Motivation
•Download as PPT, PDF•
3 likes•4,501 views
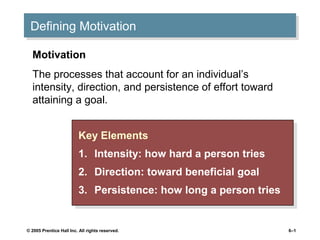
There are three key elements of motivation: intensity, direction, and persistence. Motivation is defined as the processes that account for an individual's effort toward achieving a goal. Several theories of motivation are discussed in the document, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and Vroom's expectancy theory. Emotions play an important role in work behavior and organizational behavior through concepts like emotional labor and emotional intelligence.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Stephen p. robbins chapter 17

L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E
Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter.
Who Are Leaders and What Is Leadership
Define leaders and leadership.
Explain why managers should be leaders.
Early Leadership Theories
Discuss what research has shown about leadership traits.
Contrast the findings of the four behavioral leadership
theories.
Explain the dual nature of a leader s behavior.
Chapter 4 emotions and moods

This chapter discusses emotions and moods in organizational behavior. It defines emotions and moods, identifies the basic emotions as anger, fear, sadness, happiness, disgust, and surprise. Moods are categorized as positive or negative affect. The chapter explores the functions of emotions in decision making. It examines sources of emotions and moods such as personality, time of day, weather, stress, and social activities. The impact of emotional labor on employees is discussed. Affective Events Theory holds that workplace events trigger emotional responses. The chapter reviews evidence for and against the concept of emotional intelligence. It applies concepts of emotions and moods to areas of OB like selection, decision making, creativity, and leadership. Cultural differences in the experience
Robbins chapter 3

This document summarizes key chapters from Organizational Behavior by Stephen P. Robbins. Chapter 3 covers values, attitudes, and job satisfaction. It defines values and attitudes, discusses how they relate to behavior, and frames job satisfaction in terms of its relationship to performance, absenteeism, and turnover. Responses to job dissatisfaction are also examined, including exit, voice, loyalty, and neglect.
Organizational Change and Stress Management

This document discusses organizational change and stress management. It covers topics such as planned change, resistance to change, models of change like Lewin's three-step model, and techniques for managing change like action research and organizational development. It also addresses sources of stress, consequences of stress, and approaches for managing stress at the individual and organizational level.
Ob stephen robbins

Organizational behavior is defined as the field of study that investigates how individuals, groups, and structure influence behavior within organizations in order to improve an organization's effectiveness. Managers achieve goals through directing the activities of others. The chapter discusses the importance of replacing managerial intuition with systematic study using concepts from fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology. It also outlines challenges and opportunities for applying organizational behavior concepts, such as managing workforce diversity and globalization.
Robbins ppt16

The document discusses theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, and Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory. It also discusses contemporary theories such as goal-setting theory, reinforcement theory, equity theory, and expectancy theory. Key aspects of motivation discussed include needs, goals, behavior, perception, and designing motivating jobs and rewards programs. The document provides an overview of important concepts in understanding motivation.
Chapter 3 Attitudes and Job Satisfaction

This document summarizes key topics from Chapter 3 of the textbook "Organizational Behavior" including attitudes, job satisfaction, and their impacts. It discusses how attitudes do not always determine behavior, and defines major job attitudes like job satisfaction, involvement, and commitment. Job satisfaction is described as a positive feeling towards one's job, and factors that influence it include pay, personality, and causes like the work itself, relationships, and growth opportunities. Dissatisfied employees may respond actively or passively, and constructively or destructively. Outcomes of job satisfaction are better job performance, organizational citizenship, customer satisfaction, and less absenteeism. However, managers often underestimate the importance of satisfaction.
Ch 15 motivating employees

This document summarizes key theories and concepts related to motivating employees from a management textbook. It discusses early theories like Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, and Herzberg's two-factor theory. Contemporary theories covered include goal-setting theory, reinforcement theory, job design approaches like the job characteristics model, and equity theory. The document also outlines current issues in motivation like cross-cultural challenges and motivating unique worker groups.
Recommended
Stephen p. robbins chapter 17

L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E
Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter.
Who Are Leaders and What Is Leadership
Define leaders and leadership.
Explain why managers should be leaders.
Early Leadership Theories
Discuss what research has shown about leadership traits.
Contrast the findings of the four behavioral leadership
theories.
Explain the dual nature of a leader s behavior.
Chapter 4 emotions and moods

This chapter discusses emotions and moods in organizational behavior. It defines emotions and moods, identifies the basic emotions as anger, fear, sadness, happiness, disgust, and surprise. Moods are categorized as positive or negative affect. The chapter explores the functions of emotions in decision making. It examines sources of emotions and moods such as personality, time of day, weather, stress, and social activities. The impact of emotional labor on employees is discussed. Affective Events Theory holds that workplace events trigger emotional responses. The chapter reviews evidence for and against the concept of emotional intelligence. It applies concepts of emotions and moods to areas of OB like selection, decision making, creativity, and leadership. Cultural differences in the experience
Robbins chapter 3

This document summarizes key chapters from Organizational Behavior by Stephen P. Robbins. Chapter 3 covers values, attitudes, and job satisfaction. It defines values and attitudes, discusses how they relate to behavior, and frames job satisfaction in terms of its relationship to performance, absenteeism, and turnover. Responses to job dissatisfaction are also examined, including exit, voice, loyalty, and neglect.
Organizational Change and Stress Management

This document discusses organizational change and stress management. It covers topics such as planned change, resistance to change, models of change like Lewin's three-step model, and techniques for managing change like action research and organizational development. It also addresses sources of stress, consequences of stress, and approaches for managing stress at the individual and organizational level.
Ob stephen robbins

Organizational behavior is defined as the field of study that investigates how individuals, groups, and structure influence behavior within organizations in order to improve an organization's effectiveness. Managers achieve goals through directing the activities of others. The chapter discusses the importance of replacing managerial intuition with systematic study using concepts from fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology. It also outlines challenges and opportunities for applying organizational behavior concepts, such as managing workforce diversity and globalization.
Robbins ppt16

The document discusses theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, and Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory. It also discusses contemporary theories such as goal-setting theory, reinforcement theory, equity theory, and expectancy theory. Key aspects of motivation discussed include needs, goals, behavior, perception, and designing motivating jobs and rewards programs. The document provides an overview of important concepts in understanding motivation.
Chapter 3 Attitudes and Job Satisfaction

This document summarizes key topics from Chapter 3 of the textbook "Organizational Behavior" including attitudes, job satisfaction, and their impacts. It discusses how attitudes do not always determine behavior, and defines major job attitudes like job satisfaction, involvement, and commitment. Job satisfaction is described as a positive feeling towards one's job, and factors that influence it include pay, personality, and causes like the work itself, relationships, and growth opportunities. Dissatisfied employees may respond actively or passively, and constructively or destructively. Outcomes of job satisfaction are better job performance, organizational citizenship, customer satisfaction, and less absenteeism. However, managers often underestimate the importance of satisfaction.
Ch 15 motivating employees

This document summarizes key theories and concepts related to motivating employees from a management textbook. It discusses early theories like Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, and Herzberg's two-factor theory. Contemporary theories covered include goal-setting theory, reinforcement theory, job design approaches like the job characteristics model, and equity theory. The document also outlines current issues in motivation like cross-cultural challenges and motivating unique worker groups.
Chapter 4 emotions and Moods

The document summarizes key points from a chapter on emotions and moods in organizational behavior. It defines emotions and moods, lists the basic emotions, and discusses the functions of emotions. It also covers sources of emotions and moods, the impact of emotional labor, affective events theory, evidence for and against emotional intelligence, strategies for emotion regulation, and how concepts of emotions apply to issues like decision-making, leadership, and customer service. The chapter aims to demonstrate that emotions are a natural part of human behavior and cannot be separated from workplace interactions and performance.
Dessler 08

The document discusses training and developing employees. It describes the basic training process including identifying training needs through task and performance analysis. It explains distinguishing problems that can and cannot be addressed with training. Finally, it outlines several training techniques including orientation, programmed learning, distance learning, literacy training, management development, and managing organizational change.
HRM chapter no.7 (Interviw of employee)

The document discusses different types of interviews used in employment selection. It describes selection interviews, which are used to predict job performance, appraisal interviews for performance reviews, and exit interviews. Structured interviews follow a set sequence of questions, while unstructured interviews allow more flexibility. Common question types include situational, behavioral, and job-related questions. Effective interviews are structured, use objective rating scales, and involve multiple interviewers when possible. The document provides guidelines for an effective interview, such as preparing questions linked to job duties and controlling the discussion.
Dessler hrm12e chp_08

