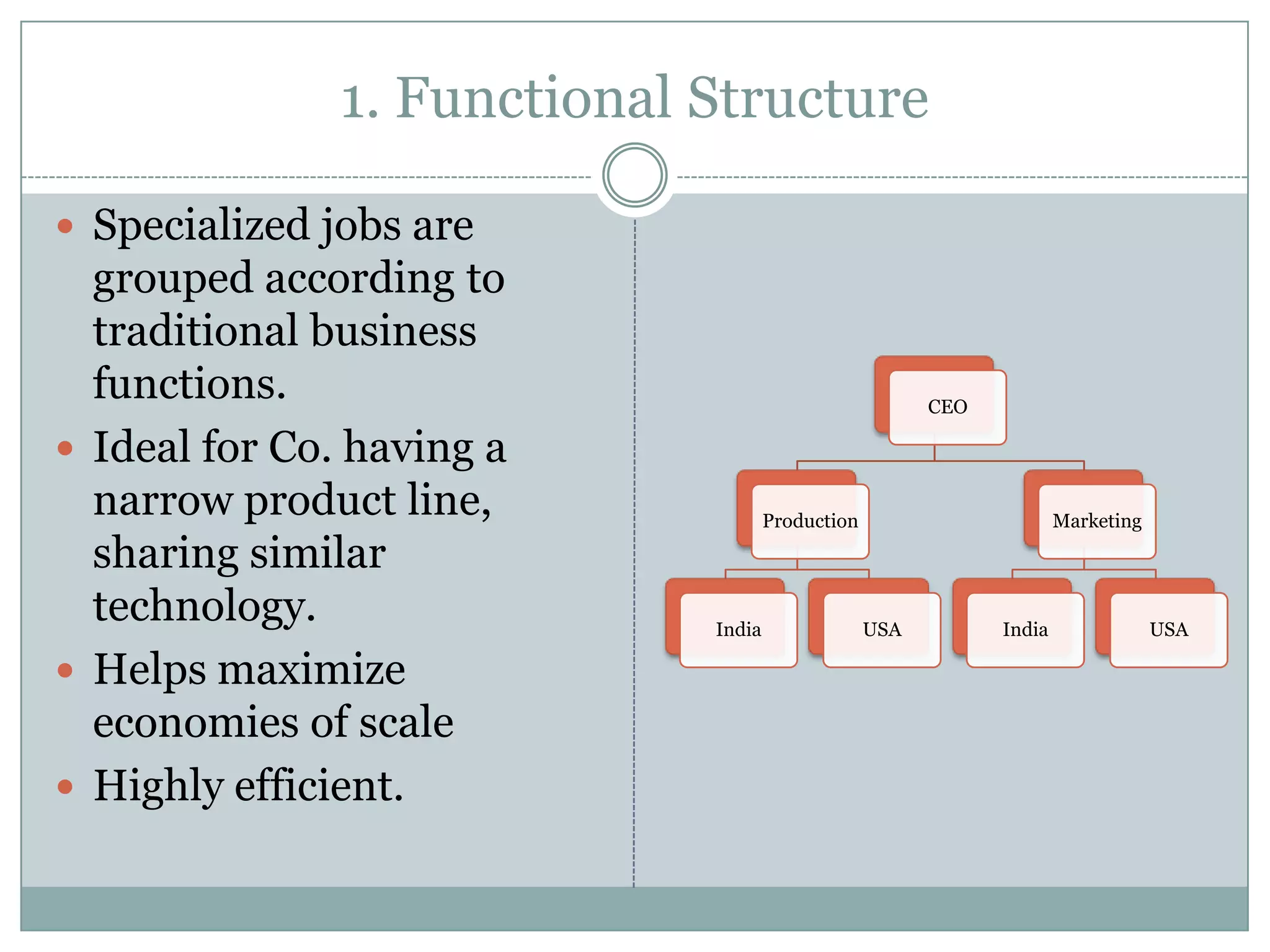
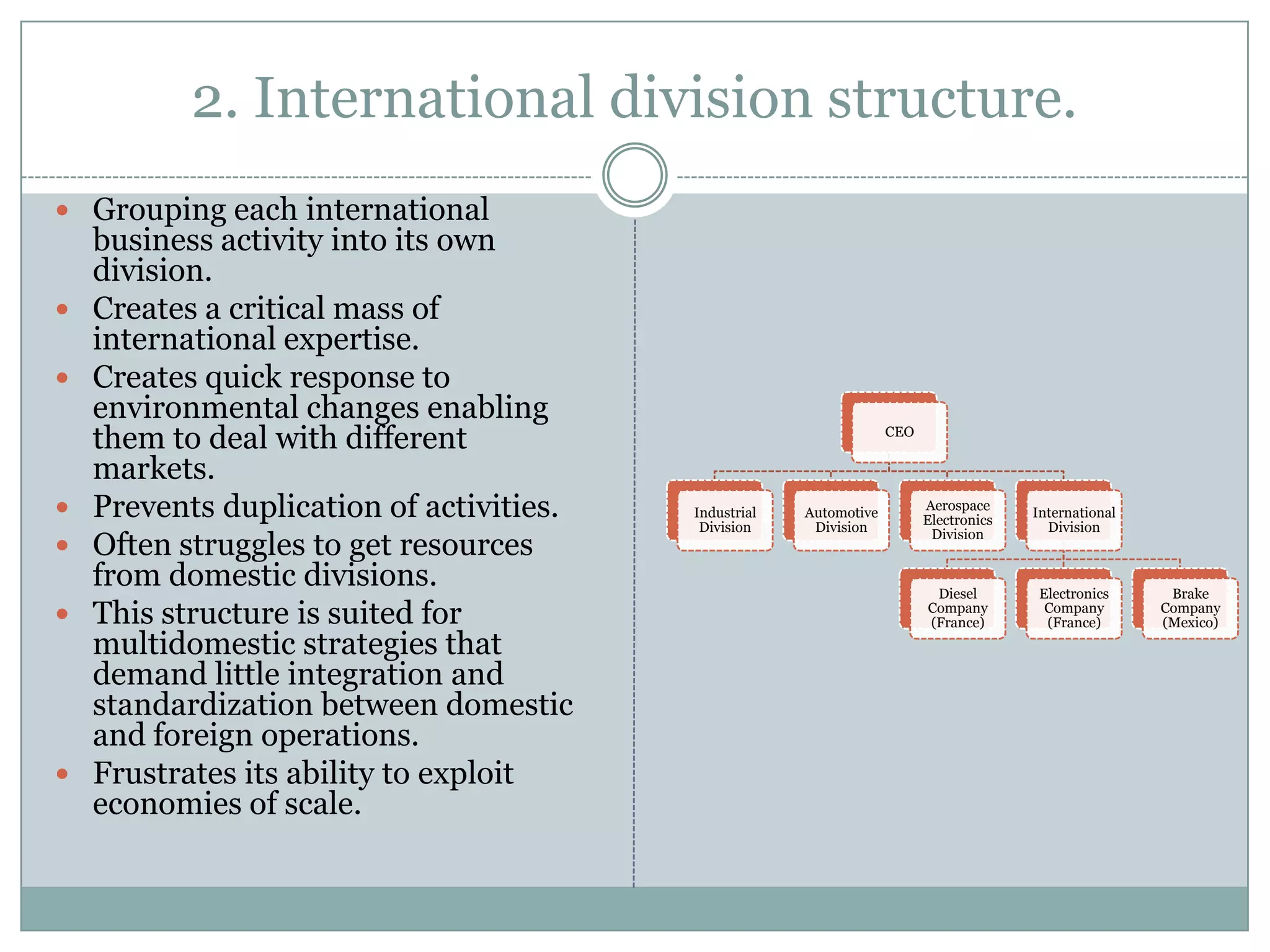
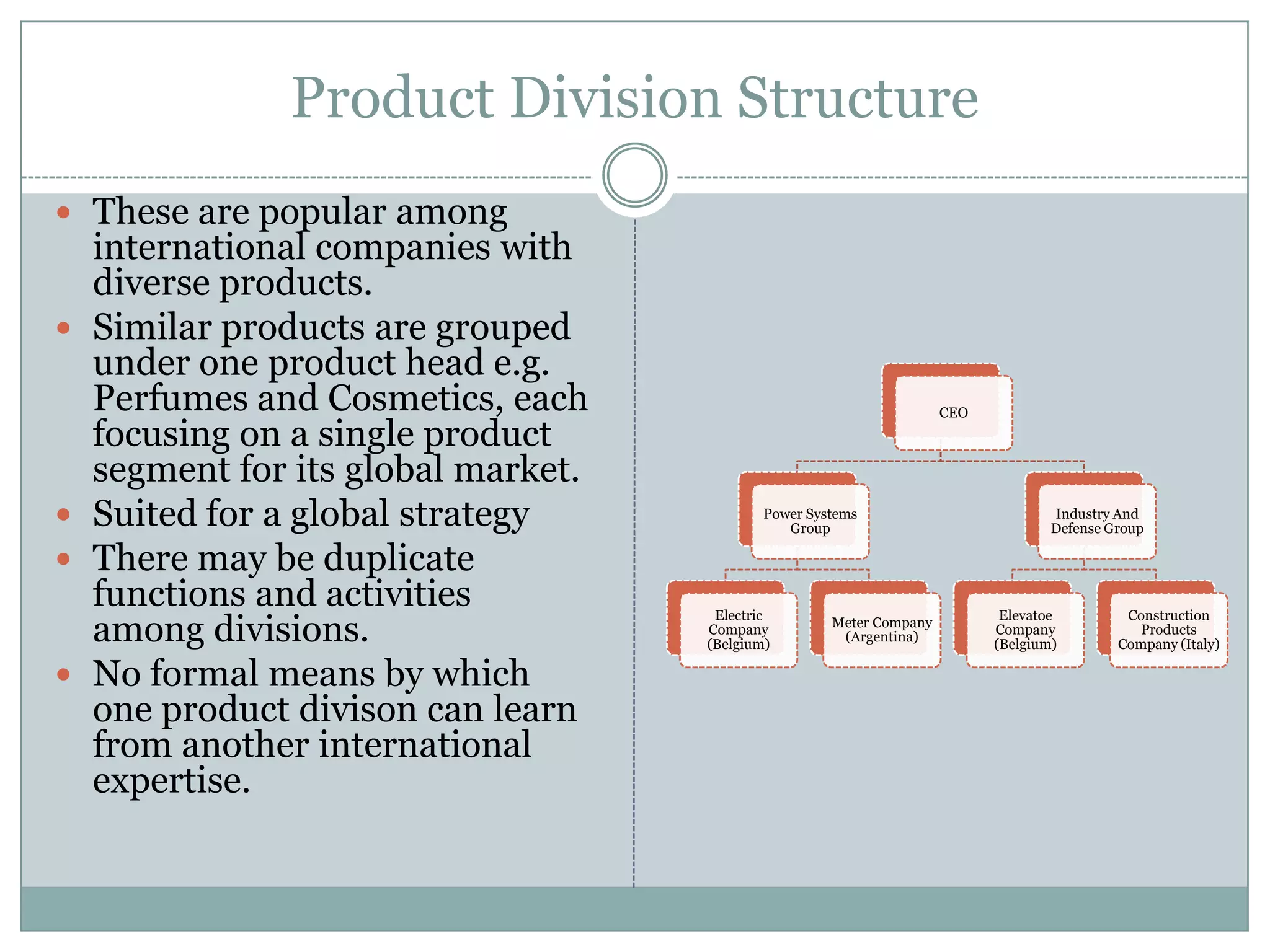
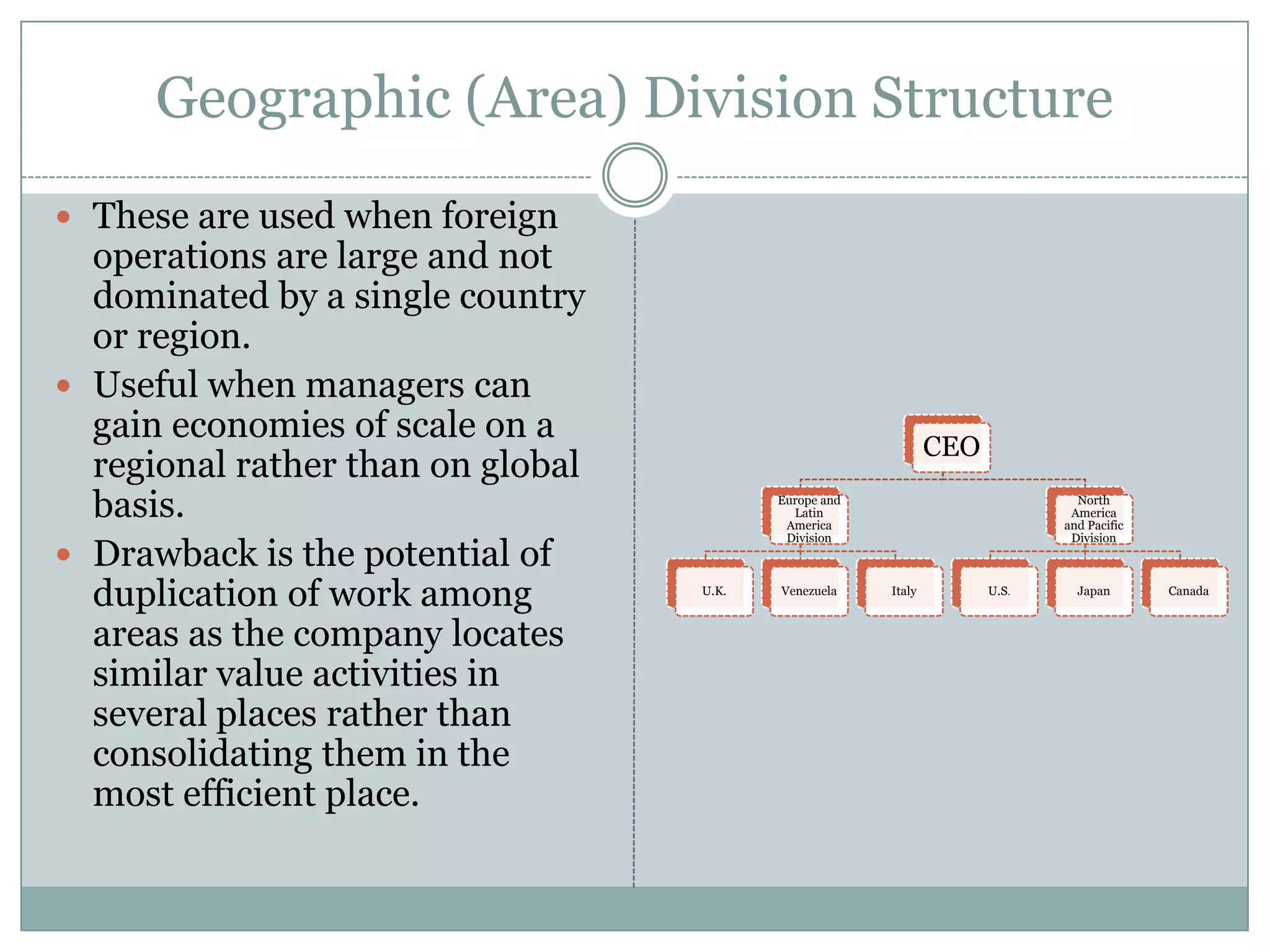
