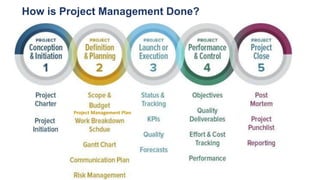
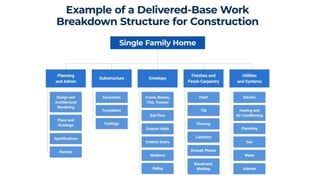
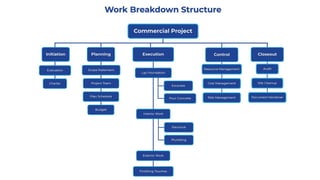
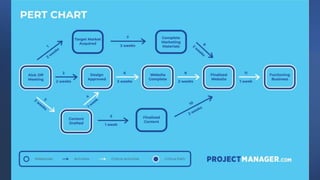
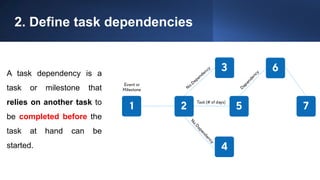
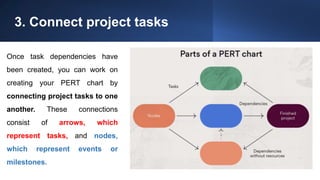
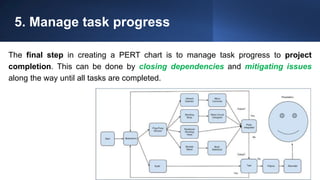
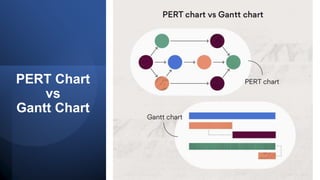
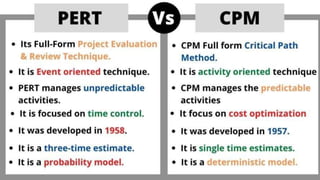
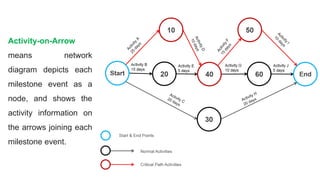
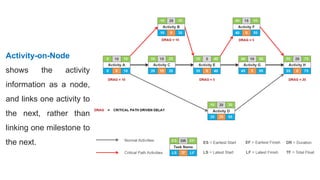
The document discusses project management tools including the work breakdown structure (WBS), Gantt chart, program evaluation and review technique (PERT), and critical path method (CPM). It explains that a WBS breaks a project into deliverables and work packages in a hierarchical structure. A Gantt chart displays project activities and timelines. PERT and CPM are used to schedule tasks, identify dependencies, and determine the critical path. PERT uses an activity-on-arrow diagram while CPM uses an activity-on-node diagram. The document provides details on how to create each of these project management tools.