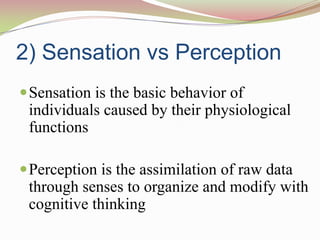
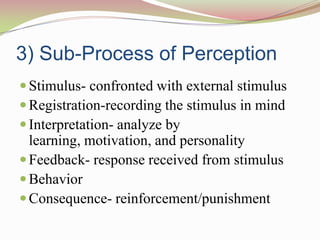
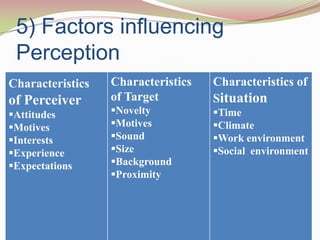
This document discusses various aspects of perception and social perception. It begins by defining perception as the process of collecting, organizing and interpreting information from the environment to derive meaning. Sensation involves basic physiological responses to stimuli, while perception involves higher-level cognitive processing of sensory inputs. Perception involves stimulus registration, interpretation based on factors like learning and personality, feedback, behavior, and consequences. Selectivity and various external and internal factors influence perception. The document also discusses perceptual organization, constancy, context, defense and social perception and the factors that influence it like stereotyping and halo effects. It concludes with a discussion of attribution theory and impression management strategies used in organizations.




































![ The motivation on the part of employees may
or may not be a deliberate attempt to enhance
themselves in terms of political
power, promotions or money rewards
A recent analysis indicated that Impression
Management might motivate employee
citizenship behaviors [going beyond normally
required and rewarded behavior]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-perception-121209235646-phpapp02/85/Presentation-1-perception-41-320.jpg)