The document discusses various topics relating to training and developing employees, including:
1) The purpose and process of employee orientation to help new employees feel welcome and understand expectations.
2) The four-step training process of instructional design, needs analysis, program implementation, and evaluation.
3) Different training methods such as on-the-job training, lectures, and programmed learning.
Diversity In Organizations, Chapter-2, Organizational Behavior

Diversity In Organizations, Chapter-2, Organizational Behavior
This PPT is based on the Organizational Behavior Book Written By Stephen P. Robbins & Timothy A. Judge, Edition -17th, Publisher Pearson
Robbins ob14 ppt_05

This chapter discusses personality and values in organizational behavior. It defines personality and describes common frameworks for understanding it, including the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and Big Five model. Key personality traits like conscientiousness, extraversion, and emotional stability are linked to job performance. Values represent preferences about how to live and differ between generations and cultures. Managers should consider person-job and person-organization fit to match personalities and values with work. Hofstede's model describes cultural dimensions like individualism and power distance that influence values internationally. Overall, personality and values assessment can aid selection and development in organizations.
Organizational Behaviour Stephen Robbins 14Ed. Chapter 6

This document discusses perception and individual decision making. It covers topics like attribution theory, biases that influence perception and judgment of others, common shortcuts and errors in decision making, and ways to improve creativity. Attribution theory examines how people make causal explanations for behaviors, looking at factors like distinctiveness, consensus and consistency. Biases discussed include the fundamental attribution error and self-serving bias. The rational and bounded reality models of decision making are presented.
Organizational Behavior Chapter 7 Motivation - From Concepts to Application

The document discusses various ways to motivate employees through job design and rewards. It describes the job characteristics model which proposes that motivating jobs are autonomous, provide feedback, and have at least one meaningfulness factor. Jobs can be redesigned through methods like job rotation, job enrichment, and alternative work arrangements. Employee involvement measures like participative management and representative participation can also increase motivation. Reward programs include variable pay, flexible benefits, and employee recognition programs which provide intrinsic rewards.
Chapter 16 management (10 th edition) by robbins and coulter

The document summarizes key concepts from a chapter on leadership from a management textbook. It defines leadership and discusses early theories on leadership traits and behaviors. It then covers contingency theories of leadership, including Fiedler's model, situational leadership theory, and path-goal theory. Contemporary views of leadership presented include transactional vs transformational leadership as well as charismatic, visionary, and team leadership.
organizational behavior

This document summarizes a chapter from an organizational behavior textbook about emotions and moods in the workplace. It defines emotions and moods, discusses common emotions and moods, and explores how emotions are influenced by factors like personality, social activities, and emotional labor. The chapter also describes affective events theory and emotional intelligence, and examines applications of emotions and moods to areas like decision-making, leadership, and global implications for different cultures. Managers are advised not to ignore or over-control the emotions of employees, as emotions impact many aspects of organizational behavior.
Organisational Behaviour

The document is a chapter from an organizational behavior textbook. It introduces key concepts in OB including:
- Defining OB as the study of how individuals, groups, and structure impact behavior in organizations.
- Describing the major challenges and opportunities managers face in areas like globalization, diversity, quality improvement, and changing workforce needs.
- Explaining the contributions of behavioral sciences like psychology, sociology, and anthropology to the development of OB as a field of study.
- Presenting a basic OB model that shows how individual, group, and organizational factors influence important dependent variables like job satisfaction, productivity, and turnover.
Ch03 attitudes and job satisfaction

This document discusses a chapter about attitudes and job satisfaction from a textbook. It covers the three components of attitudes, the relationship between attitudes and behavior, major job attitudes like job satisfaction and involvement, how job satisfaction can be measured, main causes of job satisfaction, and four employee responses to dissatisfaction like turnover. The chapter aims to explain attitudes and job satisfaction to students.
Organizational Behavior Chapter 5 Perception and Individual Decision Making

This document discusses perception and decision making. It defines perception as how individuals organize and interpret sensory impressions to understand their environment. Perception is influenced by factors like the situation, perceiver, and target. Attribution theory holds that people try to explain behaviors as either internal or external to the person. Common shortcuts used in judging others include selective perception, halo effect, contrast effects, and stereotyping. Decision making is linked to perception, which can influence problem identification, information processing, and conclusions. The document also outlines rational decision making, bounded rationality, intuitive decision making, and common decision biases. [/SUMMARY]
Robbins9 ppt12

The document is a learning outline for a chapter on human resource management. It outlines key topics in HRM including why HRM is important, the HRM process, human resource planning, recruitment and selection, orientation and training, performance management, compensation and benefits, and current HRM issues. For each topic, it lists the main points to be covered and learning objectives. The outline provides a concise guide to the content and important concepts in the chapter on HRM.
Individual behavior

The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 2 of Organizational Behavior by Stephen P. Robbins. It discusses foundations of individual behavior, including biographical characteristics, abilities, learning theories, reinforcement schedules, and behavior modification. The main topics covered are defining individual differences, exploring concepts of intelligence and learning, describing conditioning and reinforcement, and applying behavior modification in organizations.
Organizational behavior by Robbins and Judge 17th edition chapter 14 Conflict...

1. The document discusses organizational conflict and negotiation. It defines conflict, describes the conflict process in 5 stages, and discusses conflict management and resolution techniques
Ch 16 managers as leaders

This document provides an overview of chapter 16 from the textbook "Management" 10th edition by Stephen P. Robbins and Mary Coulter. The chapter discusses managers as leaders and covers topics such as early leadership theories, contingency theories of leadership, contemporary views of leadership, and leadership issues in the 21st century. Key sections summarize trait theories, behavioral theories including the Ohio State and Michigan studies, contingency theories like Fiedler's model and situational leadership theory, and differences between transactional and transformational leadership.
Organizational behavior chapter 2

This chapter discusses attitudes and job satisfaction. It defines attitudes as evaluative statements that can be favorable or unfavorable about objects, people or events. Attitudes have three main components - cognitive, affective, and behavioral. The chapter explores how attitudes relate to behavior and the relationship between cognitive dissonance and reducing inconsistencies. It also examines how job satisfaction, involvement, empowerment, and other job attitudes are measured and what causes job satisfaction. Managers are advised to focus on making work interesting in order to improve attitudes.
Robbins9 ppt16 motivation

This document provides an outline for a chapter on motivating employees. It begins by defining motivation and describing motivation as a need-satisfying process. It then summarizes several early and contemporary theories of motivation, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory, McClelland's three-needs theory, goal-setting theory, and expectancy theory. The outline also discusses designing motivating jobs, equity theory, and current issues in employee motivation.
Chapter 12 Human Resource Management Ppt12

The document outlines the key aspects of human resource management including the importance of HRM in gaining a competitive advantage, the HRM process of planning, recruiting, selecting, orienting and training employees, performance management and compensation. It also discusses current issues such as managing diversity, downsizing, work-life balance and legal compliance areas like sexual harassment. Specific topics covered include performance appraisal methods, factors influencing compensation, changing nature of career development, and suggestions for managing human resources and current workplace challenges.
Organizational behavior course model

This document provides an overview of organizational behavior and motivation theories. It discusses outcomes like job satisfaction and absenteeism that are influenced by managers. Motivation theories covered include Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, expectancy theory, equity theory, goal setting theory, and reinforcement theory. The key aspects and implications of each theory for motivating employees are summarized. Overall, the document presents motivation as important for performance and offers different theoretical approaches for managers to understand and influence employee effort.
Definition of performance management

The document discusses performance management and performance appraisal. It defines performance management as a systematic process to improve individual and organizational performance through goal setting, continuous feedback, development programs, and rewards. Performance appraisals are evaluations of employee performance and potential that are used for decisions around compensation, promotions, training, and retention. The document outlines various methods for performance appraisals, including rating scales, checklists, forced choice, and behavioral anchored rating scales. It discusses the objectives, advantages, and process of performance appraisals.
More Related Content
What's hot
Chapter 4 emotions and Moods

The document summarizes key points from a chapter on emotions and moods in organizational behavior. It defines emotions and moods, lists the basic emotions, and discusses the functions of emotions. It also covers sources of emotions and moods, the impact of emotional labor, affective events theory, evidence for and against emotional intelligence, strategies for emotion regulation, and how concepts of emotions apply to issues like decision-making, leadership, and customer service. The chapter aims to demonstrate that emotions are a natural part of human behavior and cannot be separated from workplace interactions and performance.
Dessler 08