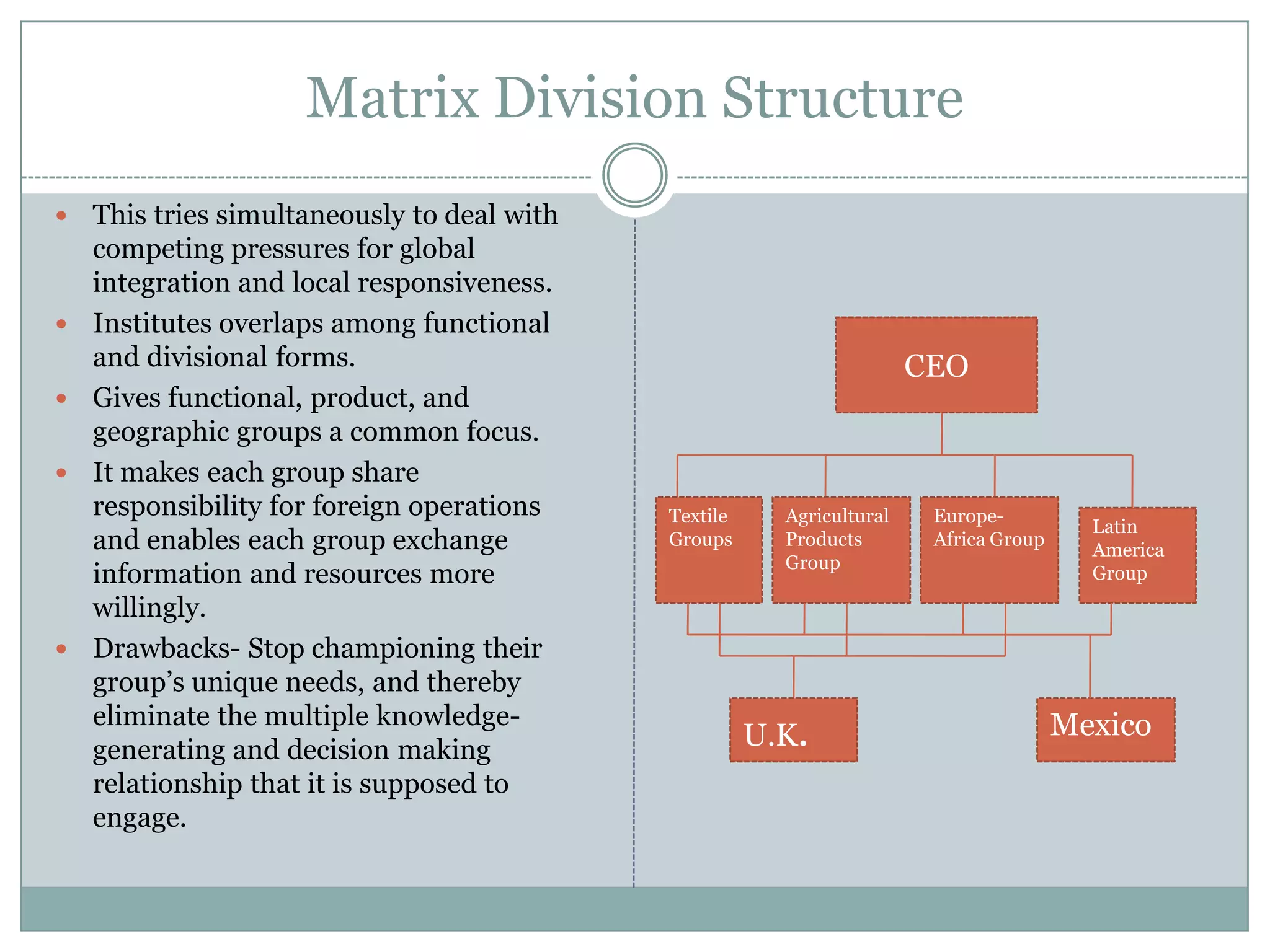
The document discusses different types of organizational structures used in international business. It describes centralization versus decentralization and the tradeoffs of each. There are five main types of organizational structures covered: functional structure, international division structure, product division structure, geographic (area) division structure, and matrix division structure. Each structure has advantages and disadvantages for coordinating and responding to activities in different markets and geographies.