The document discusses various topics related to perception and individual decision making, including:
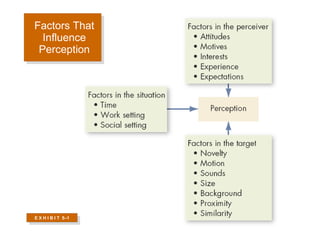
1. Perception is how individuals organize and interpret sensory impressions to make meaning of their environment. Factors like the person, situation, and biases can influence perception.
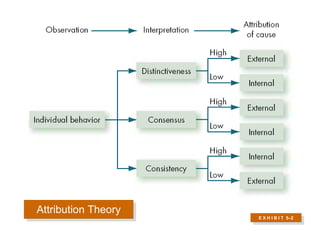
2. Attribution theory examines how people make judgments about the causes of behavior, and common biases include the fundamental attribution error and self-serving bias.
3. Shortcuts like the halo effect, stereotyping, and selective perception are frequently used when judging others. These perceptual biases can influence decisions in organizations.
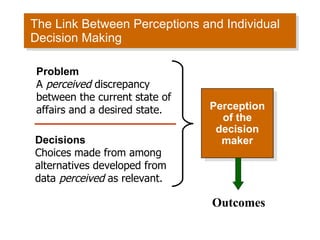
4. The rational decision-making model involves defining problems, considering alternatives and criteria, and selecting the optimal choice. However, bounded rationality and biases