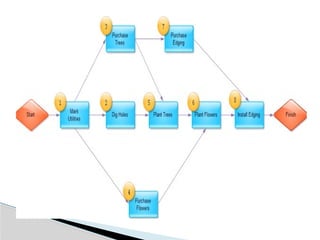
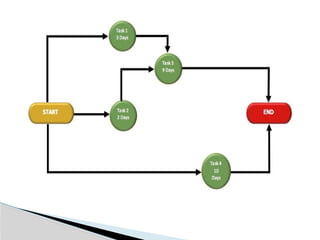
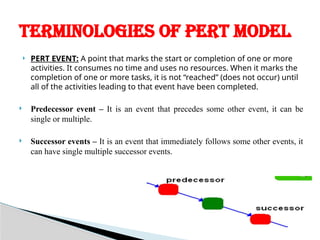
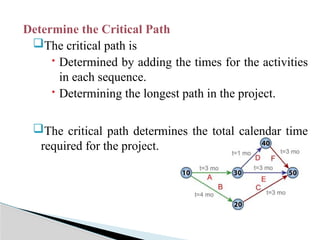
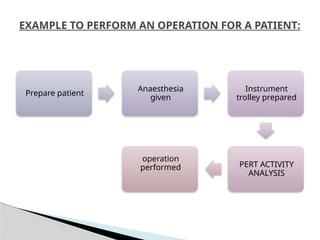
The document discusses the Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), a method for analyzing the tasks and time required to complete a project. Developed by the U.S. Navy in 1958, PERT aids in project management by identifying time estimates for activities, scheduling tasks, and tracking overall progress. Key components include event definitions, critical paths, and the benefits and limitations of using PERT for complex project planning.