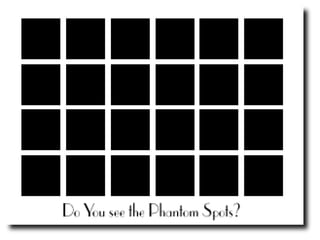
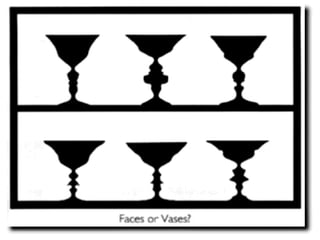
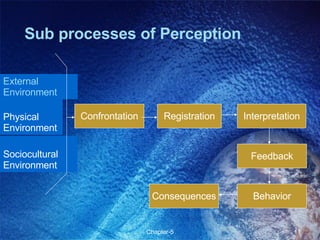
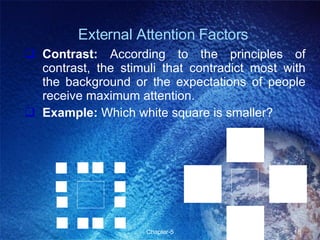
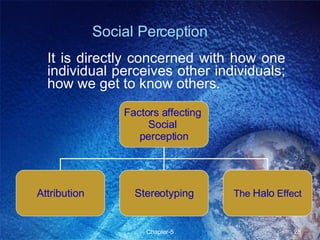
This chapter discusses perception and related concepts. It defines perception as how individuals select, organize and interpret stimuli to understand their environment. It distinguishes perception from sensation. The subprocesses of perception include registration, interpretation, and response. Factors that influence perception include attention, learning, motivation, personality and the perceiver, target, and situation. Perceptual organization involves processes like figure-ground perception, grouping, closure and constancy. Social perception examines how individuals perceive others through attribution, stereotyping and halo effects. Impression management refers to strategies individuals use to control how others perceive them. Perception ultimately influences individual decision-making.