The document discusses training and developing employees. It describes the basic training process including identifying training needs through task and performance analysis. It explains distinguishing problems that can and cannot be addressed with training. Finally, it outlines several training techniques including orientation, programmed learning, distance learning, literacy training, management development, and managing organizational change.
HRM chapter no.7 (Interviw of employee)

The document discusses different types of interviews used in employment selection. It describes selection interviews, which are used to predict job performance, appraisal interviews for performance reviews, and exit interviews. Structured interviews follow a set sequence of questions, while unstructured interviews allow more flexibility. Common question types include situational, behavioral, and job-related questions. Effective interviews are structured, use objective rating scales, and involve multiple interviewers when possible. The document provides guidelines for an effective interview, such as preparing questions linked to job duties and controlling the discussion.
Dessler hrm12e chp_08

The document discusses various topics relating to training and developing employees, including:
1) The purpose and process of employee orientation to help new employees feel welcome and understand expectations.
2) The four-step training process of instructional design, needs analysis, program implementation, and evaluation.
3) Different training methods such as on-the-job training, lectures, and programmed learning.
Diversity In Organizations, Chapter-2, Organizational Behavior

Diversity In Organizations, Chapter-2, Organizational Behavior
This PPT is based on the Organizational Behavior Book Written By Stephen P. Robbins & Timothy A. Judge, Edition -17th, Publisher Pearson
Robbins ob14 ppt_05

This chapter discusses personality and values in organizational behavior. It defines personality and describes common frameworks for understanding it, including the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and Big Five model. Key personality traits like conscientiousness, extraversion, and emotional stability are linked to job performance. Values represent preferences about how to live and differ between generations and cultures. Managers should consider person-job and person-organization fit to match personalities and values with work. Hofstede's model describes cultural dimensions like individualism and power distance that influence values internationally. Overall, personality and values assessment can aid selection and development in organizations.
Organizational Behaviour Stephen Robbins 14Ed. Chapter 6

This document discusses perception and individual decision making. It covers topics like attribution theory, biases that influence perception and judgment of others, common shortcuts and errors in decision making, and ways to improve creativity. Attribution theory examines how people make causal explanations for behaviors, looking at factors like distinctiveness, consensus and consistency. Biases discussed include the fundamental attribution error and self-serving bias. The rational and bounded reality models of decision making are presented.
Organizational Behavior Chapter 7 Motivation - From Concepts to Application

The document discusses various ways to motivate employees through job design and rewards. It describes the job characteristics model which proposes that motivating jobs are autonomous, provide feedback, and have at least one meaningfulness factor. Jobs can be redesigned through methods like job rotation, job enrichment, and alternative work arrangements. Employee involvement measures like participative management and representative participation can also increase motivation. Reward programs include variable pay, flexible benefits, and employee recognition programs which provide intrinsic rewards.
Chapter 16 management (10 th edition) by robbins and coulter

The document summarizes key concepts from a chapter on leadership from a management textbook. It defines leadership and discusses early theories on leadership traits and behaviors. It then covers contingency theories of leadership, including Fiedler's model, situational leadership theory, and path-goal theory. Contemporary views of leadership presented include transactional vs transformational leadership as well as charismatic, visionary, and team leadership.
organizational behavior

This document summarizes a chapter from an organizational behavior textbook about emotions and moods in the workplace. It defines emotions and moods, discusses common emotions and moods, and explores how emotions are influenced by factors like personality, social activities, and emotional labor. The chapter also describes affective events theory and emotional intelligence, and examines applications of emotions and moods to areas like decision-making, leadership, and global implications for different cultures. Managers are advised not to ignore or over-control the emotions of employees, as emotions impact many aspects of organizational behavior.
Organisational Behaviour

The document is a chapter from an organizational behavior textbook. It introduces key concepts in OB including:
- Defining OB as the study of how individuals, groups, and structure impact behavior in organizations.
- Describing the major challenges and opportunities managers face in areas like globalization, diversity, quality improvement, and changing workforce needs.
- Explaining the contributions of behavioral sciences like psychology, sociology, and anthropology to the development of OB as a field of study.
- Presenting a basic OB model that shows how individual, group, and organizational factors influence important dependent variables like job satisfaction, productivity, and turnover.
Ch03 attitudes and job satisfaction

This document discusses a chapter about attitudes and job satisfaction from a textbook. It covers the three components of attitudes, the relationship between attitudes and behavior, major job attitudes like job satisfaction and involvement, how job satisfaction can be measured, main causes of job satisfaction, and four employee responses to dissatisfaction like turnover. The chapter aims to explain attitudes and job satisfaction to students.
Organizational Behavior Chapter 5 Perception and Individual Decision Making

This document discusses perception and decision making. It defines perception as how individuals organize and interpret sensory impressions to understand their environment. Perception is influenced by factors like the situation, perceiver, and target. Attribution theory holds that people try to explain behaviors as either internal or external to the person. Common shortcuts used in judging others include selective perception, halo effect, contrast effects, and stereotyping. Decision making is linked to perception, which can influence problem identification, information processing, and conclusions. The document also outlines rational decision making, bounded rationality, intuitive decision making, and common decision biases. [/SUMMARY]
Robbins9 ppt12

The document is a learning outline for a chapter on human resource management. It outlines key topics in HRM including why HRM is important, the HRM process, human resource planning, recruitment and selection, orientation and training, performance management, compensation and benefits, and current HRM issues. For each topic, it lists the main points to be covered and learning objectives. The outline provides a concise guide to the content and important concepts in the chapter on HRM.
Individual behavior

The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 2 of Organizational Behavior by Stephen P. Robbins. It discusses foundations of individual behavior, including biographical characteristics, abilities, learning theories, reinforcement schedules, and behavior modification. The main topics covered are defining individual differences, exploring concepts of intelligence and learning, describing conditioning and reinforcement, and applying behavior modification in organizations.
Organizational behavior by Robbins and Judge 17th edition chapter 14 Conflict...

1. The document discusses organizational conflict and negotiation. It defines conflict, describes the conflict process in 5 stages, and discusses conflict management and resolution techniques
Ch 16 managers as leaders

This document provides an overview of chapter 16 from the textbook "Management" 10th edition by Stephen P. Robbins and Mary Coulter. The chapter discusses managers as leaders and covers topics such as early leadership theories, contingency theories of leadership, contemporary views of leadership, and leadership issues in the 21st century. Key sections summarize trait theories, behavioral theories including the Ohio State and Michigan studies, contingency theories like Fiedler's model and situational leadership theory, and differences between transactional and transformational leadership.
Organizational behavior chapter 2

This chapter discusses attitudes and job satisfaction. It defines attitudes as evaluative statements that can be favorable or unfavorable about objects, people or events. Attitudes have three main components - cognitive, affective, and behavioral. The chapter explores how attitudes relate to behavior and the relationship between cognitive dissonance and reducing inconsistencies. It also examines how job satisfaction, involvement, empowerment, and other job attitudes are measured and what causes job satisfaction. Managers are advised to focus on making work interesting in order to improve attitudes.
Robbins9 ppt16 motivation

This document provides an outline for a chapter on motivating employees. It begins by defining motivation and describing motivation as a need-satisfying process. It then summarizes several early and contemporary theories of motivation, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory, McClelland's three-needs theory, goal-setting theory, and expectancy theory. The outline also discusses designing motivating jobs, equity theory, and current issues in employee motivation.
Chapter 12 Human Resource Management Ppt12

The document outlines the key aspects of human resource management including the importance of HRM in gaining a competitive advantage, the HRM process of planning, recruiting, selecting, orienting and training employees, performance management and compensation. It also discusses current issues such as managing diversity, downsizing, work-life balance and legal compliance areas like sexual harassment. Specific topics covered include performance appraisal methods, factors influencing compensation, changing nature of career development, and suggestions for managing human resources and current workplace challenges.
What's hot (20)
Diversity In Organizations, Chapter-2, Organizational Behavior

Diversity In Organizations, Chapter-2, Organizational Behavior
Organizational Behaviour Stephen Robbins 14Ed. Chapter 6

Organizational Behaviour Stephen Robbins 14Ed. Chapter 6
Organizational Behavior Chapter 7 Motivation - From Concepts to Application

Organizational Behavior Chapter 7 Motivation - From Concepts to Application
Chapter 16 management (10 th edition) by robbins and coulter

Chapter 16 management (10 th edition) by robbins and coulter
Organizational Behavior Chapter 5 Perception and Individual Decision Making

Organizational Behavior Chapter 5 Perception and Individual Decision Making
Organizational behavior by Robbins and Judge 17th edition chapter 14 Conflict...

