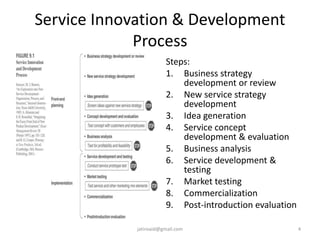
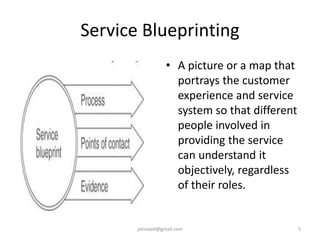
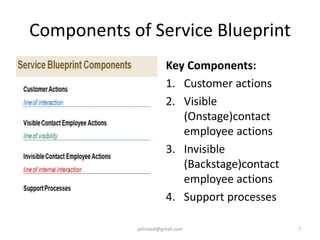
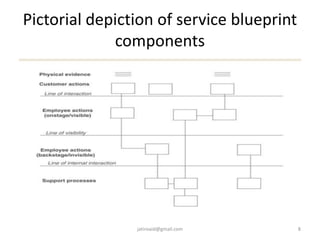
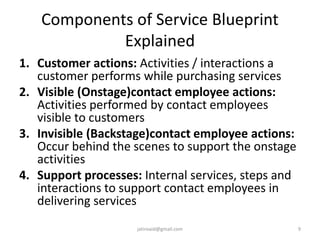
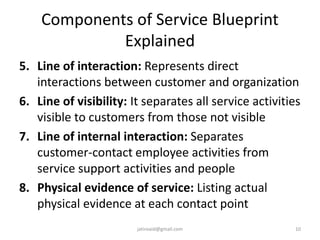
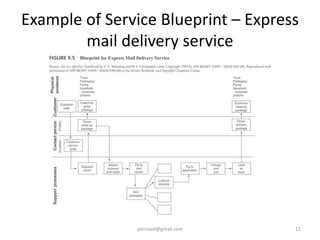
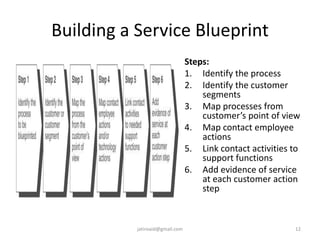
This document discusses service design and blueprinting. It describes the challenges in service design due to the intangible and heterogeneous nature of services. It then outlines different types of service innovations and the process of service innovation and development. The core topic is service blueprinting, which is defined as a visual map that depicts the customer experience and service system from the customer's perspective. The key components of a service blueprint - customer actions, visible employee actions, invisible employee actions, and support processes - are explained. An example blueprint for express mail delivery is provided. Finally, the uses and benefits of service blueprinting for new service development, employee training, and facilitating innovation are outlined.