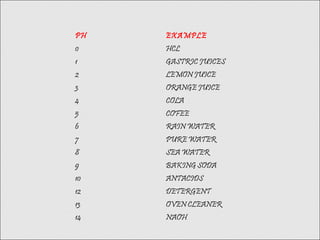
1. The pH meter was invented in 1934 to measure the acidity and alkalinity of fluids on a scale from 0 to 14.
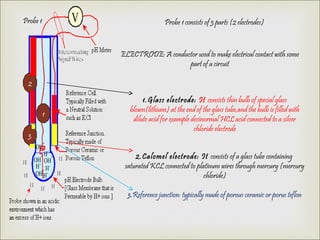
2. A pH meter uses two probes - a glass electrode that measures the hydrogen ion concentration and a reference electrode - to measure the voltage difference between the solutions and translate it into a pH value.
3. The pH meter must be calibrated using buffer solutions of known pH before taking measurements, and temperature compensation is required as pH electrodes are temperature sensitive.


![
The logarithm of the reciprocal of hydrogen-ion concentration in
gram atoms per litre; provides a measure on a scale from 0 to 14 of the
acidity or alkalinity of a solution (where 7 is neutral and greater than 7 is
more basic and less than 7 is more acidic);
pH
(Potential of Hydrogen)
The formal definition of pH is the
negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion
activity.
pH = -log[H+]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmeter17062014-140617054641-phpapp02/85/pH-METER-3-320.jpg)