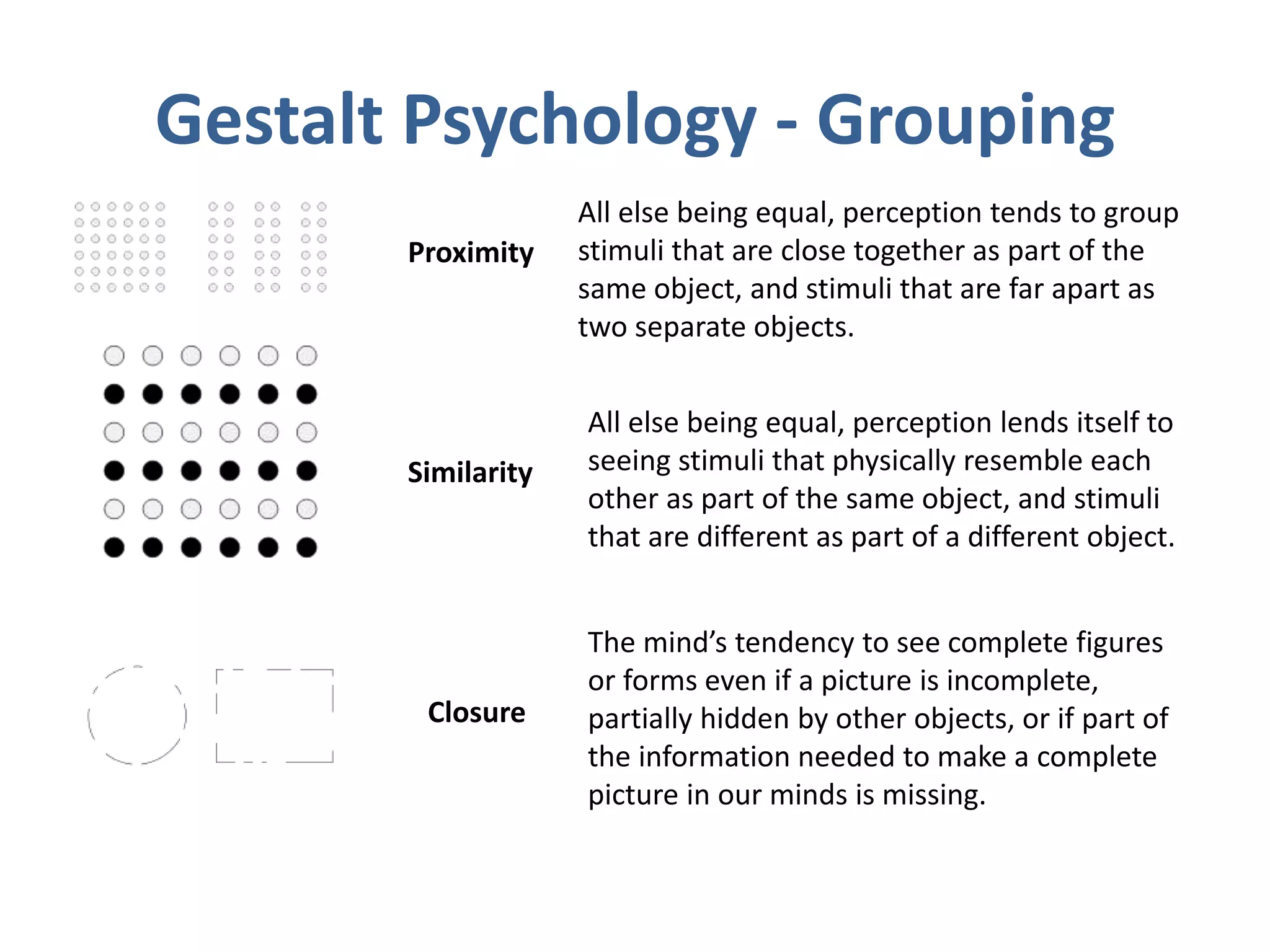
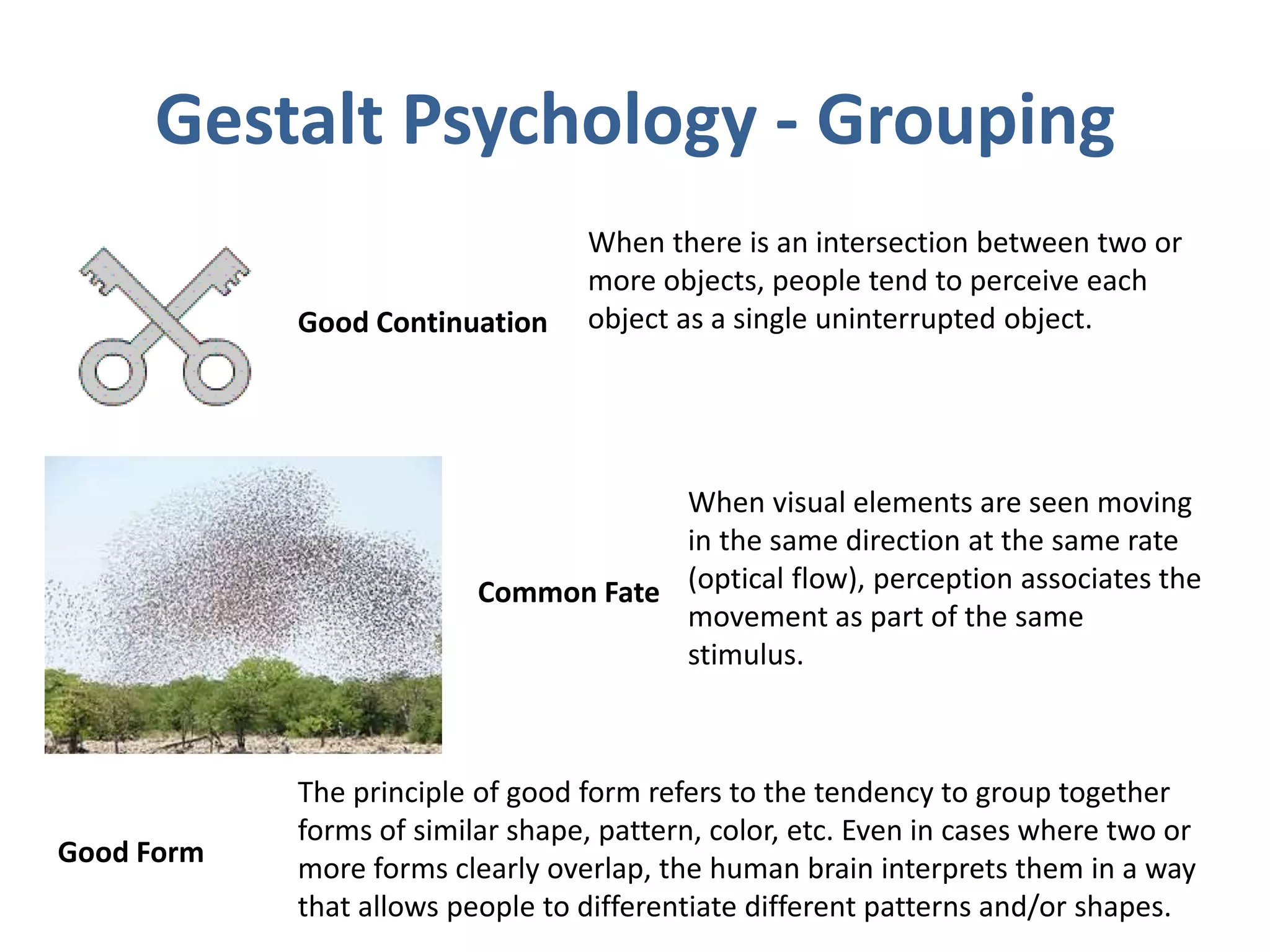
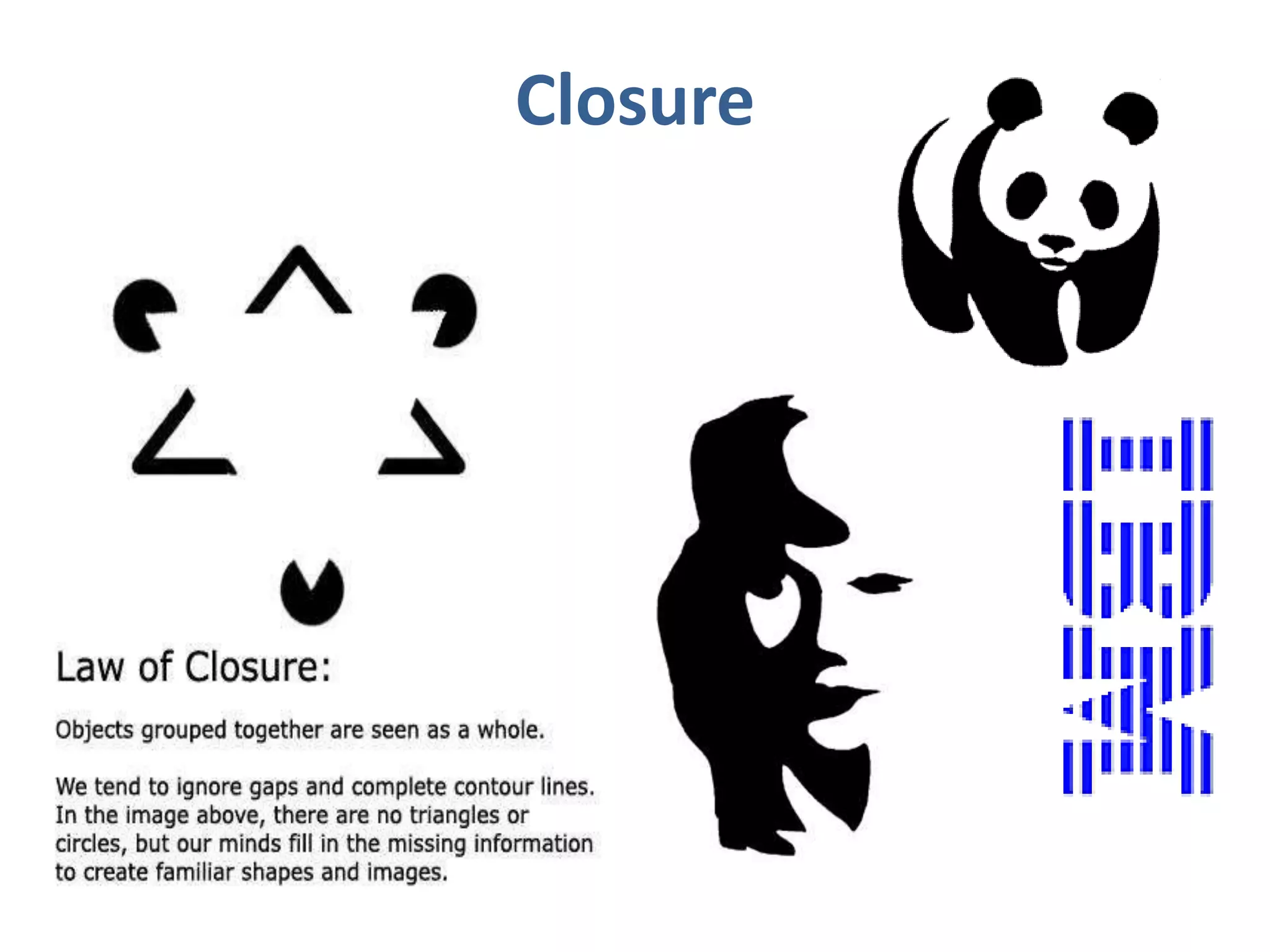
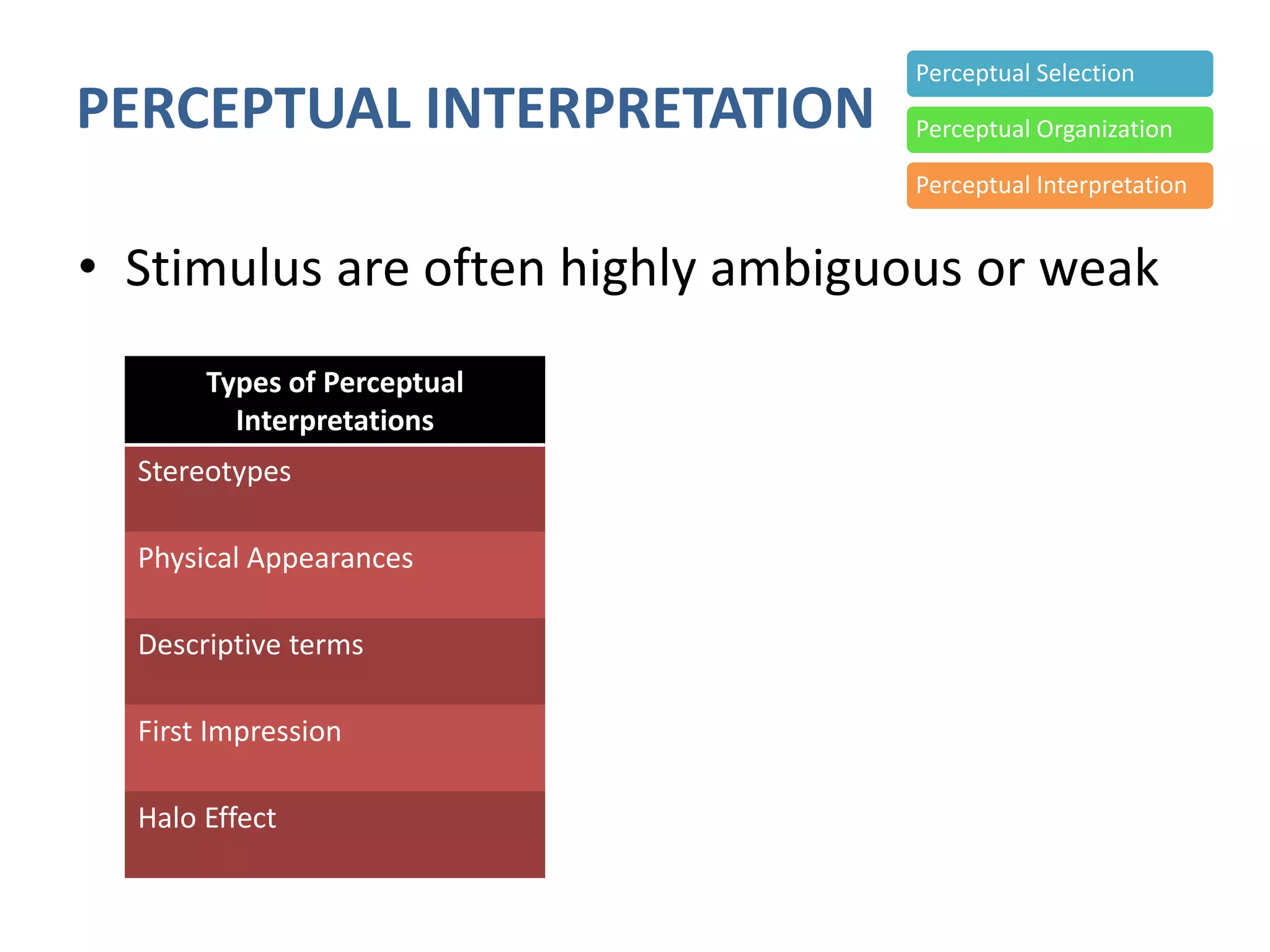
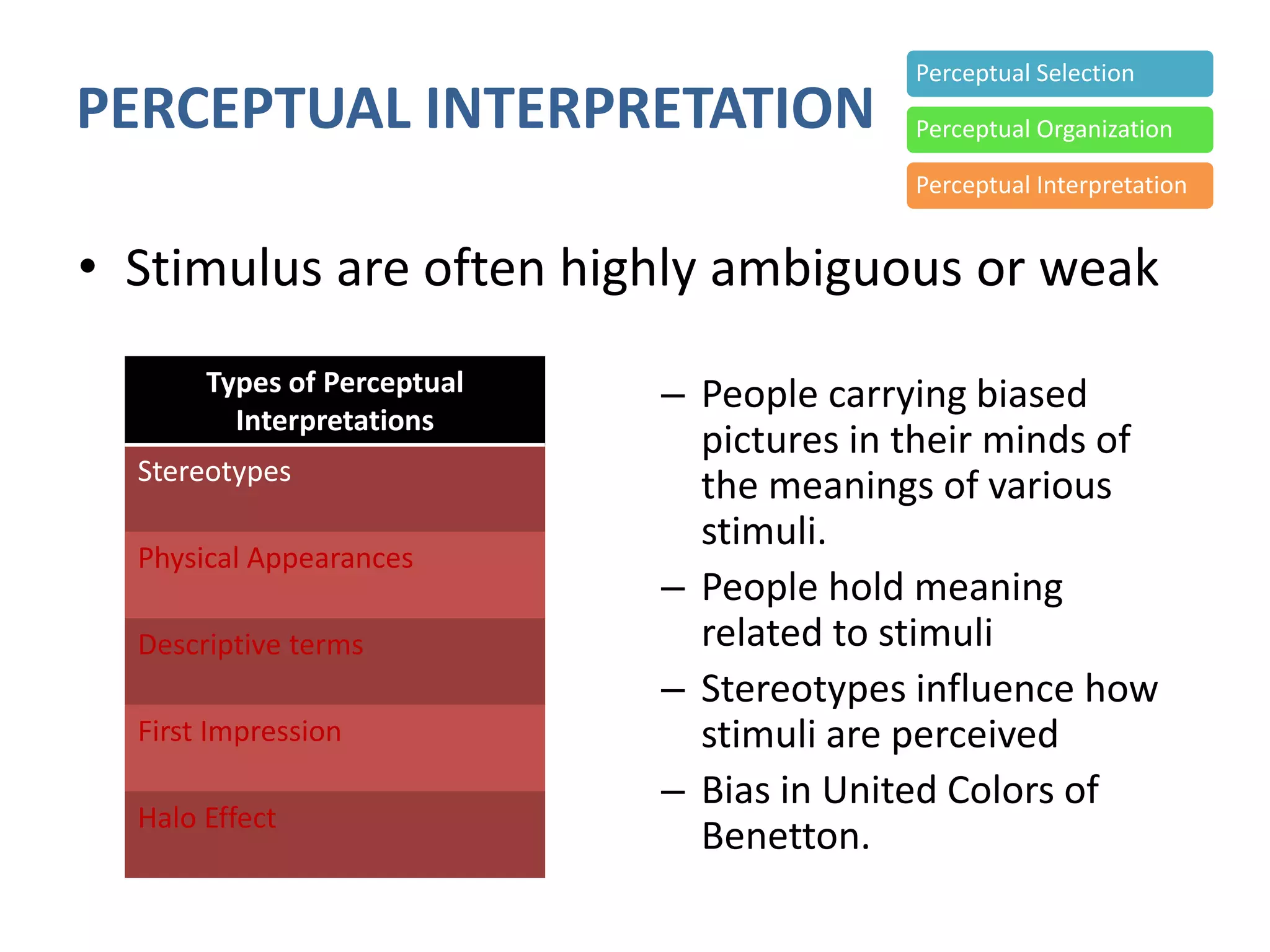
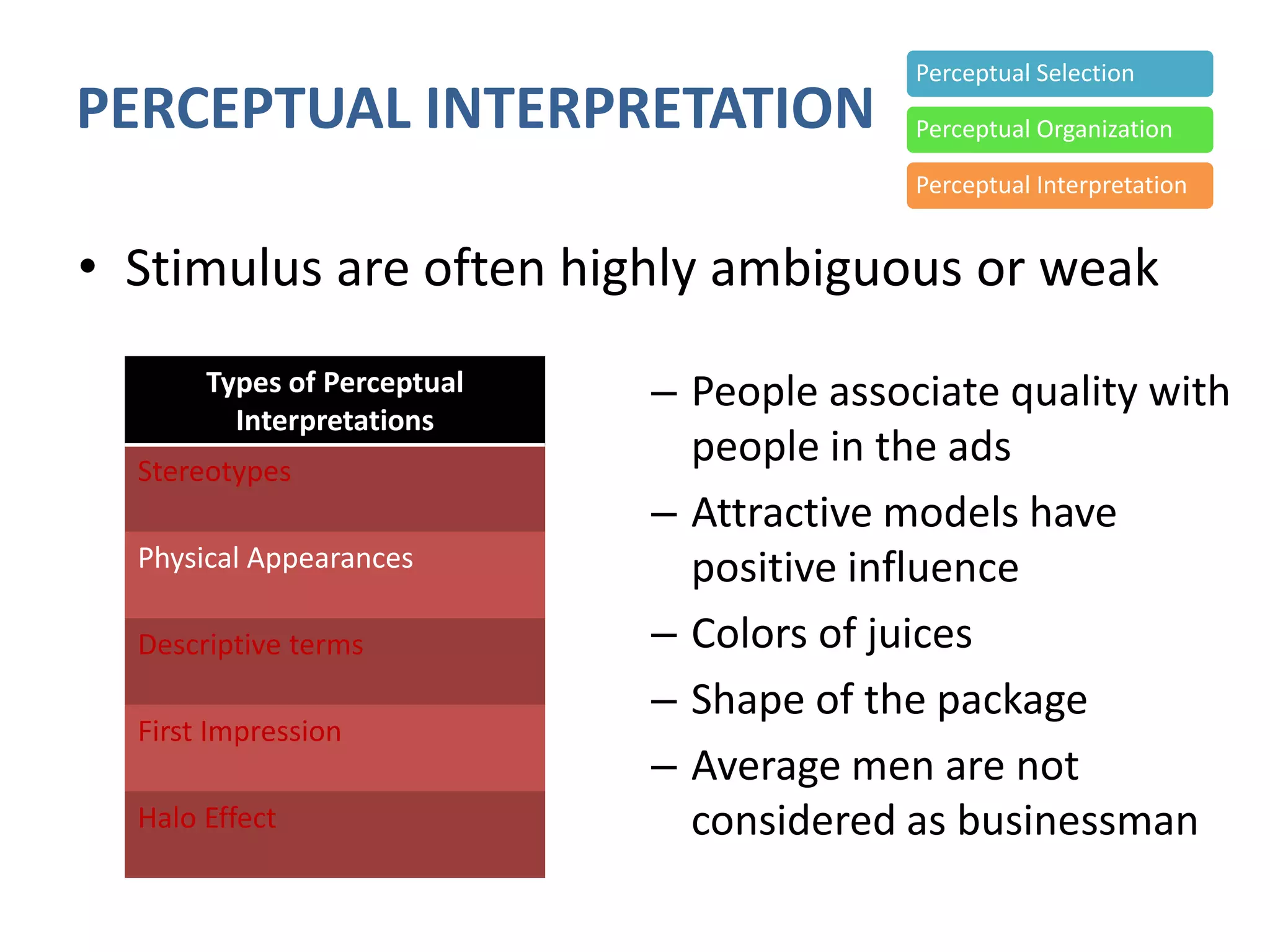
