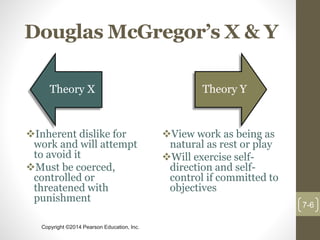
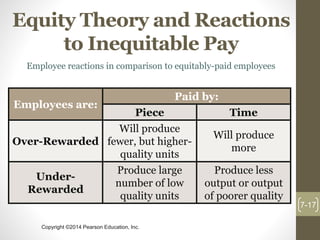
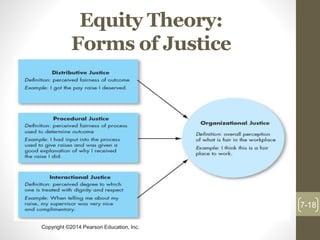
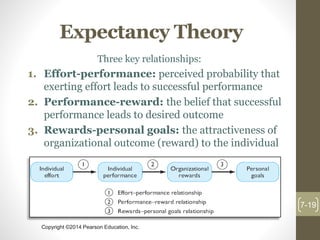
This chapter discusses theories of motivation. It begins by defining motivation as the processes that account for an individual's intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward attaining an organizational goal. Early theories discussed include Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and McClelland's three needs theory. Contemporary theories covered are self-determination theory, job engagement, goal-setting theory and management by objectives, self-efficacy theory, equity theory, and expectancy theory.