Organizational behavior by Robbins and Judge 17th edition chapter 14 Conflict...
Viewers also liked
Organizational behavior course model

This document provides an overview of organizational behavior and motivation theories. It discusses outcomes like job satisfaction and absenteeism that are influenced by managers. Motivation theories covered include Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, expectancy theory, equity theory, goal setting theory, and reinforcement theory. The key aspects and implications of each theory for motivating employees are summarized. Overall, the document presents motivation as important for performance and offers different theoretical approaches for managers to understand and influence employee effort.
Definition of performance management

The document discusses performance management and performance appraisal. It defines performance management as a systematic process to improve individual and organizational performance through goal setting, continuous feedback, development programs, and rewards. Performance appraisals are evaluations of employee performance and potential that are used for decisions around compensation, promotions, training, and retention. The document outlines various methods for performance appraisals, including rating scales, checklists, forced choice, and behavioral anchored rating scales. It discusses the objectives, advantages, and process of performance appraisals.
Chapter 16 Motivation

Richard L. Daft addresses themes and issues directly relevant to both the everyday demands and significant challenges facing businesses today. Comprehensive coverage helps develop managers able to look beyond traditional techniques and ideas to tap into a full breadth of management skills. With the best in proven management and new competencies that harness creativity, D.A.F.T. is Management!
Practical ways to boost strategy execution

By now, most organizations have completed their strategic planning process for 2017 and are ready to execute brilliantly. These organizations, just like yours, are now at a fork in the road. At least 75% will take the road of failed execution. These companies, teams and individuals will struggle, and fall short of their 2017 goals.
But the other 25% will take another path – the road to explosive growth, results and success. The strategic leaders heading these organizations are able to:
- Drive their organizations to results with confidence
- Close the gap that exists between what they say they’re going to do (in strategy), and what actually gets done (in execution)
- Execute, assess, adjust and drive results in a repeatable, consistent and predictable way
Customer Relationship Management And Organizational Performance: A Conceptual...

Customers have become crucial for every organization. Due to the competitive environment,
customer relationship management (CRM) is one of the important business strategy for companies. Banks can
benefit from focusing and concentrating on Customer Relationship Management . There is a stiff competition
in the banking industry in Iran . So Iranian banks try to reform their strategies and process to achieve
competitive advantage. The customers are an important element that helps the bank to achieve this objective .
Banks try to notice the customers requirements and needs for satisfying their customers . Iranian Banks went
through reform from product orientation to customer orientation. More importantly, the banks realized that
building long-term relationship with their customer is crucial for achieving sustainable competitive advantage
and improving performance. This study examined the link between customer relationship management and
different measures of performance on the banking sector. Data were collected from the bank sectors in Iran.
Based on extensive review of literature, the sub processes in implementing CRM were extracted and also four
measures of Balanced scorecard applied to performance. The results indicated that CRM processes are
associated with bank performance.
Performance Management and Performance Appraisal

These Slides describes about the Performance Management and Performance Appraisal system in an organization
Employer Induction Pack- Employer documentation for apprenticeship provision

Employer Induction Pack, employer induction pack template, apprenticeship induction for employers, apprenticeship employer handbook, guide for apprenticeship for employers, guide to apprenticeships for employers,
Notes in Psychology: The Theory of Motivation

The etymology of the word ‘motivate’ descends from Old French motif, from late Latin motivus, from movere ‘to move’ in the 1800’s. Motivation is a reason or reasons for acting or behaving in a particular way.
Organization Development - Intervention Processes

Provides an overview of organization development (OD), focusing particularly on the intervention processes available. Categories or types of intervention are noted, and the depth of intervention is recognised as a key decision point for OD practitioners.
Designing a Results Driven Digital Strategy: Customers and Corporations’ Digi...

This document discusses designing a results-driven digital strategy for corporations. It argues that digital strategies are now a top priority for strategic planning as disruptive digital business models become the new normal. A digital strategy can transform a company by joining business, operations, and technology around a shared digital vision. A key part of a digital strategy is improving digital customer experience maturity by deeply understanding customer needs and journeys. However, achieving high digital customer experience is challenging as it requires constant change and adaptation to how customers interact with new technologies. Personalization is also increasingly important, such as using data analytics to provide personalized offers and advice to customers in real-time. A digital strategy must be omnichannel but will likely prioritize mobile experiences as they
Continuous Performance Management: How To Make It Work

The document discusses the arrival of continuous performance management and whether organizations are ready for it. It outlines factors disrupting organizations like demographic shifts, digital technology, and accelerated rate of change. A new social contract between companies and workers is emerging where younger workers demand rapid career growth and flexibility. Continuous performance management replaces annual reviews with continuous check-ins, transparent goals, feedback, and regular evaluation integrated into daily work. It shifts control from managers to teams and uses data instead of subjective assessments. Organizations must invest in training managers and change management to successfully adopt continuous performance management.
Fiedler's Contingency Model, Path Goal and Situational Theories

Fiedler's contingency model, path-goal theory, and situational leadership theory all provide frameworks for understanding effective leadership based on situational factors. Fiedler's model matches leadership style to situational favorability. Path-goal theory focuses on how a leader influences subordinates to achieve goals based on their characteristics and the work environment. Situational leadership theory proposes that effective leadership requires assessing follower readiness and adapting the level of task behavior and relationship behavior accordingly.
Motivation and Compensation of Sales People

The document discusses different types of compensation plans for motivating salespeople, including straight salary plans, straight commission plans, and combination plans. Straight salary plans provide secure income but lack financial incentives for performance. Straight commission plans strongly incentivize performance but may lack focus on customer relationships. Combination plans combine elements to reward performance while providing some security. The optimal plan depends on the sales role and company's objectives.
Viewers also liked (13)
Customer Relationship Management And Organizational Performance: A Conceptual...

Customer Relationship Management And Organizational Performance: A Conceptual...
Employer Induction Pack- Employer documentation for apprenticeship provision

Employer Induction Pack- Employer documentation for apprenticeship provision
Designing a Results Driven Digital Strategy: Customers and Corporations’ Digi...

Designing a Results Driven Digital Strategy: Customers and Corporations’ Digi...
Continuous Performance Management: How To Make It Work

Continuous Performance Management: How To Make It Work
Fiedler's Contingency Model, Path Goal and Situational Theories

Fiedler's Contingency Model, Path Goal and Situational Theories
Similar to Motivation
Motivation

The document discusses several theories of motivation:
1) Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory which states that as lower level needs are met, higher level needs emerge as motivators. It identifies physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs.
2) ERG theory proposes three core needs: existence, relatedness, and growth that can all be operative at the same time.
3) Expectancy theory suggests that motivation depends on the strength of the expectation that effort will lead to performance and rewards.
(Mb asubjects.com)ob11 06st

This document summarizes several theories of motivation from organizational behavior:
1. It describes Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory that humans have physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs that become dominant as lower needs are satisfied.
2. It outlines McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y which propose different assumptions about employee motivation - Theory X sees employees as lazy and Theory Y sees them as ambitious.
3. It discusses Herzberg's two-factor theory that proposes intrinsic and extrinsic factors influence satisfaction versus dissatisfaction at work.
(Mb asubjects.com)ob11 06st

This document provides an overview of various theories of motivation. It summarizes key concepts from Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, McGregor's Theory X and Y, Herzberg's two-factor theory, Alderfer's ERG theory, McClelland's needs theory, cognitive evaluation theory, goal-setting theory, reinforcement theory, job design theory, social information processing model, equity theory, and expectancy theory. For each theory, it outlines important concepts, principles, and relationships between variables that help explain work motivation.
Lecture 2 motivation for friday 28 aug 2010

The document summarizes several theories of motivation from organizational behavior literature. It discusses Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y, Herzberg's two-factor theory, Alderfer's ERG theory, McClelland's needs theory, goal-setting theory, equity theory, expectancy theory, and job characteristics model among others. The theories help explain factors that influence employee motivation, satisfaction, and performance in work settings.
Lecture 2 motivation for friday 28 aug 2010

The document summarizes several theories of motivation from organizational behavior literature. It discusses Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, Herzberg's two-factor theory, Alderfer's ERG theory, McClelland's needs theory, goal setting theory, equity theory, expectancy theory, and job characteristics model among others. The theories help explain factors that influence employee motivation, satisfaction, and performance in work settings.
Ob12 06st

