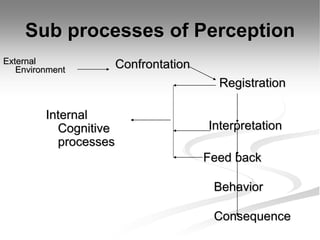
Perception is a complex cognitive process that involves selecting, organizing, and interpreting stimuli. It differs between individuals based on their needs, expectations, and past experiences. Perception involves both internal cognitive processes and external environmental factors. There are several factors that can influence perception, including the perceiver's attitudes and motives, the target stimulus, and the surrounding situation. Perceptual processes like figure-ground perception, grouping, and constancy help organize sensory information. Social perception involves processes like attribution and impression management that influence how people perceive and evaluate others. Stereotyping and halo effects are common problems that can occur in social perception.