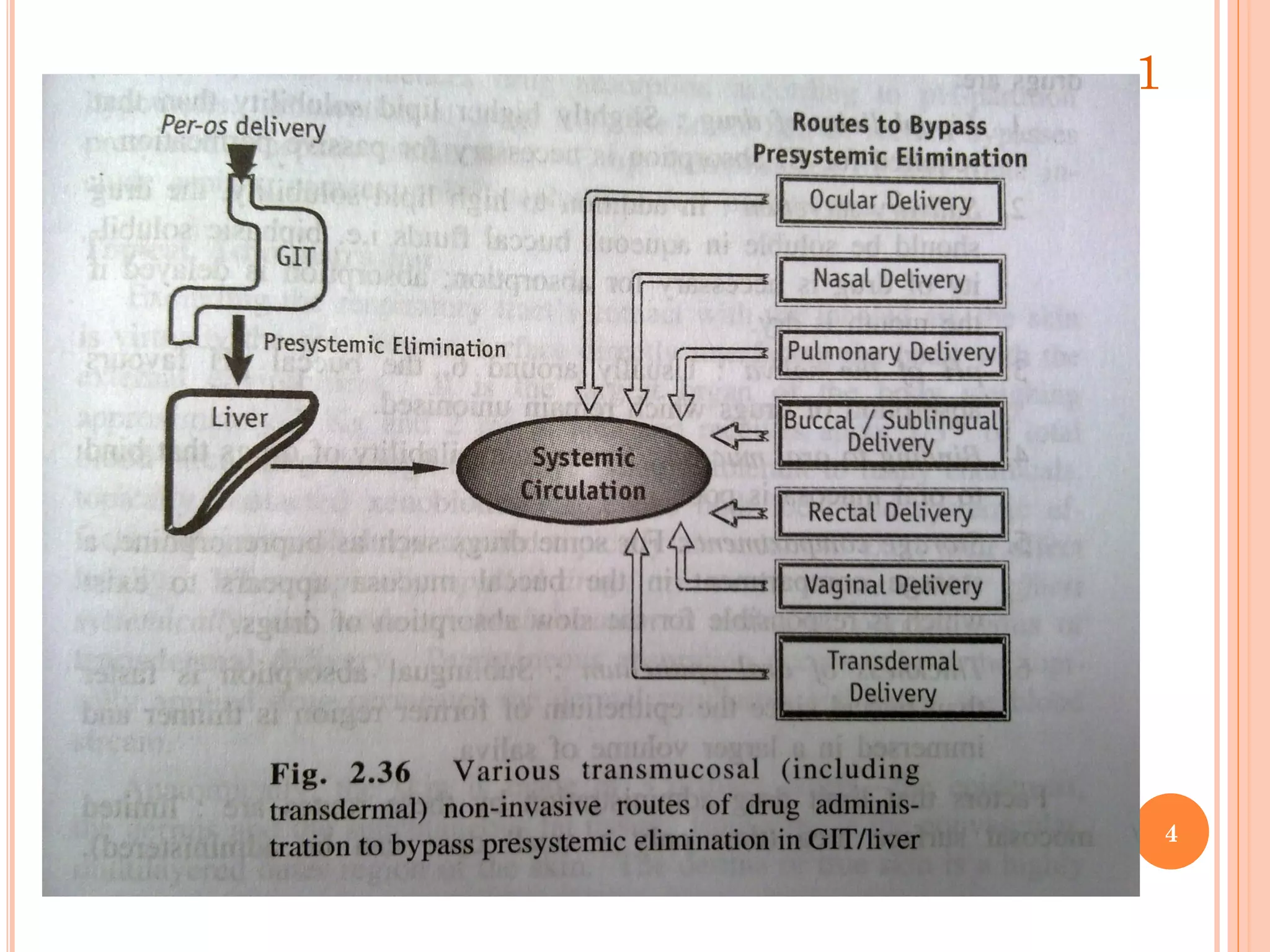