The document discusses several theories of motivation:
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to other needs.
- Herzberg's two-factor theory separates motivators like achievement and responsibility from hygiene factors like salary.
- Expectancy theory states that motivation depends on expecting effort will lead to performance and performance will lead to rewards.
- Equity theory suggests people are motivated to achieve fair outcomes compared to others.
Ob11 06st

1. The document discusses several theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and Vroom's expectancy theory.
2. Motivation is defined as the processes that account for an individual's intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward attaining a goal.
3. Motivation theories provide frameworks to understand factors that influence employee effort, performance, and satisfaction.
Motivation theories (organizational behaviour)2017

Motivation theories (organizational behaviour)2017
Leadership rules.
manager responsibilties
Employees roles
Motivation

The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 6 of Organizational Behavior by Stephen P. Robbins on motivation. It discusses [1] Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory which proposes humans have physiological, safety, social, esteem and self-actualization needs that become dominant as lower needs are met. It also discusses [2] McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y about assumptions about employee motivation and [3] Herzberg's two-factor theory that proposes motivators like achievement and recognition lead to job satisfaction while hygiene factors prevent dissatisfaction.
Motivation

The document outlines learning objectives and concepts from a chapter on motivation in organizational behavior. It discusses several theories of motivation, including: Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, Herzberg's two-factor theory, McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y, ERG theory, McClelland's needs theory, goal-setting theory, equity theory, expectancy theory, and job characteristics model. It provides summaries of each theory and highlights key concepts related to motivating employees.
Management ch16

This document is a chapter from a textbook on organizational behavior that discusses theories of motivation. It provides learning outlines to guide students in understanding key topics related to motivation, including early theories from Maslow, McGregor, and Herzberg, as well as contemporary theories such as McClelland's three needs, goal setting theory, reinforcement theory, job design models, equity theory, and expectancy theory. For each theory, it defines important constructs and explains how managers can apply the theories to improve employee motivation.
Motivation

The document discusses several theories of motivation. It begins by defining motivation as the intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward attaining a goal. It then summarizes key theories:
1) Maslow's hierarchy of needs theorizes that lower-level needs like physical needs must be met before higher-level needs can motivate.
2) McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y propose two approaches to managing people - Theory X assumes people dislike work while Theory Y assumes people can exercise self-direction.
3) Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory distinguishes between motivators like achievement that boost satisfaction and hygiene factors like policy that prevent dissatisfaction.
It discusses several other theories
3-4 pages Explain Internal and External recruiting. Discuss the pro.docx

3-4 pages Explain Internal and External recruiting. Discuss the pro's and Con's of internal and external recruiting.Write it in 3-4 pagespaper should have at least three (3-4) reputable sources.
Essentials of Organizational Behavior
Fourteenth Edition
Chapter 7
Motivation Concepts
Copyright © 2018, 2016, 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Copyright © 2018, 2016, 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Copyright © 2018, 2016, 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
1
After studying this chapter you should be able to:
Describe the three key elements of motivation.
Compare the early theories of motivation.
Contrast the elements of self-determination theory and goal-setting theory.
Demonstrate the differences between self-efficacy theory, reinforcement theory, equity theory, and expectancy theory.
Identify the implications of employee job engagement for managers.
Describe how the contemporary theories of motivation complement one another.
Copyright © 2018, 2016, 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
2
What Is Motivation?
Motivation: The processes that account for an individual’s intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward attaining an organizational goal
Intensity: the amount of effort put forth to meet the goal
Direction: efforts are channeled toward organizational goals
Persistence: how long the effort is maintained
Copyright © 2018, 2016, 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
It is easy to see that some individuals are more motivated than others. However, the reasons for that motivation are more difficult to determine. When defining motivation, it is important to look at the interaction between the individual and the situation. There are three key elements that help us define motivation. The first is intensity, or how hard the person tries to accomplish the task. The second is direction, or the effort that is channeled toward organizational goals. The final element is persistence, or how long a person can maintain the effort.
3
Early Theories of Motivation
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory
Herzberg’s Two-Factor (Motivation-Hygiene) Theory
McClellan’s Theory of Needs (Three Needs Theory)
Copyright © 2018, 2016, 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
There are a number of theories of motivation that help us gain a better understanding of the concept. Some of the earlier theories are not entirely valid anymore, but they are still used by many managers.
4
Hierarchy of Needs Theory (1 of 2)
Copyright © 2018, 2016, 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The Hierarchy of Needs Theory was developed by Abraham Maslow in the 1950s. His theory states that with every individual there is a hierarchy of five needs. As each need is met or satisfied, the next need becomes dominant. His theory posits that individuals are stuck in their existing need level until it is satisfied, and then they can move on to the next level. For example, until their s.
Ch6 ob

1. Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory proposes that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs like physical survival and safety before pursuing higher needs like relationships, esteem, and self-actualization.
2. Herzberg's two-factor theory distinguishes between hygiene factors like salary that prevent dissatisfaction and motivator factors like achievement that create satisfaction.
3. Goal-setting theory suggests that specific, difficult goals lead to higher performance when people are committed to the goals and receive feedback on their progress.
Robbins9 ppt16

This document provides an overview of theories of motivation discussed in Chapter 16 of a management textbook. It summarizes key theories including: Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, McClelland's three needs theory, goal-setting theory, reinforcement theory, equity theory, and expectancy theory. For each theory, it outlines the core concepts and how managers can apply the theories to motivate employees. The document also discusses designing motivating jobs using job characteristics model and contemporary issues in motivating diverse and unique groups of employees.
Organizational BehaviorSeventeenth EditionChapter 7Motivat.docx

Organizational Behavior
Seventeenth Edition
Chapter 7
Motivation Concepts
Copyright © 2017, 2015, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Copyright © 2017, 2015, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
If this PowerPoint presentation contains mathematical equations, you may need to check that your computer has the following installed:
1) MathType Plugin
2) Math Player (free versions available)
3) NVDA Reader (free versions available)
Combine rational analysis with intuition. These are not conflicting approaches to decision making. By using both, you can actually improve your decision making effectiveness.
Try to enhance your creativity. Actively look for novel solutions to problems, attempt to see problems in new ways, use analogies, and hire creative talent. Try to remove work and organizational barriers that might impede your creativity.
Chapter 7: Motivation Concepts
1
Learning Objectives
7.1 Describe the three key elements of motivation.
7.2 Compare the early theories of motivation.
7.3 Contrast the elements of self-determination theory and goal-setting theory.
7.4 Demonstrate the differences among self-efficacy theory, reinforcement theory, equity theory, and expectancy theory.
7.5 Identify the implications of employee job engagement for managers.
7.6 Describe how the contemporary theories of motivation complement one another.
Copyright © 2017, 2015, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
Describe the three key elements of motivation.
Compare the early theories of motivation.
Contrast the elements of self-determination theory and goal-setting theory.
Demonstrate the differences among self-efficacy theory, reinforcement theory, equity theory, and expectancy theory.
Identify the implications of employee job engagement for managers.
Describe how the contemporary theories of motivation complement one another.
2
Describe the Three Key Elements of Motivation (1 of 2)
Motivation is the processes that account for an individual’s intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward attaining a goal.
The level of motivation varies both between individuals and within individuals at different times.
Copyright © 2017, 2015, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Motivation is the processes that account for an individual’s intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward attaining a goal. We will narrow the focus to organizational goals in order to reflect our singular interest in work-related behavior. Keep in mind that the level of motivation varies both between individuals and within individuals at different times.
3
Describe the Three Key Elements of Motivation (2 of 2)
The three key elements of motivation are:
Intensity: concerned with how hard a person tries.
Direction: the orientation that benefits the organization.
Persistence: a measure of how long a person can maintain his/her effort.
Copyright © 2017, 2015, 2013 Pearson Educat ...
(Mb asubjects.com)ob11 03st

This document discusses organizational behavior concepts such as values, attitudes, job satisfaction, and culture. It defines values as basic convictions about preferable modes of conduct or existence. Attitudes are evaluative statements about objects, people, or events. Job satisfaction represents positive or negative feelings toward one's job. The document also presents frameworks for assessing cultures, such as Hofstede's model of power distance, individualism, and uncertainty avoidance. It explores how values and attitudes influence behavior in organizations.
(Mb asubjects.com)ob11 03st

This document discusses organizational behavior concepts related to values, attitudes, and job satisfaction. It defines values and value systems, and describes types of values and Hofstede's framework for assessing cultures based on power distance, individualism vs collectivism, and other dimensions. It also defines attitudes, describes types of attitudes like job involvement and organizational commitment, and theories related to attitudes like cognitive dissonance theory and self-perception theory. Finally, it covers the topics of job satisfaction, factors that influence satisfaction, and the relationship between satisfaction and employee performance, customer satisfaction, and other outcomes.
Motivating Employees

