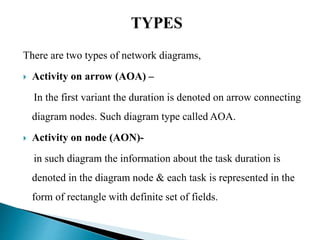
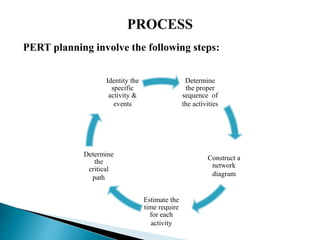
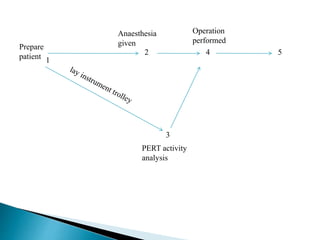
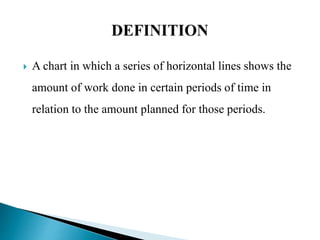
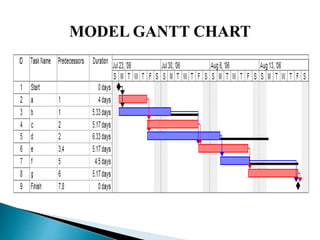
The document discusses project evaluation and review technique (PERT). It begins by explaining that PERT was developed in the 1950s for the Polaris submarine missile program to reduce time and costs of projects. PERT breaks projects down into activities, events, and relationships between them in a network diagram. It estimates optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic durations for activities to account for uncertainty. The critical path showing the longest sequence of activities determining the project duration is identified. PERT is useful for planning resources, reviewing progress, and evaluating performance. Limitations include not directly considering costs and variable activity times.