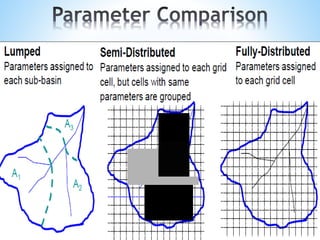
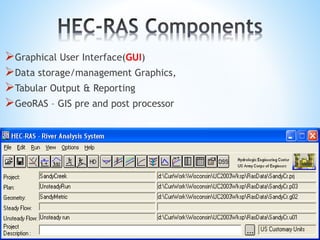
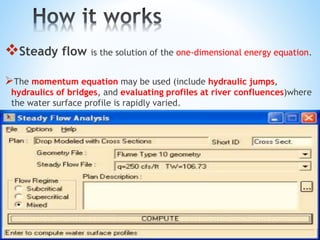
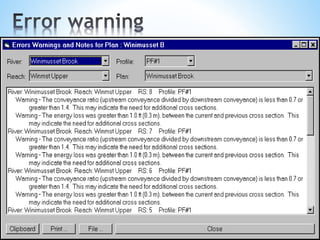
The document outlines a seminar on hydrological modeling, focusing on the HEC-RAS model, which is used for channel flow analysis and floodplain management by hydraulic engineers. It discusses the types of hydrological models (lumped, semi-distributed, and distributed), their uses, advantages, and limitations. The HEC-RAS model is highlighted for its user-friendly interface and functionalities, including steady and unsteady flow simulations, though it has certain constraints such as accuracy in large data and steep slopes.