In these slides we will understand that how to Motivates the employees to work in an organization. And also see the importance of it.
Motivating employees

What Is Motivation?
Define motivation.
Explain motivation as a need-satisfying process.
Early Theories of Motivation
Describe the five levels in Maslow’s hierarchy and how Maslow’s hierarchy can be used in motivational efforts.
Discuss how Theory X and Theory Y managers approach motivation.
Describe Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory.
Explain Herzberg’s views of satisfaction and dissatisfaction.
Similar to Motivation (20)
Motivation theories (organizational behaviour)2017

Motivation theories (organizational behaviour)2017
3-4 pages Explain Internal and External recruiting. Discuss the pro.docx

3-4 pages Explain Internal and External recruiting. Discuss the pro.docx
Organizational BehaviorSeventeenth EditionChapter 7Motivat.docx

Organizational BehaviorSeventeenth EditionChapter 7Motivat.docx
More from rakesh m
Hdfc

HDFC Bank Limited is an Indian banking and financial services company headquartered in Mumbai. It was incorporated in 1994 and is now the fifth largest bank in India in terms of assets. As of 2015, HDFC Bank had over 4,000 branches across 2,464 cities in India and provides both retail and wholesale banking services as well as services for NRIs, SMEs, and corporate clients.
1 wipro new

Wipro is an Indian multinational IT company founded in 1945 that provides IT consulting and services. It has over 158,000 employees worldwide and annual revenues of $7.5 billion. Azim Premji took over the company in 1966 and transformed it into a global IT leader, known for innovative business solutions and sustainability.
Dabur 1

Dabur India Limited is one of India's leading FMCG companies that was founded in 1884 by Dr. S.K. Burman to produce and dispense Ayurvedic medicines. It is currently the 4th largest Indian consumer goods manufacturing company with a turnover of Rs. 7800 crores from products like hair oils, shampoos, oral care, health supplements, foods, skin care, digestives, and home care that are marketed in over 50 countries. The company has expanded over time through mergers and new product introductions, and its CEO Sunil Duggal has received several awards and recognition for his leadership.
Ipr & com con

The document discusses interpersonal relationships and communication. It defines interpersonal relationships as social connections between two or more people that can range from brief to enduring. Good communication skills, competence, self-awareness and other factors are described as important for relationship success. The document also discusses communication climates, confirming and disconfirming responses, types of conflict, and strategies for resolving conflict such as negotiating solutions. It addresses formal and informal communication channels in organizations.
Group dynamics 1

This document discusses groups and teams in organizations. It defines groups and teams, and describes different types of groups like formal vs informal groups and task vs command vs interest groups. It also discusses characteristics that distinguish teams from groups. The document outlines factors that influence group dynamics and effectiveness, such as group size, task interdependence, roles, leadership, stages of group development, norms, conformity/deviance, and cohesiveness. It provides guidance for managers to motivate groups, reduce social loafing, and manage groups for high performance. Various group decision making techniques are also summarized.
Karur vysya bank

Karur Vysya Bank is a private sector Indian bank established in 1916 in Tamil Nadu. It has over 650 branches across 18 states and union territories. The bank offers various deposit, loan, insurance, and investment products and services. It has expanded its service channels to include internet banking, mobile banking, debit/credit cards, and bill payment facilities. Karur Vysya Bank has received several awards recognizing its performance and growth.
Icici bank

ICICI Bank is the largest private sector bank in India. It was established in 1994 and has a network of over 4,000 branches across India and a presence in 17 other countries. The bank offers personal and commercial banking services including deposits, loans, credit and debit cards, insurance, investments, and bill payment. ICICI Bank has received several awards for its banking services and security systems. It is working on initiatives like mobile banking and branch expansion to rural areas of India.
Lipid profile in acs

Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) occurs when blood flow to the heart is reduced, preventing the heart muscle from receiving enough oxygen. It is usually caused by atherosclerosis. The main symptom of ACS is chest pain. Other symptoms can include sweating, breathlessness, and palpitations. Risk factors for ACS include diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, smoking, lack of exercise, and stress. Lipid profiles of ACS patients show higher total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL levels compared to healthy individuals.
Female labour1

Female labour has historically played an important role in India's workforce. While women were once treated equally to men, social changes led to women becoming dependent on men with fewer rights and opportunities. The spread of Western education helped women realize their subordinate status and improved their position over time. Today, women make up over half of the community and social services workforce but still face discrimination, safety issues while traveling, and health problems. Various labor acts aim to protect women's rights and prevent harassment and unsafe working conditions.
Agricultural labour

The document discusses agricultural labor in India. It notes that around 58% of India's population depends on agriculture and that the number of cultivators has declined from 50% in 1951 to 24% in 2011. It outlines the classification, characteristics, laws, and welfare measures regarding agricultural laborers. Some key challenges faced by agricultural laborers are excess supply, seasonal employment, small land holdings, limited other occupations, indebtedness, and regional variations in issues. Solutions proposed include cooperatives, irrigation development, improved marketing/distribution, and agricultural insurance.
Medicare

This document provides an overview of Medicare, including:
- Medicare has different parts (A, B, D) that provide different types of coverage such as hospital insurance, medical insurance, and prescription drug coverage.
- People qualify for Medicare if they are 65 or older, or under 65 with certain disabilities. It is administered by CMS.
- Medigap plans are private insurance policies that help cover gaps in Original Medicare costs. There are standardized Medigap plans A through L.
- Medicare Advantage plans are run by private insurers and provide Medicare benefits through HMOs, PPOs, and other plans.
- Medicaid provides additional coverage for some low-income individuals beyond what Medicare covers. Eligibility
E compensation

E-compensation systems allow companies to manage employee compensation electronically through software packages accessible via intranet or internet. They automate tasks like payroll processing and provide tools for compensation planning. PeopleSoft and Oracle offer e-compensation solutions that integrate with other HR systems like performance reviews. E-compensation provides benefits like uniform compensation management, easy access to records, budget tracking, and language support for multinational companies.
E training

This document discusses e-training (electronic training), which involves using computers or other electronic devices to provide training or educational materials. Some key points made include:
- Over 41% of Fortune 500 companies now use some form of online training for employees. Asia is the fastest growing market, projected to grow 17.3% annually.
- E-training can reduce employee learning time by up to 60% and is the second most valuable training method for many companies as it saves 50% compared to traditional training.
- E-training provides instant access to information for employees anywhere, anytime, reducing the need for travel and making expertise more readily available.
E compensation

E-compensation systems allow companies to manage employee compensation electronically through software packages accessible via intranet or internet. They automate tasks like payroll processing and provide tools for compensation planning. PeopleSoft and Oracle offer e-compensation solutions that integrate with other HR systems like performance reviews. E-compensation provides benefits like uniform compensation management, easy access to records, budget tracking, and language support for multinational companies.
More from rakesh m (14)
Recently uploaded
The Genesis of BriansClub.cm Famous Dark WEb Platform

BriansClub.cm, a famous platform on the dark web, has become one of the most infamous carding marketplaces, specializing in the sale of stolen credit card data.
Digital Marketing with a Focus on Sustainability

Digital Marketing best practices including influencer marketing, content creators, and omnichannel marketing for Sustainable Brands at the Sustainable Cosmetics Summit 2024 in New York
How MJ Global Leads the Packaging Industry.pdf

MJ Global's success in staying ahead of the curve in the packaging industry is a testament to its dedication to innovation, sustainability, and customer-centricity. By embracing technological advancements, leading in eco-friendly solutions, collaborating with industry leaders, and adapting to evolving consumer preferences, MJ Global continues to set new standards in the packaging sector.
3 Simple Steps To Buy Verified Payoneer Account In 2024

Buy Verified Payoneer Account: Quick and Secure Way to Receive Payments
Buy Verified Payoneer Account With 100% secure documents, [ USA, UK, CA ]. Are you looking for a reliable and safe way to receive payments online? Then you need buy verified Payoneer account ! Payoneer is a global payment platform that allows businesses and individuals to send and receive money in over 200 countries.
If You Want To More Information just Contact Now:
Skype: SEOSMMEARTH
Telegram: @seosmmearth
Gmail: seosmmearth@gmail.com
Part 2 Deep Dive: Navigating the 2024 Slowdown

Introduction
The global retail industry has weathered numerous storms, with the financial crisis of 2008 serving as a poignant reminder of the sector's resilience and adaptability. However, as we navigate the complex landscape of 2024, retailers face a unique set of challenges that demand innovative strategies and a fundamental shift in mindset. This white paper contrasts the impact of the 2008 recession on the retail sector with the current headwinds retailers are grappling with, while offering a comprehensive roadmap for success in this new paradigm.
Taurus Zodiac Sign: Unveiling the Traits, Dates, and Horoscope Insights of th...

