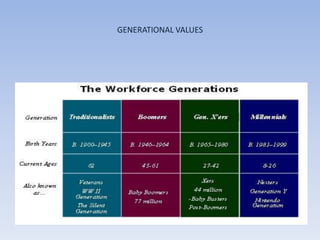
The document discusses personality, personality traits, and values. It defines personality as the dynamic organization of psychophysical systems that determine adjustments to the environment. Personality traits are enduring characteristics that describe individual behavior. Common personality tests like the Rorschach inkblot test and Thematic Appreciation Test are used to analyze personality characteristics. Personality is determined by factors like heredity, environment, and the Big 5 personality model. Values provide understanding of attitudes and behaviors and influence perception. Types of values include terminal and instrumental values. Generational and cultural values can differ. An individual's personality and values are linked to workplace satisfaction and turnover through personality-job fit theory.