1. Perception is the process by which individuals select, organize, and interpret stimuli from their environment to form a meaningful picture.
2. Perception is influenced by individual factors like needs, values, and expectations, so it can differ between people regarding the same situation.
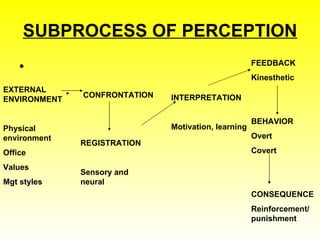
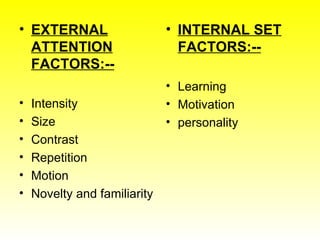
3. Key aspects of perception include sensation (receiving stimuli through senses), interpretation (refining raw sensory data), and factors like attention, learning, motivation, and personality.