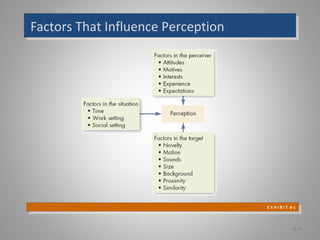
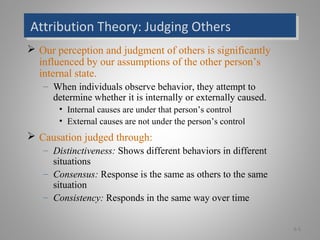
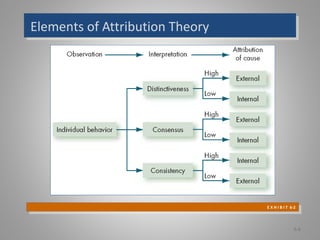
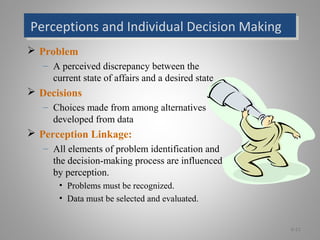
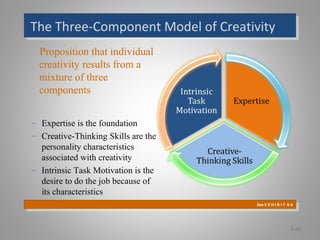
The document discusses perception and individual decision-making, highlighting how perception influences behavior and decision processes. It explores attribution theory, cognitive biases in decision-making, and the impact of individual differences and organizational constraints. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of ethical criteria in decision-making and presents a model for enhancing creativity.