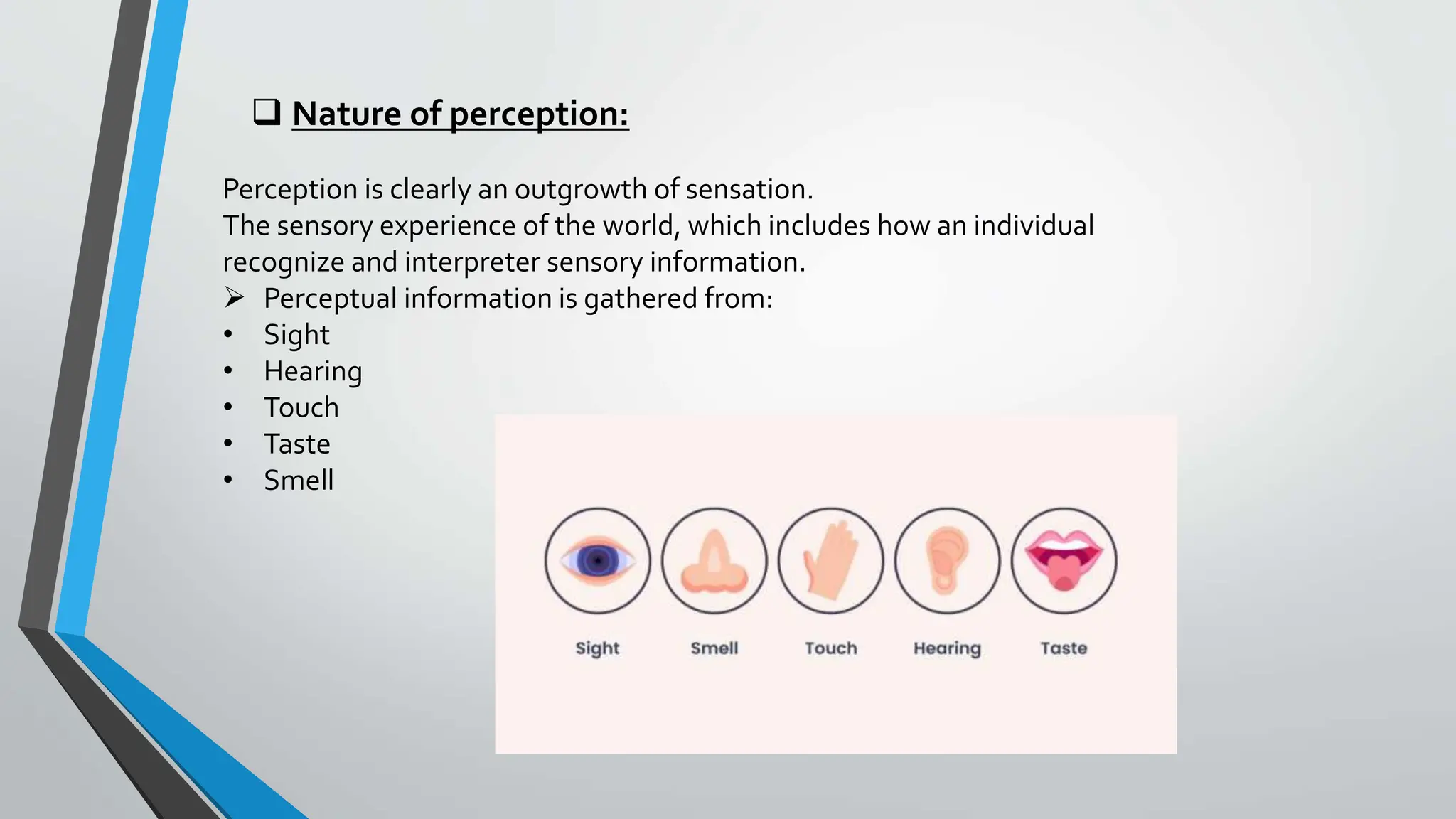
Perception is the process by which individuals interpret and give meaning to sensory information about their environment. It involves both bottom-up processing of sensory data and top-down processing based on factors like prior knowledge and expectations. Perception is influenced by characteristics of the perceiver such as attitudes, motives, experiences, and self-concept as well as characteristics of the target being perceived and the situation. There are different types of perception including form, depth, motion, and time perception. Laws of perceptual organization like figure-ground relationship, proximity, similarity, and closure influence how humans group sensory information.