Dive into the steadfast world of the Taurus Zodiac Sign. Discover the grounded, stable, and logical nature of Taurus individuals, and explore their key personality traits, important dates, and horoscope insights. Learn how the determination and patience of the Taurus sign make them the rock-steady achievers and anchors of the zodiac.
DearbornMusic-KatherineJasperFullSailUni

My powerpoint presentation for my Music Retail and Distribution class at Full Sail University
Maksym Vyshnivetskyi: PMO KPIs (UA) (#12)

Maksym Vyshnivetskyi: PMO KPIs (UA)
Lemberg PMO School 2024
Website – https://lembs.com/pmoschool
Youtube – https://www.youtube.com/startuplviv
FB – https://www.facebook.com/pmdayconference
Top mailing list providers in the USA.pptx

Discover the top mailing list providers in the USA, offering targeted lists, segmentation, and analytics to optimize your marketing campaigns and drive engagement.
Innovation Management Frameworks: Your Guide to Creativity & Innovation

Innovation Management Frameworks: Your Guide to Creativity & InnovationOperational Excellence Consulting
[To download this presentation, visit:
https://www.oeconsulting.com.sg/training-presentations]
This PowerPoint compilation offers a comprehensive overview of 20 leading innovation management frameworks and methodologies, selected for their broad applicability across various industries and organizational contexts. These frameworks are valuable resources for a wide range of users, including business professionals, educators, and consultants.
Each framework is presented with visually engaging diagrams and templates, ensuring the content is both informative and appealing. While this compilation is thorough, please note that the slides are intended as supplementary resources and may not be sufficient for standalone instructional purposes.
This compilation is ideal for anyone looking to enhance their understanding of innovation management and drive meaningful change within their organization. Whether you aim to improve product development processes, enhance customer experiences, or drive digital transformation, these frameworks offer valuable insights and tools to help you achieve your goals.
INCLUDED FRAMEWORKS/MODELS:
1. Stanford’s Design Thinking
2. IDEO’s Human-Centered Design
3. Strategyzer’s Business Model Innovation
4. Lean Startup Methodology
5. Agile Innovation Framework
6. Doblin’s Ten Types of Innovation
7. McKinsey’s Three Horizons of Growth
8. Customer Journey Map
9. Christensen’s Disruptive Innovation Theory
10. Blue Ocean Strategy
11. Strategyn’s Jobs-To-Be-Done (JTBD) Framework with Job Map
12. Design Sprint Framework
13. The Double Diamond
14. Lean Six Sigma DMAIC
15. TRIZ Problem-Solving Framework
16. Edward de Bono’s Six Thinking Hats
17. Stage-Gate Model
18. Toyota’s Six Steps of Kaizen
19. Microsoft’s Digital Transformation Framework
20. Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)
To download this presentation, visit:
https://www.oeconsulting.com.sg/training-presentationsAnny Serafina Love - Letter of Recommendation by Kellen Harkins, MS.

This letter, written by Kellen Harkins, Course Director at Full Sail University, commends Anny Love's exemplary performance in the Video Sharing Platforms class. It highlights her dedication, willingness to challenge herself, and exceptional skills in production, editing, and marketing across various video platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram.
Authentically Social by Corey Perlman - EO Puerto Rico

Authentically Social by Corey Perlman - EO Puerto RicoCorey Perlman, Social Media Speaker and Consultant
Social media for business Income Tax exemption for Start up : Section 80 IAC

A presentation on the concept of Exemption of Profits of Start ups from Income Tax
Easily Verify Compliance and Security with Binance KYC

Use our simple KYC verification guide to make sure your Binance account is safe and compliant. Discover the fundamentals, appreciate the significance of KYC, and trade on one of the biggest cryptocurrency exchanges with confidence.
Building Your Employer Brand with Social Media

Presented at The Global HR Summit, 6th June 2024
In this keynote, Luan Wise will provide invaluable insights to elevate your employer brand on social media platforms including LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, X (formerly Twitter) and TikTok. You'll learn how compelling content can authentically showcase your company culture, values, and employee experiences to support your talent acquisition and retention objectives. Additionally, you'll understand the power of employee advocacy to amplify reach and engagement – helping to position your organization as an employer of choice in today's competitive talent landscape.
Best practices for project execution and delivery

A select set of project management best practices to keep your project on-track, on-cost and aligned to scope. Many firms have don't have the necessary skills, diligence, methods and oversight of their projects; this leads to slippage, higher costs and longer timeframes. Often firms have a history of projects that simply failed to move the needle. These best practices will help your firm avoid these pitfalls but they require fortitude to apply.
Unveiling the Dynamic Personalities, Key Dates, and Horoscope Insights: Gemin...

Explore the fascinating world of the Gemini Zodiac Sign. Discover the unique personality traits, key dates, and horoscope insights of Gemini individuals. Learn how their sociable, communicative nature and boundless curiosity make them the dynamic explorers of the zodiac. Dive into the duality of the Gemini sign and understand their intellectual and adventurous spirit.
The 10 Most Influential Leaders Guiding Corporate Evolution, 2024.pdf

In the recent edition, The 10 Most Influential Leaders Guiding Corporate Evolution, 2024, The Silicon Leaders magazine gladly features Dejan Štancer, President of the Global Chamber of Business Leaders (GCBL), along with other leaders.
Recently uploaded (20)
The Genesis of BriansClub.cm Famous Dark WEb Platform

The Genesis of BriansClub.cm Famous Dark WEb Platform
3 Simple Steps To Buy Verified Payoneer Account In 2024

3 Simple Steps To Buy Verified Payoneer Account In 2024
Taurus Zodiac Sign: Unveiling the Traits, Dates, and Horoscope Insights of th...

Taurus Zodiac Sign: Unveiling the Traits, Dates, and Horoscope Insights of th...
Innovation Management Frameworks: Your Guide to Creativity & Innovation

Innovation Management Frameworks: Your Guide to Creativity & Innovation
Anny Serafina Love - Letter of Recommendation by Kellen Harkins, MS.

Anny Serafina Love - Letter of Recommendation by Kellen Harkins, MS.
Authentically Social by Corey Perlman - EO Puerto Rico

Authentically Social by Corey Perlman - EO Puerto Rico
Income Tax exemption for Start up : Section 80 IAC

Income Tax exemption for Start up : Section 80 IAC
Easily Verify Compliance and Security with Binance KYC

Easily Verify Compliance and Security with Binance KYC
Unveiling the Dynamic Personalities, Key Dates, and Horoscope Insights: Gemin...

Unveiling the Dynamic Personalities, Key Dates, and Horoscope Insights: Gemin...
The 10 Most Influential Leaders Guiding Corporate Evolution, 2024.pdf

