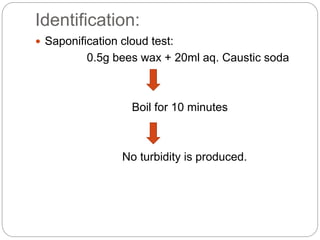
Beeswax, derived from honeycombs of Apis mellifera, is a yellow to yellowish-brown non-crystalline solid with a pleasant, honey-like odor. It is utilized in various applications such as ointments, cosmetics, and candles, and has specific chemical properties, including a melting point of 62 to 65°C and a saponification value of 90 to 103. Adulteration can occur with substances like colophony and stearic acid, which can be detected through solubility and melting point tests.