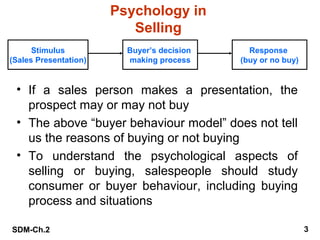
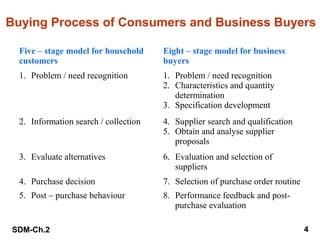
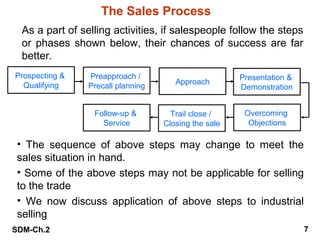
This document summarizes key aspects of the personal selling process. It discusses understanding buyer psychology and the buying process. It outlines the typical steps in the sales process, including prospecting, pre-approach planning, the sales presentation, overcoming objections, closing the sale, and follow-up. It also addresses developing sales knowledge, different presentation methods, using demonstrations, negotiation skills, and relationship building. The overall goal is to equip salespeople with the tools and understanding needed to successfully navigate interactions with prospects and customers.