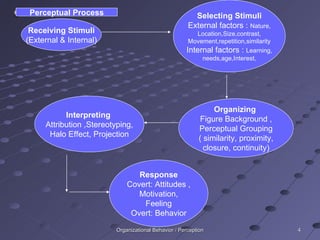
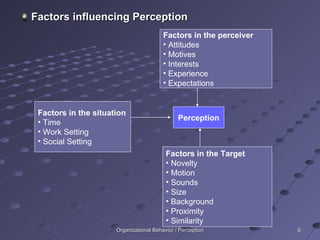
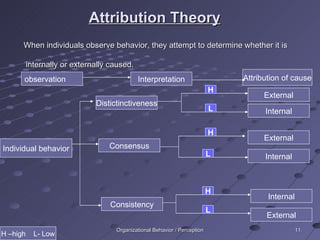
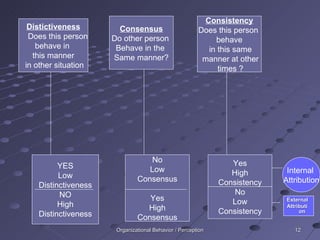
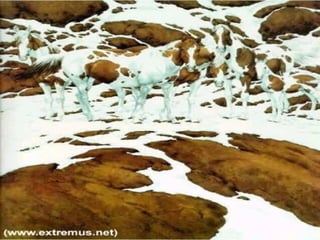
Perception is the process of receiving and interpreting sensory information from the environment. It involves selecting stimuli, organizing them into patterns, and translating them into meaningful interpretations. Several factors influence perception, including characteristics of the perceiver, the target being perceived, and the surrounding situation. When perceiving others, people tend to make judgments based on attribution theory and shortcuts like the halo effect and stereotyping.