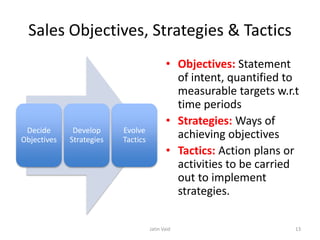
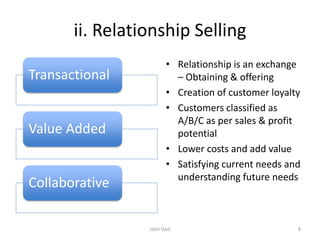
The document provides an overview of sales management, discussing its evolution from small-scale manufacturing to the establishment of separate functional departments post-industrial revolution. It outlines the roles of sales managers, the importance of sales in generating revenue, and the impact of emerging trends such as CRM and technology on the field. Additionally, it emphasizes the integration of sales management with marketing, the significance of relationship selling, and the various skills required for effective sales management.



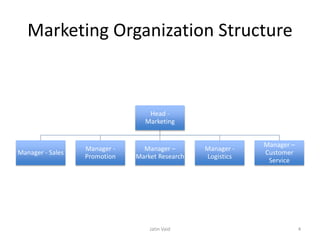






![Sales Management positions
Strategic
/ Top
Tactical /
Middle
Operational /
First
1. Strategic: [President; V.P;
National sales head] – Long
term sales planning,
environment scanning,
strategy formulation, control
performance
2. Tactical: [Regional sales
head; Zonal sales manager] –
Manage regions, implement
strategies
3. Operational: [Branch / Area
sales managers] – Achieve
sales goals, supervising sales
force, implement rules
Jatin Vaid 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontosalesmanagement-160826042645/85/Introduction-to-sales-management-12-320.jpg)