The 10 Most Influential Leaders Guiding Corporate Evolution, 2024.pdf
Motivation
- 1. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–1 Defining MotivationDefining Motivation Key Elements 1. Intensity: how hard a person tries 2. Direction: toward beneficial goal 3. Persistence: how long a person tries Key Elements 1. Intensity: how hard a person tries 2. Direction: toward beneficial goal 3. Persistence: how long a person tries Motivation The processes that account for an individual’s intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward attaining a goal.
- 2. DefinitionDefinition According to Stephen P.Robbins “ Motivation is the willingness to exert high levels of efforts towards organization goals, conditioned by the effort ability to satisfy some individual need. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–2
- 3. NatureNature Motivation is internal to man Single motive can cause different behavior Different motive may result in single behavior Motives come and go Motives interact with the environment © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–3
- 4. Motivation cycleMotivation cycle Motives Goals Behaviors © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–4
- 5. Theories of MotivationTheories of Motivation Content Theory Hierarchy of Needs Theory (Maslow) Theory X and Theory Y (Douglas McGregor) Two-Factor Theory (Frederick Herzberg) ERG Theory (Clayton Alderfer) David McClelland’s Theory of Needs Process Theory Vroom’ Expectancy theory Porter and Lawers theory Equity theory © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–5
- 6. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–6 Hierarchy of Needs Theory (Maslow)Hierarchy of Needs Theory (Maslow) Hierarchy of Needs Theory There is a hierarchy of five needs —physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization; as each need is substantially satisfied, the next need becomes dominant. Self-Actualization The drive to become what one is capable of becoming.
- 7. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–7 Maslow’s Hierarchy of NeedsMaslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Lower-Order Needs Needs that are satisfied externally; physiological and safety needs. Higher-Order Needs Needs that are satisfied internally; social, esteem, and self-actualization needs. E X H I B I T 6–1 E X H I B I T 6–1Source: Motivation and Personality , 2nd ed,, by A.H. Maslow, 1970. Reprinted by permission of Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- 8. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–8 Theory X and Theory Y (Douglas McGregor)Theory X and Theory Y (Douglas McGregor) Theory X Assumes that employees dislike work, lack ambition, avoid responsibility, and must be directed and coerced to perform. Theory Y Assumes that employees like work, seek responsibility, are capable of making decisions, and exercise self-direction and self-control when committed to a goal.
- 9. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–9 Two-Factor Theory (Frederick Herzberg)Two-Factor Theory (Frederick Herzberg) Two-Factor (Motivation-Hygiene) Theory Intrinsic factors are related to job satisfaction, while extrinsic factors are associated with dissatisfaction. Hygiene Factors Factors—such as company policy and administration, supervision, and salary—that, when adequate in a job, placate workers. When factors are adequate, people will not be dissatisfied.
- 10. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–10 Comparison of Satisfiers and Dissatisfiers Comparison of Satisfiers and Dissatisfiers Factors characterizing events on the job that led to extreme job dissatisfaction Factors characterizing events on the job that led to extreme job satisfaction E X H I B I T 6–2 E X H I B I T 6–2 Source: Reprinted by permission of Harvard Business Review. An exhibit from One More Time: How Do You Motivate Employees? by Frederick Herzberg, September–October 1987. Copyright © 1987 by the President and Fellows of Harvard College: All rights reserved.
- 11. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–11 Contrasting Views of Satisfaction and DissatisfactionContrasting Views of Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction E X H I B I T 6–3 E X H I B I T 6–3
- 12. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–12 ERG Theory (Clayton Alderfer)ERG Theory (Clayton Alderfer) Core Needs Existence: provision of basic material requirements. Relatedness: desire for relationships. Growth: desire for personal development. Core Needs Existence: provision of basic material requirements. Relatedness: desire for relationships. Growth: desire for personal development. Concepts: More than one need can be operative at the same time. If a higher-level need cannot be fulfilled, the desire to satisfy a lower- level need increases. Concepts: More than one need can be operative at the same time. If a higher-level need cannot be fulfilled, the desire to satisfy a lower- level need increases. ERG Theory There are three groups of core needs: existence, relatedness, and growth.
- 13. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–13 David McClelland’s Theory of NeedsDavid McClelland’s Theory of Needs nAch nPow nAff Need for Achievement The drive to excel, to achieve in relation to a set of standards, to strive to succeed. Need for Affiliation The desire for friendly and close personal relationships. Need for Power The need to make others behave in a way that they would not have behaved otherwise.
- 14. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–14 Matching High Achievers and JobsMatching High Achievers and Jobs E X H I B I T 6–4 E X H I B I T 6–4
- 15. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–15 Equity Theory (cont’d)Equity Theory (cont’d) Distributive Justice Perceived fairness of the amount and allocation of rewards among individuals. Procedural Justice The perceived fairness of the process to determine the distribution of rewards.
- 16. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–16 Expectancy TheoryExpectancy Theory Expectancy Theory (Victor Vroom) The strength of a tendency to act in a certain way depends on the strength of an expectation that the act will be followed by a given outcome and on the attractiveness of that outcome to the individual. E X H I B I T 6–8 E X H I B I T 6–8
- 17. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–17 Expectancy Theory RelationshipsExpectancy Theory Relationships Effort–Performance Relationship – The probability that exerting a given amount of effort will lead to performance. Performance–Reward Relationship – The belief that performing at a particular level will lead to the attainment of a desired outcome. Rewards–Personal Goals Relationship – The degree to which organizational rewards satisfy an individual’s goals or needs and the attractiveness of potential rewards for the individual.
- 18. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–18 Performance DimensionsPerformance Dimensions E X H I B I T 6–9 E X H I B I T 6–9 Source: Adapted from M. Blumberg and C.D. Pringle, “The Missing Opportunity in Organizational Research: Some Implications for a Theory of Work Performance,” Academy of Management Review, October 1982, p. 565.
- 19. Motivational toolsMotivational tools Incentives Financial incentive Non Financial incentive Appreciation of work done Competition Group incentives Workers participation in management Opportunity for growth Suggestion system Job enrichment © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–19
- 20. Motivational toolsMotivational tools Job Design Job enlargement Job enrichment Job simplification Job rotation Quality of work life Job involvement Job satisfaction Goal setting Goal acceptance Performance monitoring © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–20
- 21. EMOTIONSEMOTIONS © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–21
- 22. ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIORORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR S T E P H E N P. R O B B I N SS T E P H E N P. R O B B I N S E L E V E N T H E D I T I O NE L E V E N T H E D I T I O N W W W . P R E N H A L L . C O M / R O B B I N SW W W . P R E N H A L L . C O M / R O B B I N S© 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook EMOTIONS According to N.H. Frijda “ emotions are intense feelings that are directed at someone or something” © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–22
- 23. EmotionsEmotions Carroll Izard (1977) isolated 10 emotions. Most of them are present in infancy, except for contempt, shame, and guilt NancyBrown/TheImageBankTomMcCarthy/Rainbow
- 24. Types of EmotionsTypes of Emotions Primary Emotions 1) Are evident in all cultures 2) Are based in survival 3) Correlate with facial expressions – Positive primary emotions (Love, Affection, Joy) – Negative primary emotions( Fear, Sadness, anger)
- 25. Sources of EmotionsSources of Emotions Gender Age Personality Time Stress Relaxation Exercise Social activities © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–25
- 26. Emotional LaborEmotional Labor Emotions play an important part in how employees function during the work day. Emotional labor and emotional dissonance reflect how challenging it can be for employees to maintain a helpful, caring attitude - when inside, they may be dealing with negative personal or work issues. According to Hochschild (1983), jobs involving emotional labor are defined as those that: require face-to-face or voice-to-voice contact with the public. require the worker to produce an emotional state in another person. allow the employer, through training and supervision, to exercise a degree of control over the emotional activities of employees. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–26
- 27. Types Of Emotional LaborTypes Of Emotional Labor Deep acting is about a person trying to feel a specific emotion that they are thinking about in their mind. Surface acting, however, is when a person has to fake emotion to meet certain social or work rules. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–27
- 28. Emotional IntelligenceEmotional Intelligence “Emotional intelligence is an array of emotional, social and personal abilities which influences one’s overall ability to cope effectively with environmental demands and pressures. Linguistic Intelligence Logical – Mathematical intelligence Bodily – Kinesthetic Intelligence © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–28
- 29. © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–29
- 30. Essential ingredientsEssential ingredients Emotional literacy Emotional fitness Emotional domain Emotional alchemy © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–30
- 31. FrameworkFramework Personal competence Self awareness Self management Social competence Social awareness Relationship management © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–31
- 32. BenefitsBenefits Increased performance Effective leaders More teamwork Improved and enhanced innovation courage © 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 6–32
- 33. The Physiological Component A Historical Perspective James-Lange Theory of Emotion The Physiological Component A Historical Perspective James-Lange Theory of Emotion Emotion arises from physiological arousal – Happiness comes from smiling – Sadness comes from crying
- 34. The Cognitive Component Schachter’s Two-Factor Theory of Emotion The Cognitive Component Schachter’s Two-Factor Theory of Emotion Physiological arousal – Sweaty palms – Increased heart rate – Rapid breathing Cognitive Label – Attribute source of arousal to a cause. To have an emotion, both factors are required.
- 35. The Physiological Component A Historical Perspective Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion The Physiological Component A Historical Perspective Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion Emotion originates in the thalamus “Body” (physiological systems) and “Mind” (emotional experience) are independently activated at the same time
- 36. Orgn Behaviour Application of emotionsOrgn Behaviour Application of emotions Employee selection Motivation Leadership Decision making Employee conflict Job attitude 36
Editor's Notes
- Figure 9.2 from: Kassin, S. (2001). Psychology, third edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Figure 9.9 from: Kassin, S. (2001). Psychology, third edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Source: Schachter, S. (1964). The interaction of cognitive and physiological determinants of emotional state. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 1, 49-80. New York: Academic Press.
- Figure 9.3 from: Kassin, S. (2001). Psychology, third edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Source: