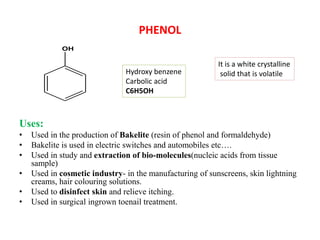
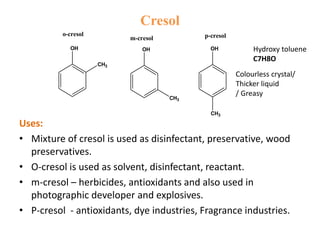
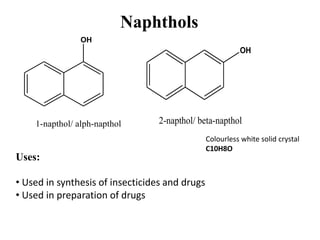
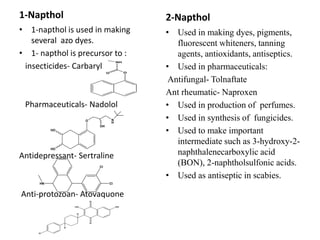
The document describes 5 qualitative tests used to detect phenols:
1. Litmus test detects phenol's acidity by changing blue litmus to red.
2. Ferric chloride test produces different colored complexes with different phenols.
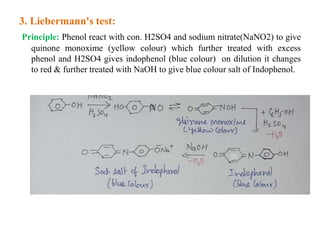
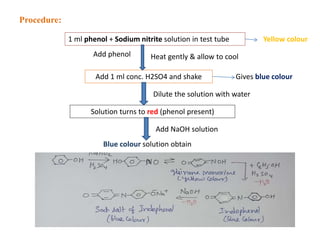
3. Liebermann's test produces a yellow compound then blue or red colors.
4. Bromine water test causes bromine color to disappear and a white precipitate to form.
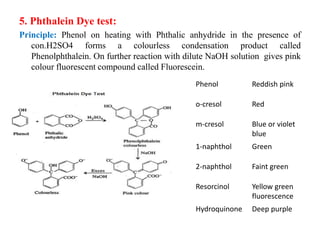
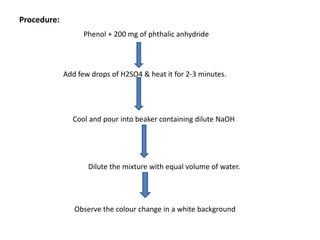
5. Phthalein dye test produces different colored compounds with phenols and bases.