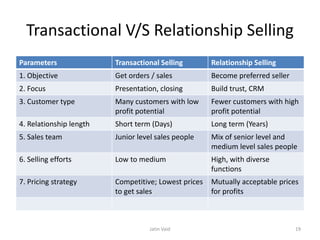
The document outlines the consumer buying process, which consists of stages from problem recognition to post-purchase behavior, and highlights the significance of personal selling in building customer relationships. It describes various personal selling steps including prospecting, approach, presentation, and closing techniques, alongside methods to overcome objections. Additionally, it contrasts transactional and relationship selling in terms of objectives, customer focus, and relationship duration.