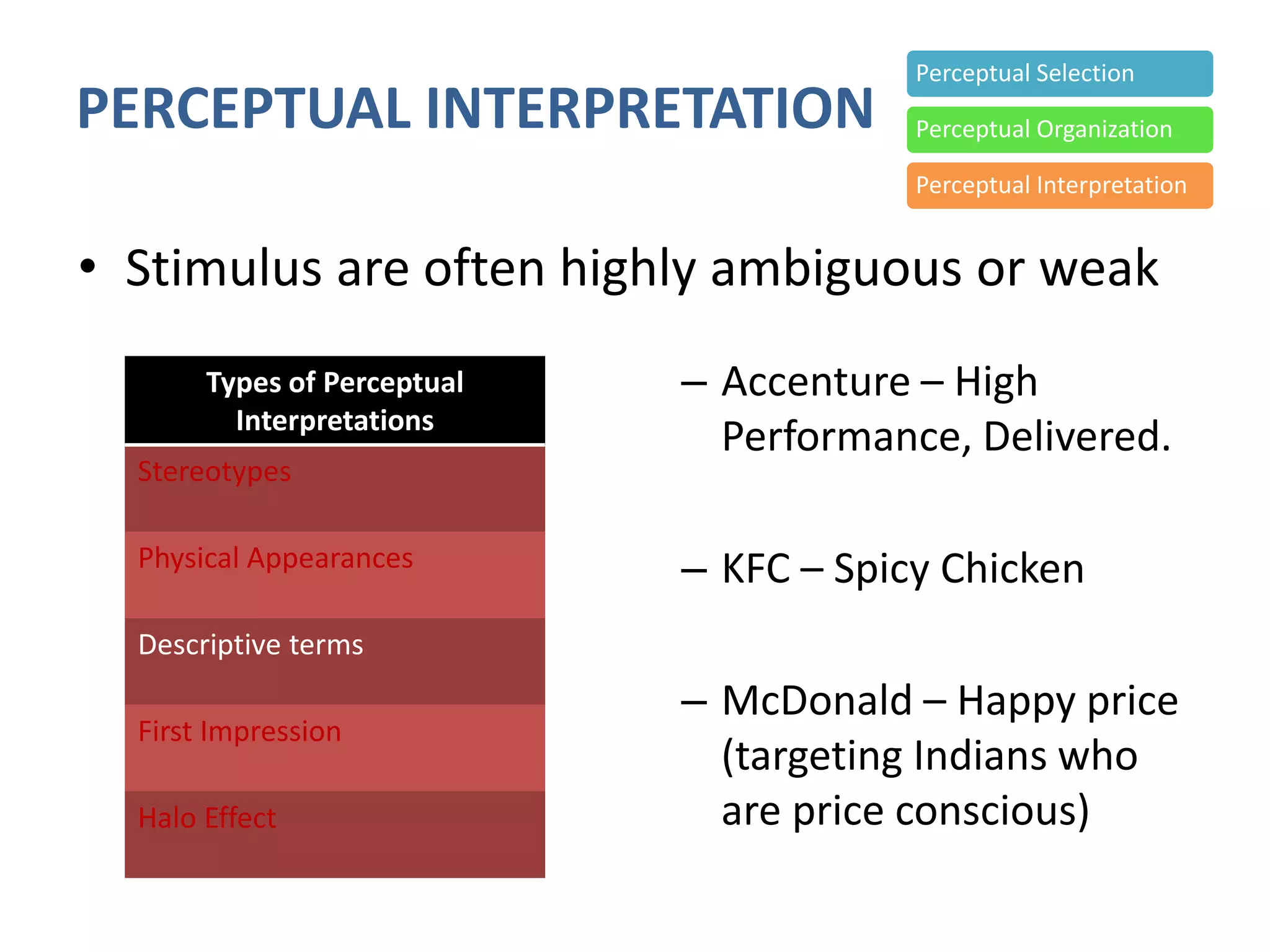
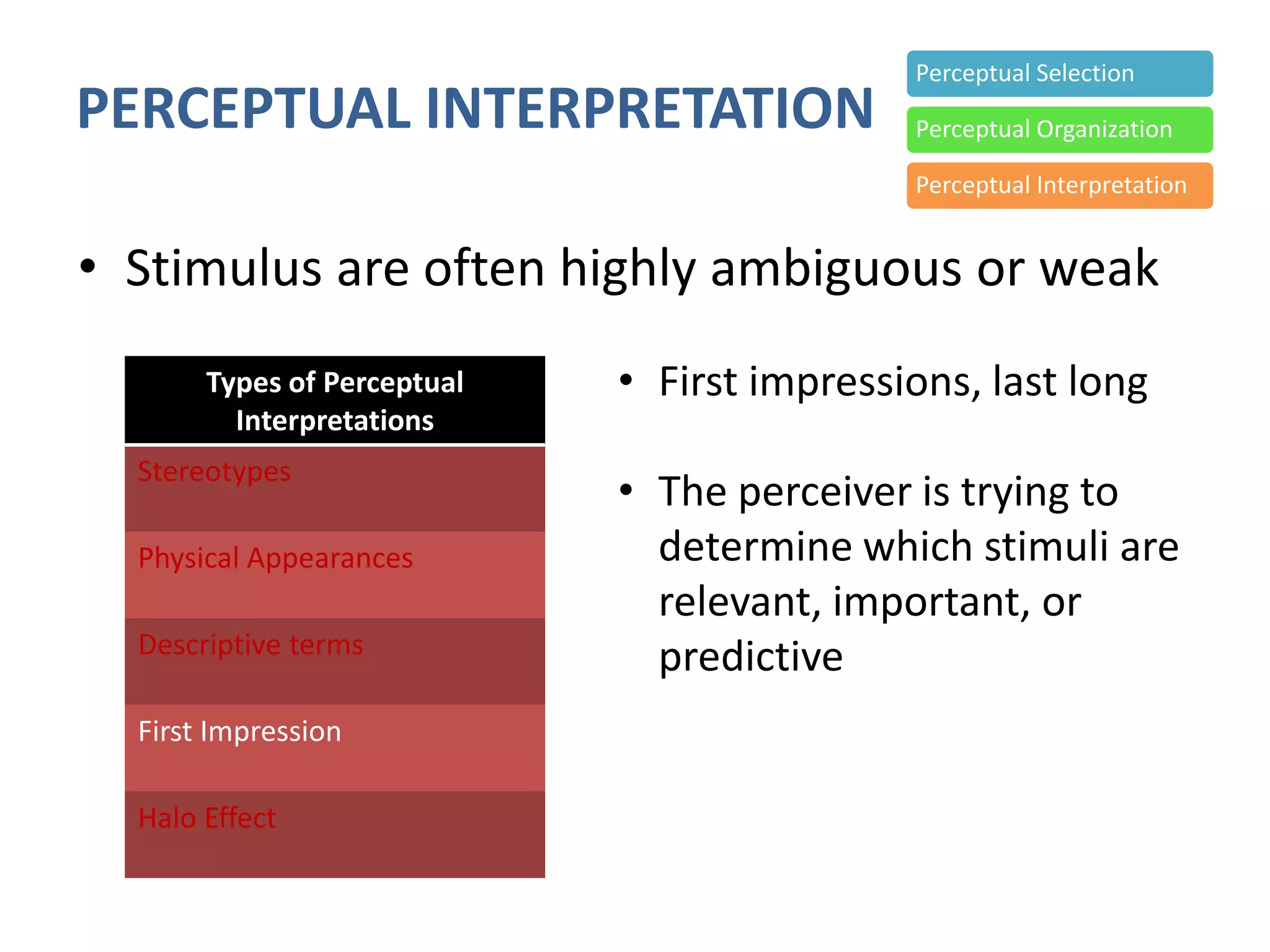
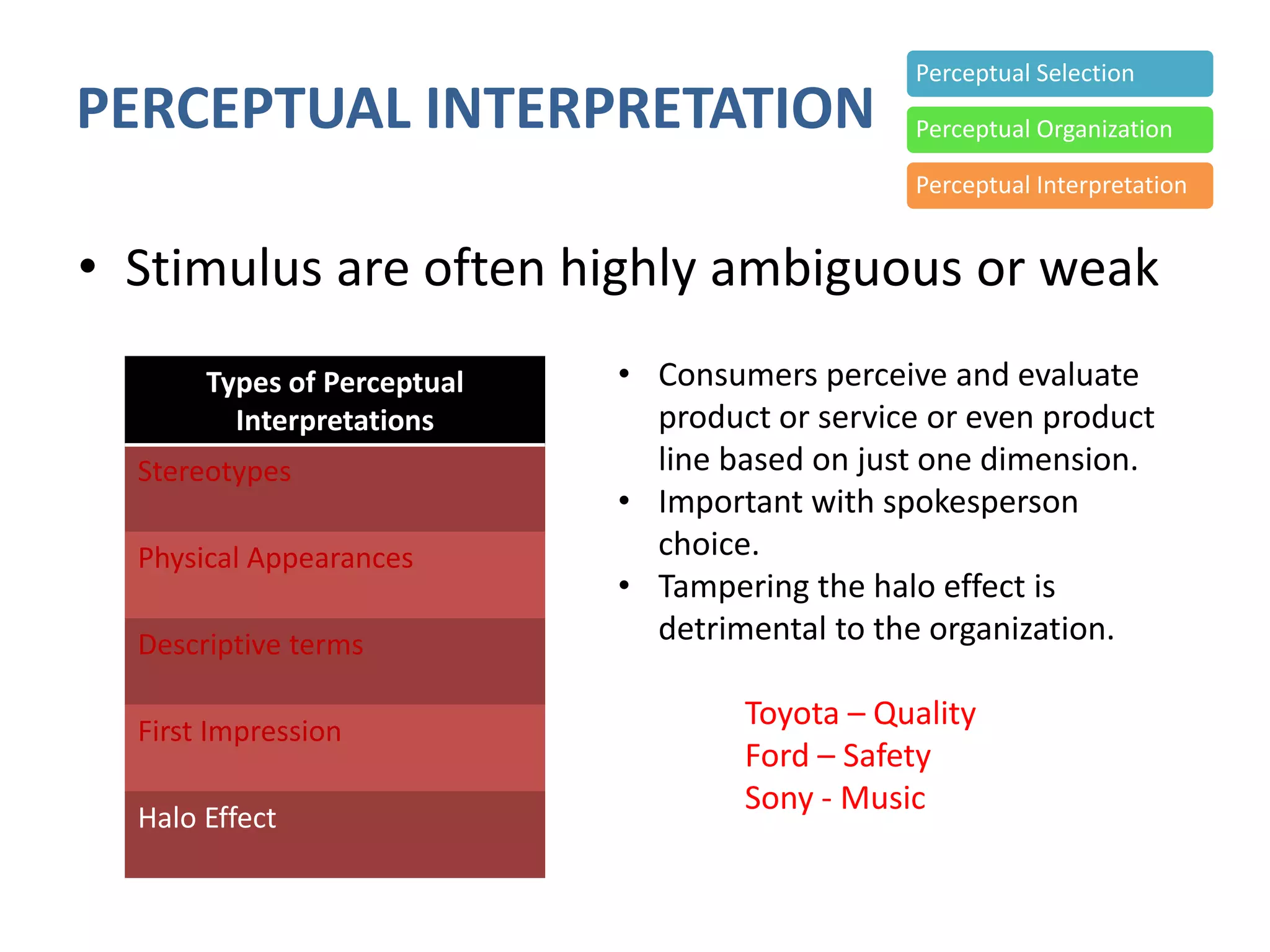
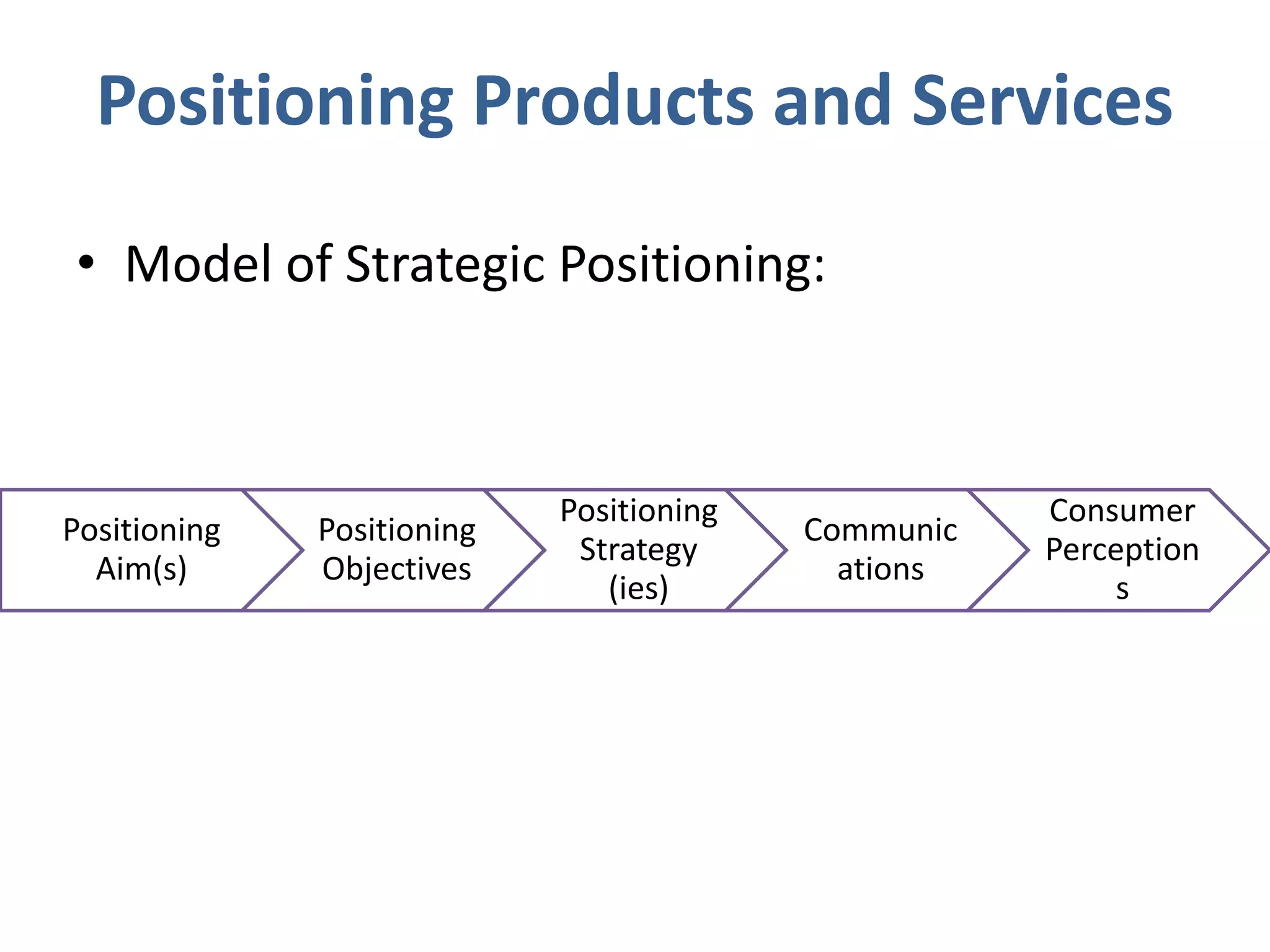
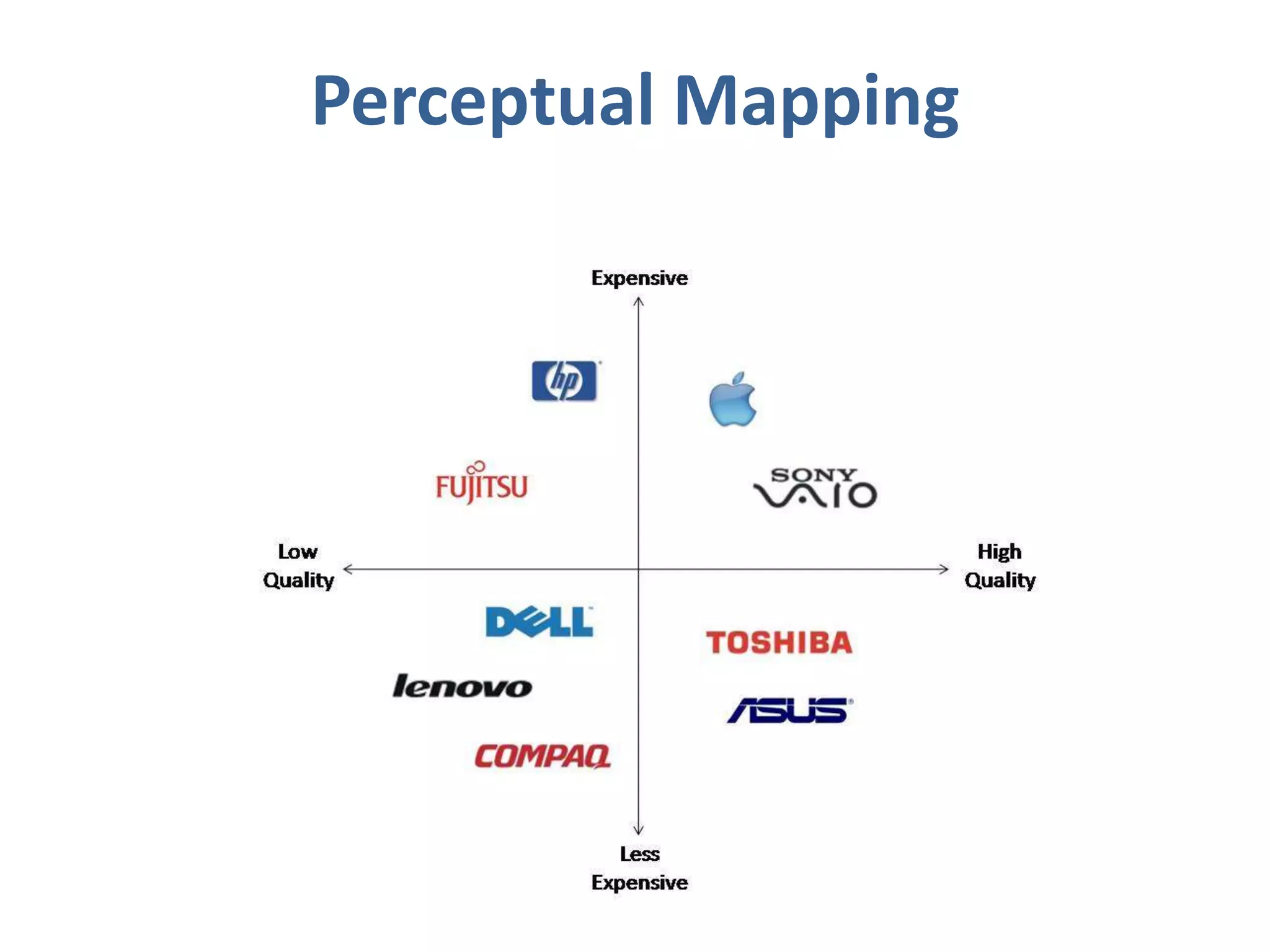
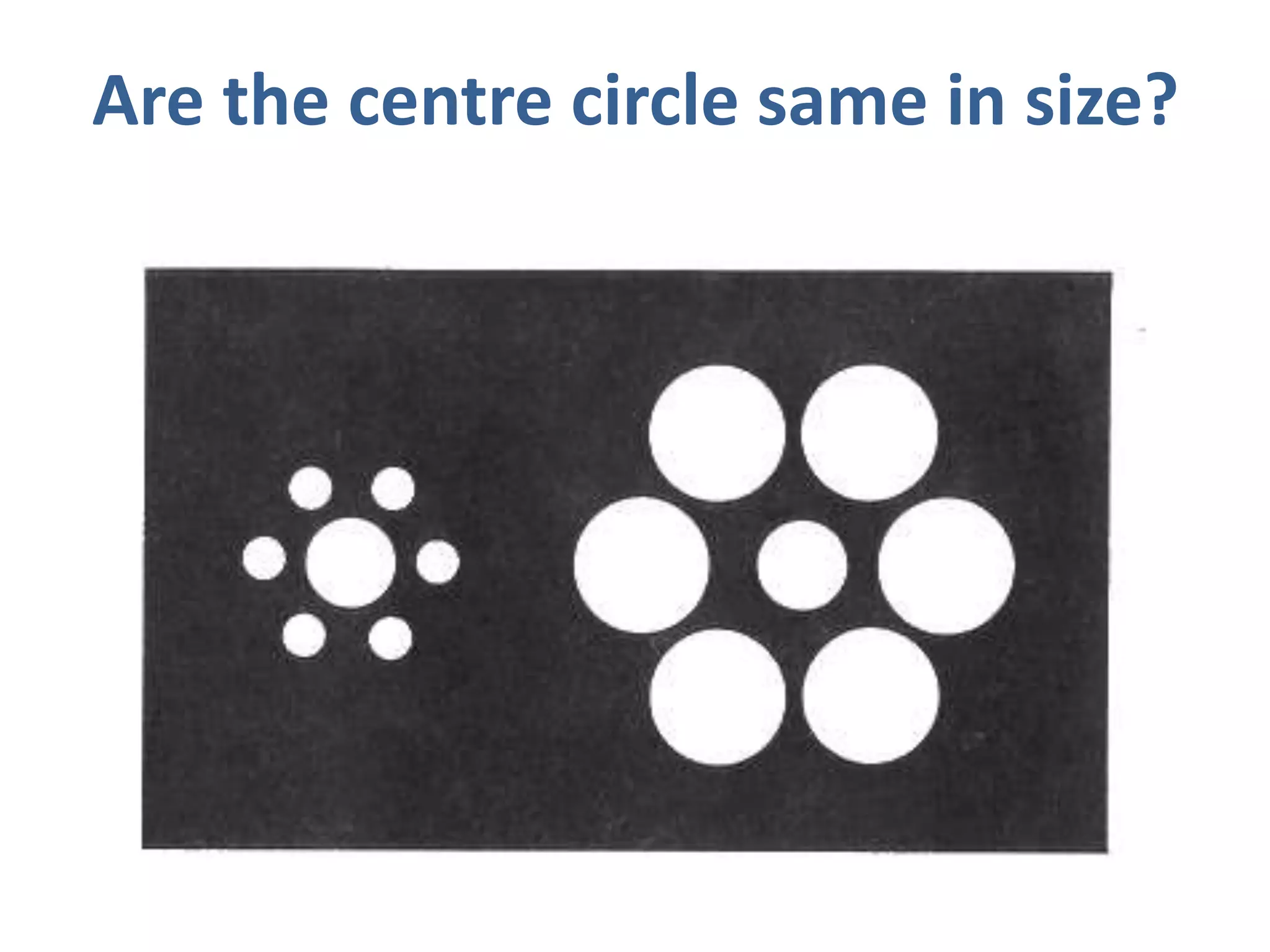
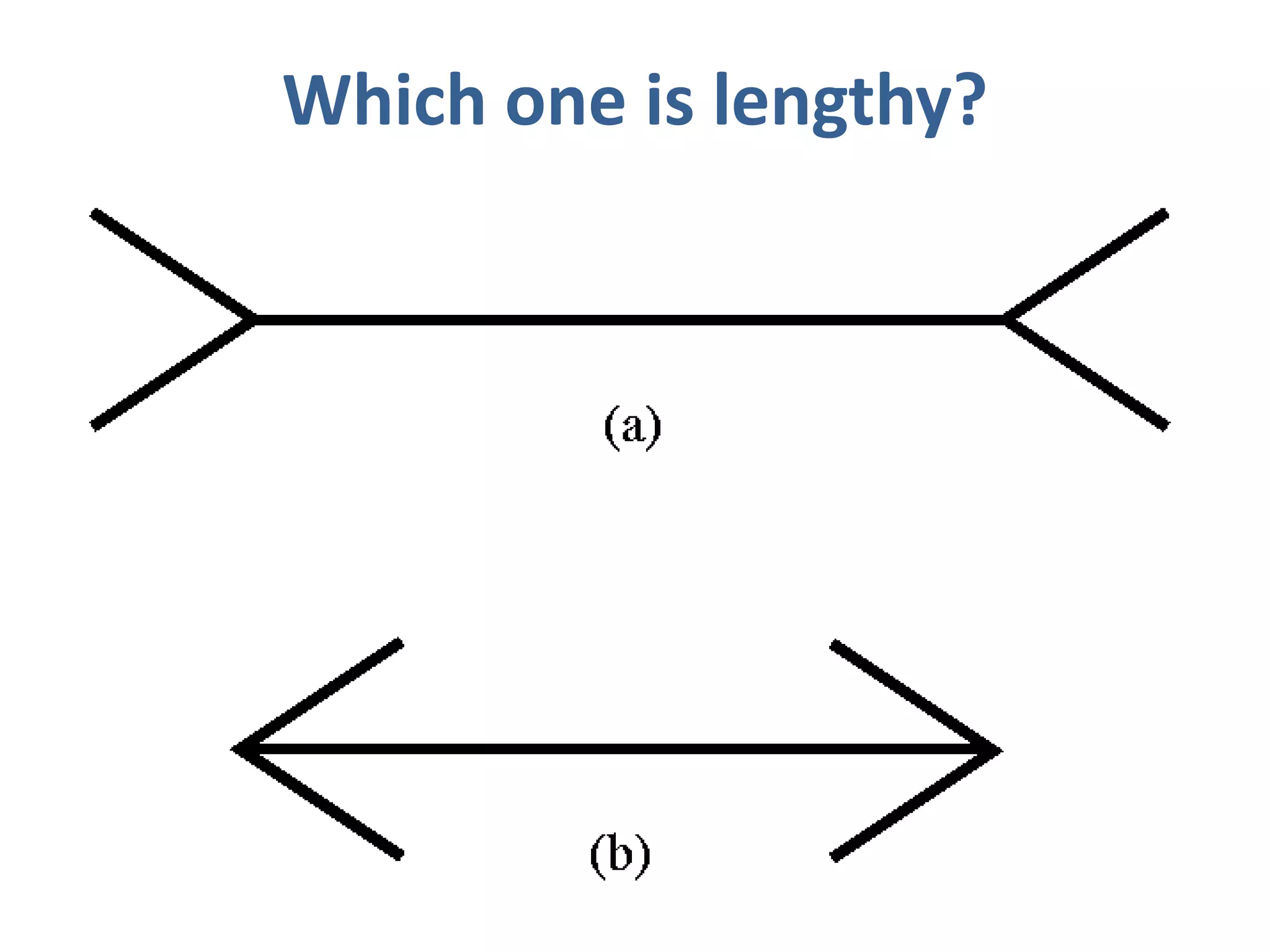
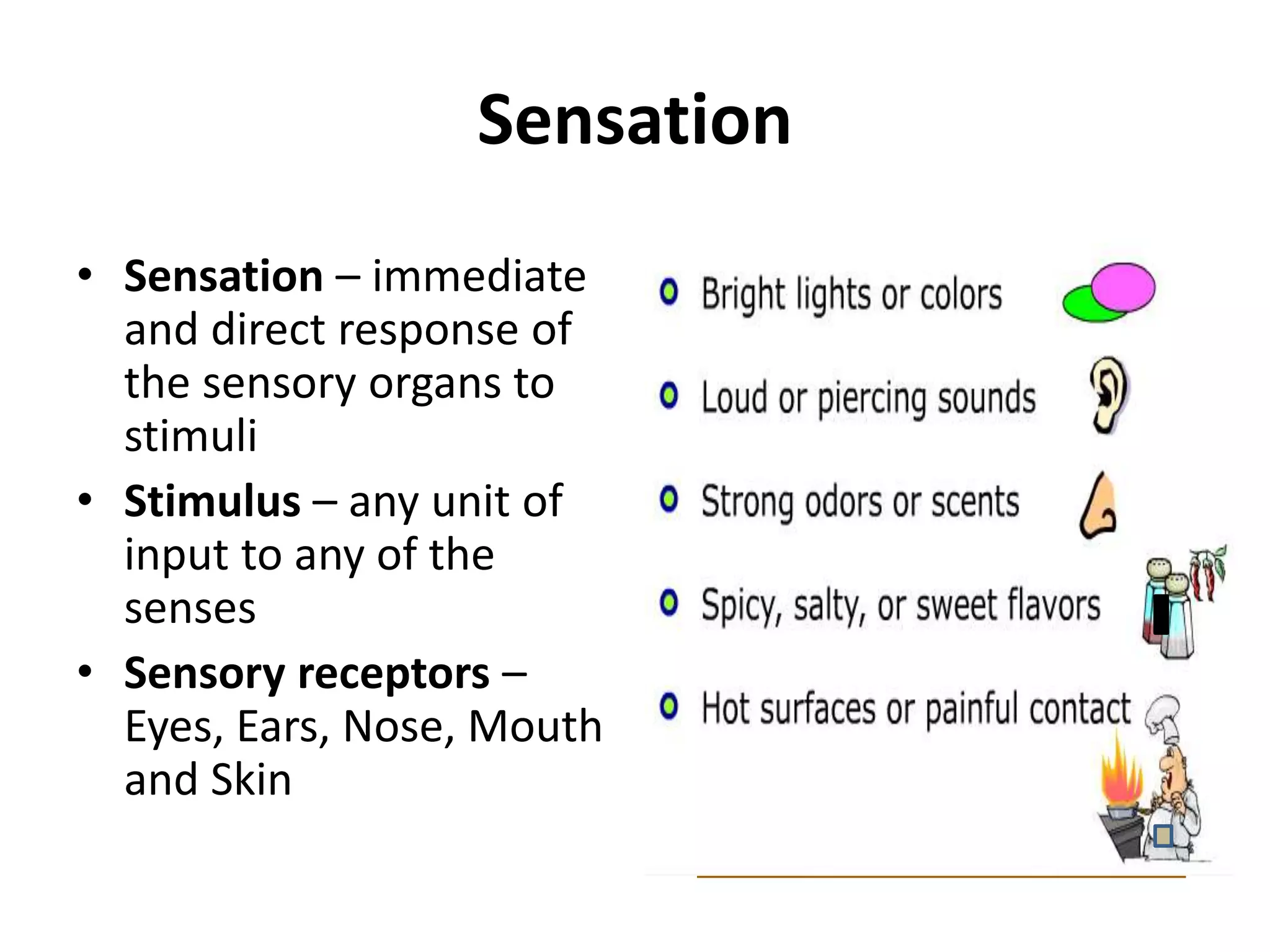
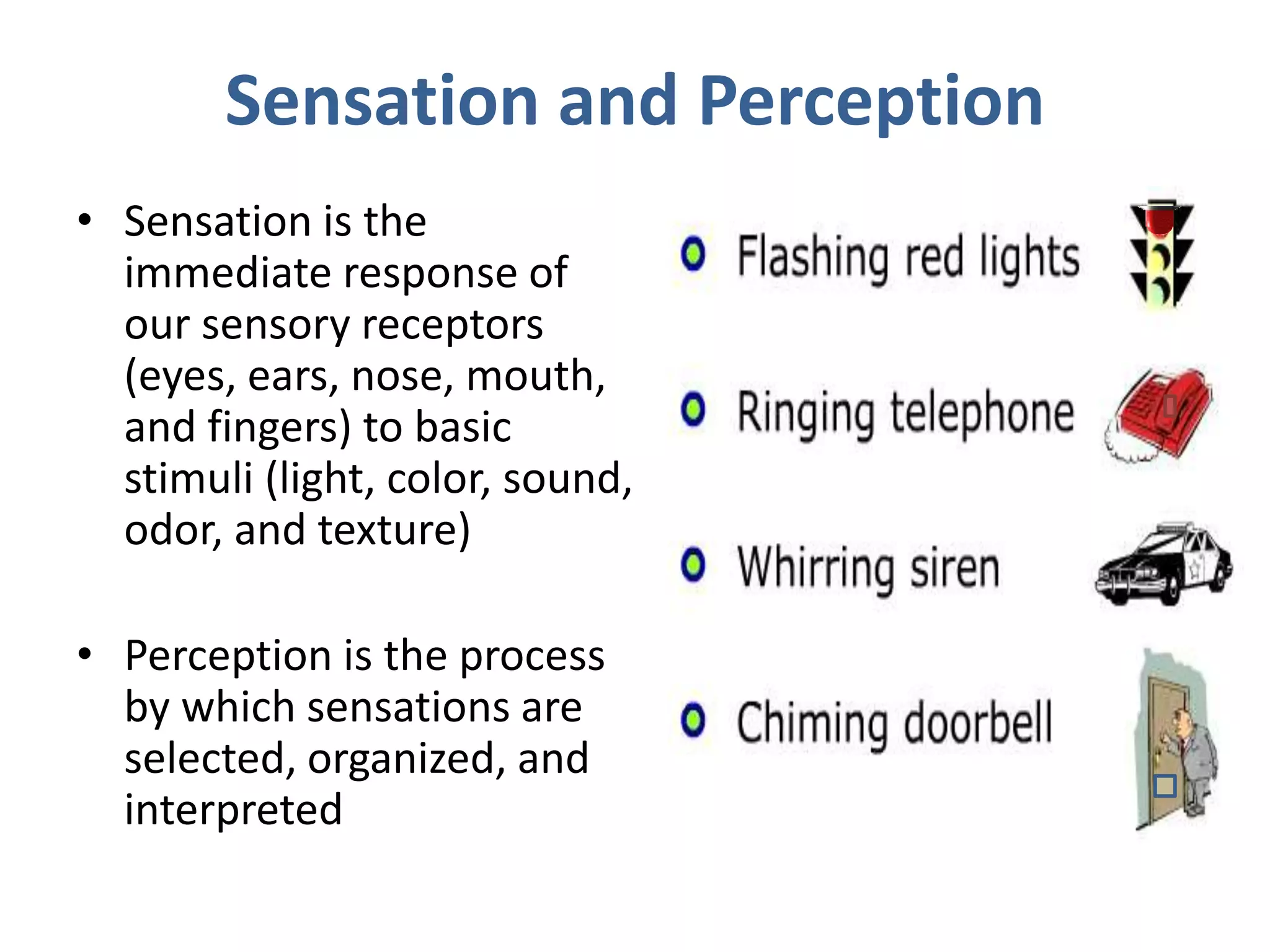
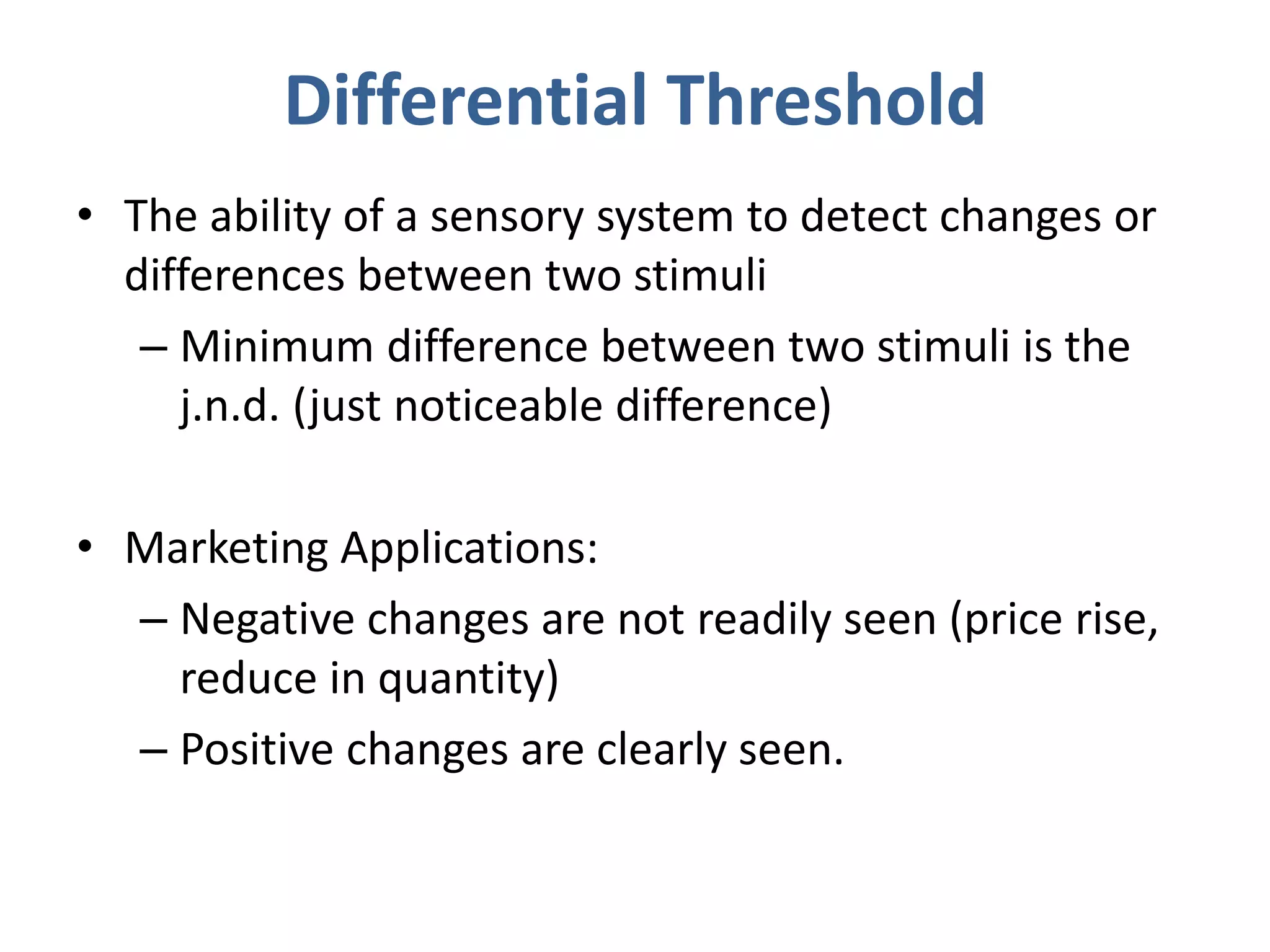
Perception involves selecting, organizing, and interpreting sensory information. Sensation is the immediate response to stimuli, while perception adds interpretation. Selective perception means we notice some things more than others based on internal factors like motivation and external ones like size and motion. Gestalt principles of perceptual organization include figure/ground, grouping, closure, and good continuation. Perceptual interpretation involves applying stereotypes, judging appearances, using descriptive terms, forming first impressions, and halo effects. Positioning creates an image for a product or service in consumers' minds through communications and benefits rather than attributes. Repositioning may be needed due to competitors, lifestyle changes, or target segments.











![SELECTIVE PERCEPTION
• Selective exposure:-
– People look for pleasant and sympathetic
messages and avoid painful or
threatening ones
• Selective attention:-
– People look into ads which will satisfy
their need
• Perceptual Defense:-
– People avoid psychologically threatening
ones. Hence constantly change the ad
nature. [ Smoking – warning with words,
and now with images ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session10-consumerperception-150402044634-conversion-gate01/75/Consumer-Perception-21-2048.jpg)