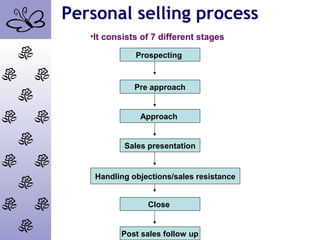
This chapter discusses personal selling, including the types of selling jobs, sales force objectives and strategies, theories of personal selling, the personal selling process, and issues related to customers and automation. The personal selling process involves 7 stages: prospecting, pre-approach, approach, sales presentation, handling objections, closing, and post-sales follow-up. Different theories of personal selling are also examined, such as AIDA, the buying formula, and behavior equation theories. The chapter also explores sales force strategies like using company salespeople, distributors, telemarketing and strategic alliances.