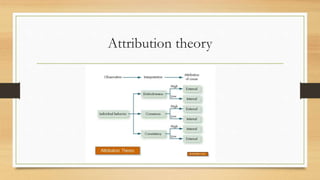
Perception is how individuals organize and interpret sensory impressions to understand their environment. People's behavior is based on their perceived reality rather than objective reality. When judging others, people use attribution theory to determine if behaviors are internally or externally caused based on distinctiveness, consensus, and consistency. Common shortcuts in judging others include selective perception, halo effect, contrast effect, stereotyping, and projection. Decision making is influenced by perception and individual differences like personality, gender, abilities, and culture as well as organizational constraints like performance evaluations, rewards systems, and time pressures. Ethical decision making considers utilitarianism, respecting rights, and impartial justice. Improving decisions involves understanding biases, combining rational and intuitive thinking, and enhancing creativity.