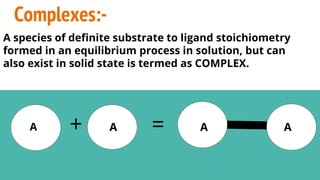
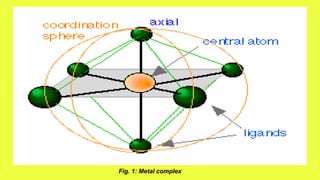
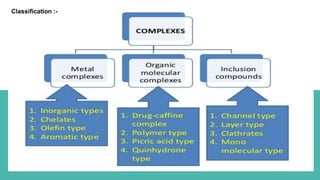
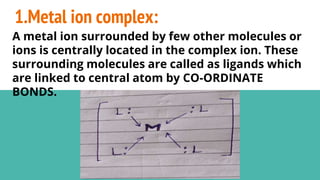
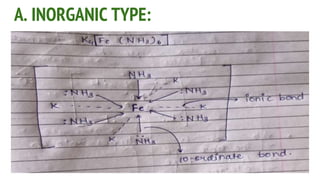
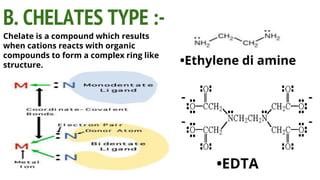
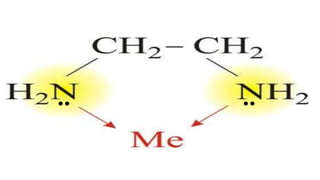
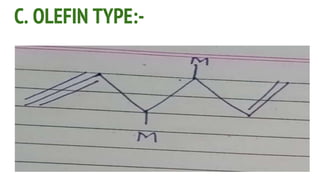
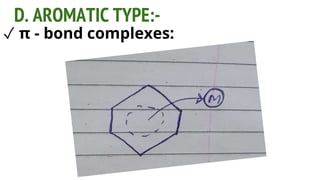
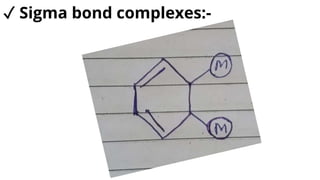
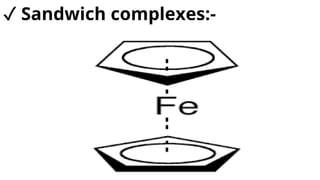
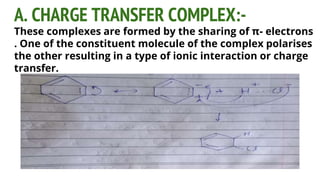
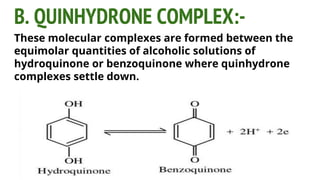
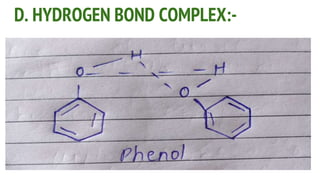
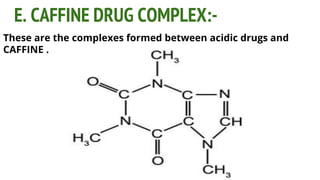
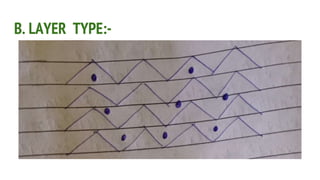
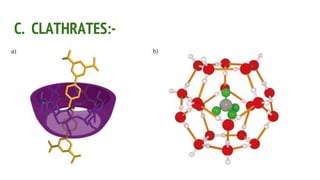
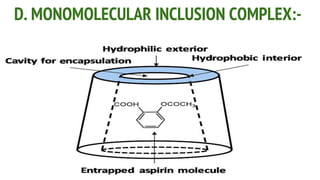
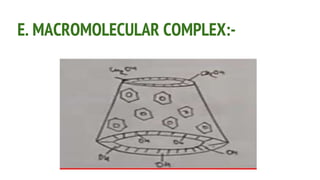
Complexes are formed when ligands bond to a central metal atom through coordinate covalent bonds. Coordination complexes result from a Lewis acid-base reaction between ligands, which donate electron pairs, and metal ions, which accept them. There are several types of complexes including inorganic complexes based on primary and secondary valency and coordination number, and organic complexes such as chelates, charge transfer complexes, and inclusion complexes where one molecule is trapped within the crystal structure of another. Coordination complexes feature a central metal ion surrounded by ligands in a fixed coordination number.