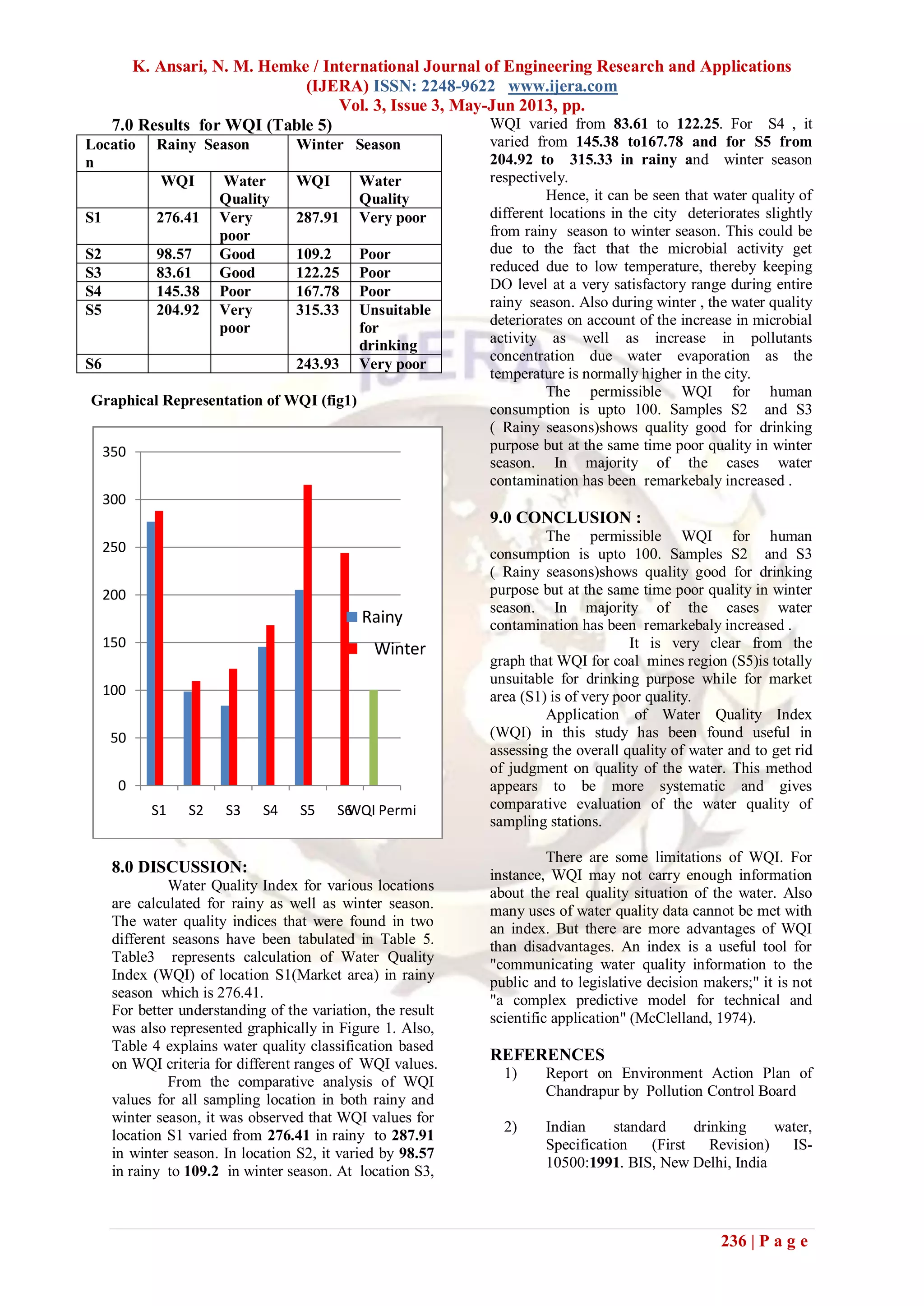
6.0 Determination of Water Quality
Index(WQI)
The Water Quality Index was calculated using
Weighted Arithmetic Index Method. Essentially a
WQI is a compilation of number of parameters that
can be used to determine the overall quality of a
water.
The mathematical relation used to calculate WQI
is given as-
WQI= Σ Q i Wi / ΣWi
Where Q i – Quality rating scale
Wi - Relative weight , Wi = 1/Si
Si- Std. permissible value
Q i = 100 [ (Vn-Vi) /(Vs- Vi) ]
Vn- actual or test value of the parameter
Vi- ideal value of the parameter
Vs- recommended WHO std of the
parameter
In this study, the WQI for human consumption is
considered and permissible WQI for drinking water
is taken as 100.
Sample Calculation for S1(Rainy Season) Table
3
S.No. Parameter Test
value
Si Qi Wi=1/Si QiWi
1 pH 7.0 7.0 0 0.143 0
2 Total
Hardness
268 500 53.6 0.002 0.1072
3 Chlorides 40 200 20 0.005 0.1
4 Alkalinity 300 200 150 0.005 0.75
5 D.O. 4.2 6.0 121 0.17 20.6
6 B.O.D 60 6.0 1000 0.17 170
7 MPN 900 10 9000 0.1 900
8 Turbidity 3.8 10 38 0.1 3.8
9 Fluoride 1.1 1.5 73.33 0.7 51.33
10 Iron 0.1 0.3 33.33 3.33 111
ΣWi=
4.55
ΣQ iW
i =
1257.68
WQI
=
276.41
Water Quality Classification (Table 4)
WQI Value Water Quality
Less than 50 Excellent
50 – 100 Good Water
100 – 200 Poor Water
200 – 300 Very Poor Water
Above 300 Water unsuitable for
drinking](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/an33233237-130511054837-phpapp02/75/An33233237-3-2048.jpg)