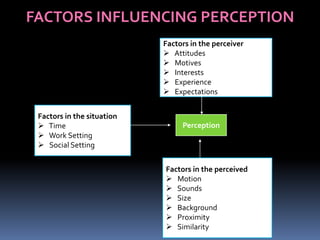
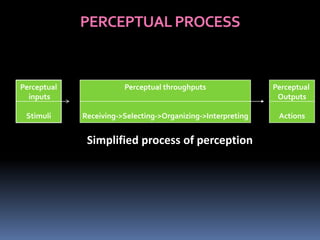
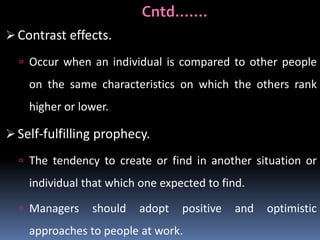
The document discusses perception and the perceptual process. It defines perception as the process by which individuals select, organize, interpret and respond to sensory information. Perception is influenced by factors related to the perceiver, such as attitudes and experiences, and factors related to the perceived situation, such as size and motion. The perceptual process involves receiving stimuli and then selecting, organizing and interpreting that information. Common perceptual distortions that can occur include stereotypes, halo effects, and selective perception. The perceptual process can be managed through impression management and reducing cognitive distortions.