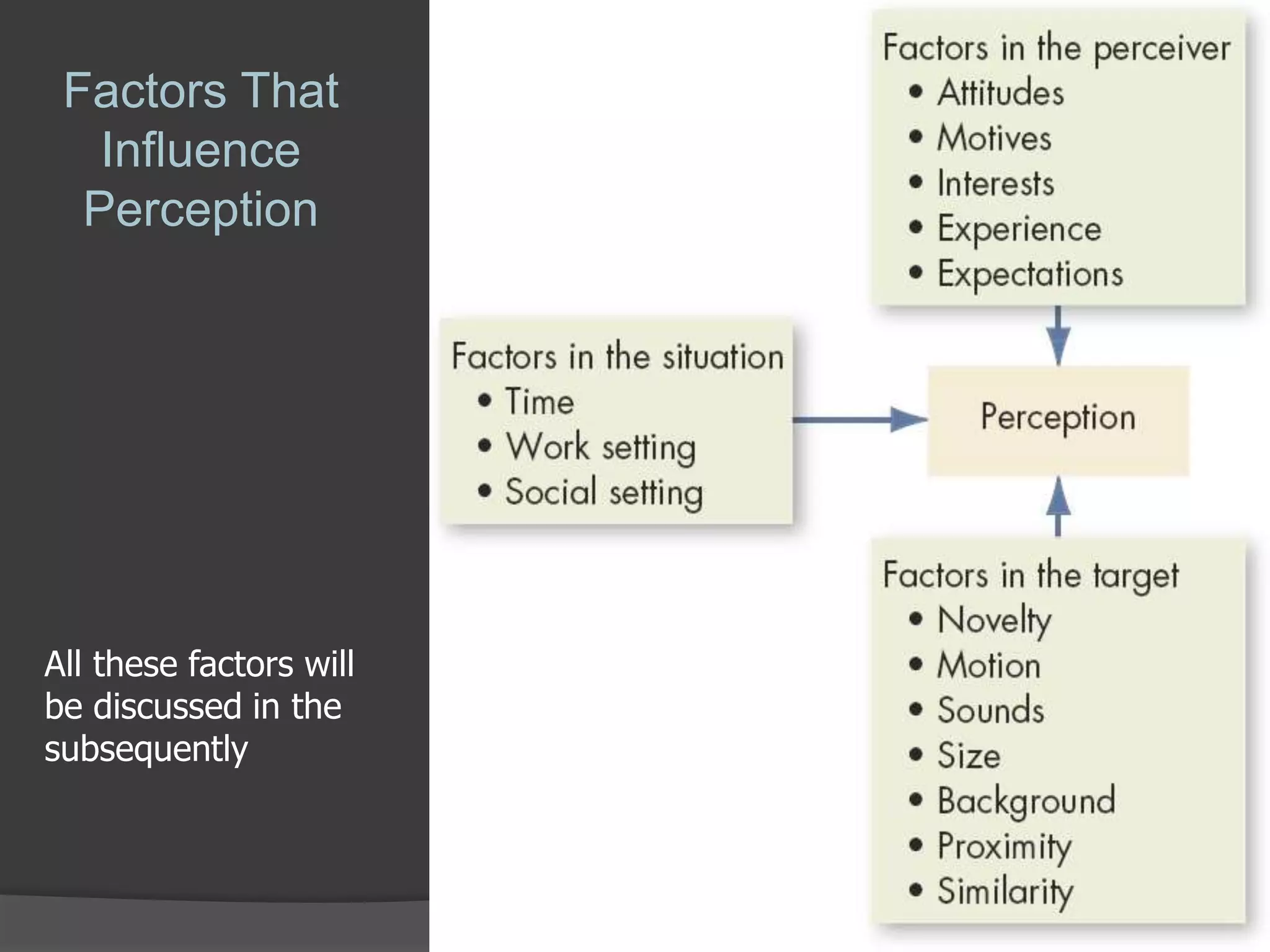
The document discusses perceptual organization and the factors that influence human perception. It defines perceptual organization as the process of grouping external stimuli into recognizable patterns and objects. It describes the Gestalt laws of perceptual organization, which were principles developed by Gestalt psychologists to explain how smaller objects are grouped into larger ones. The document also lists and briefly explains several factors that can influence human perception, including characteristics of the perceiver, target, and situation.