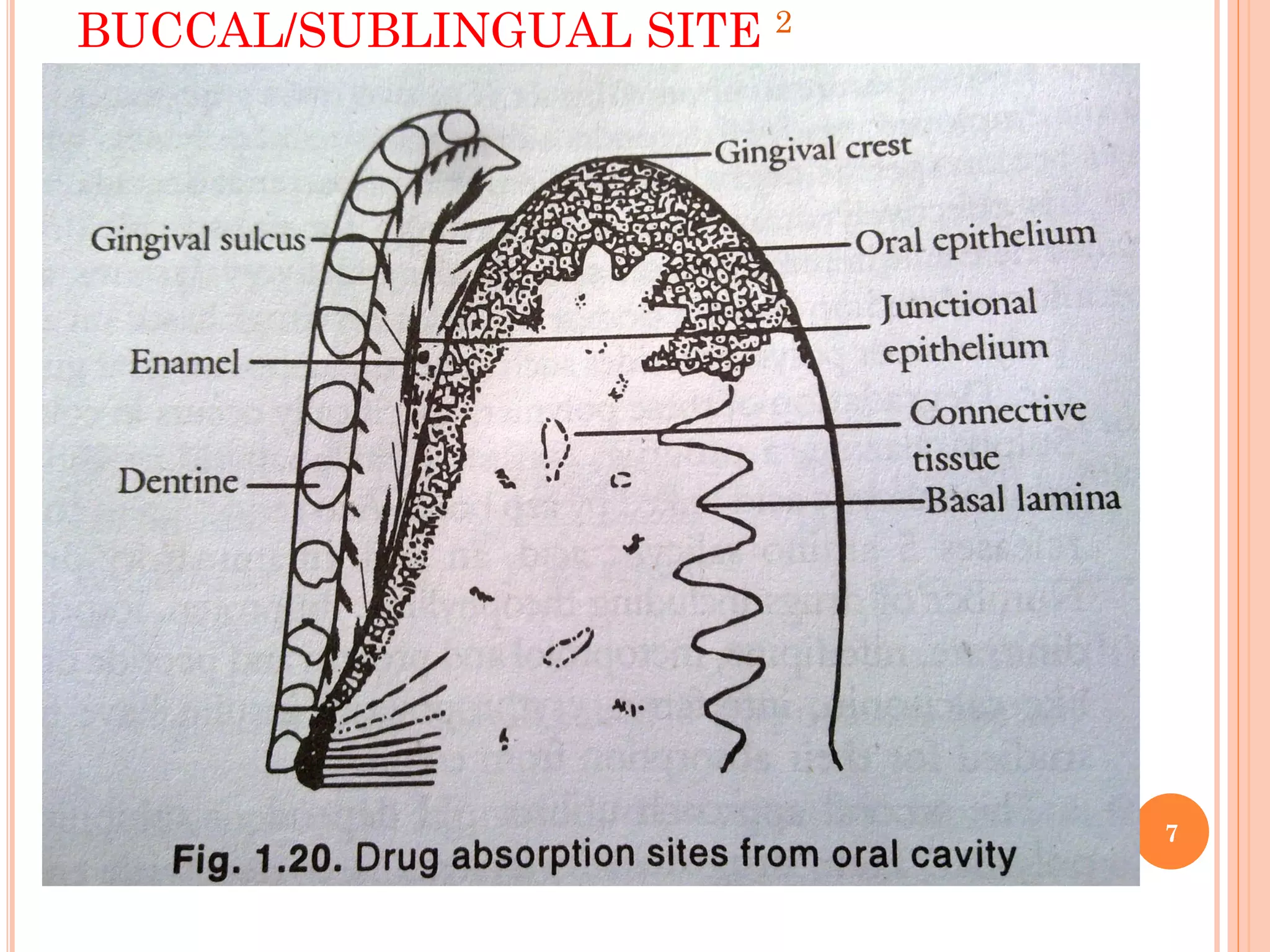
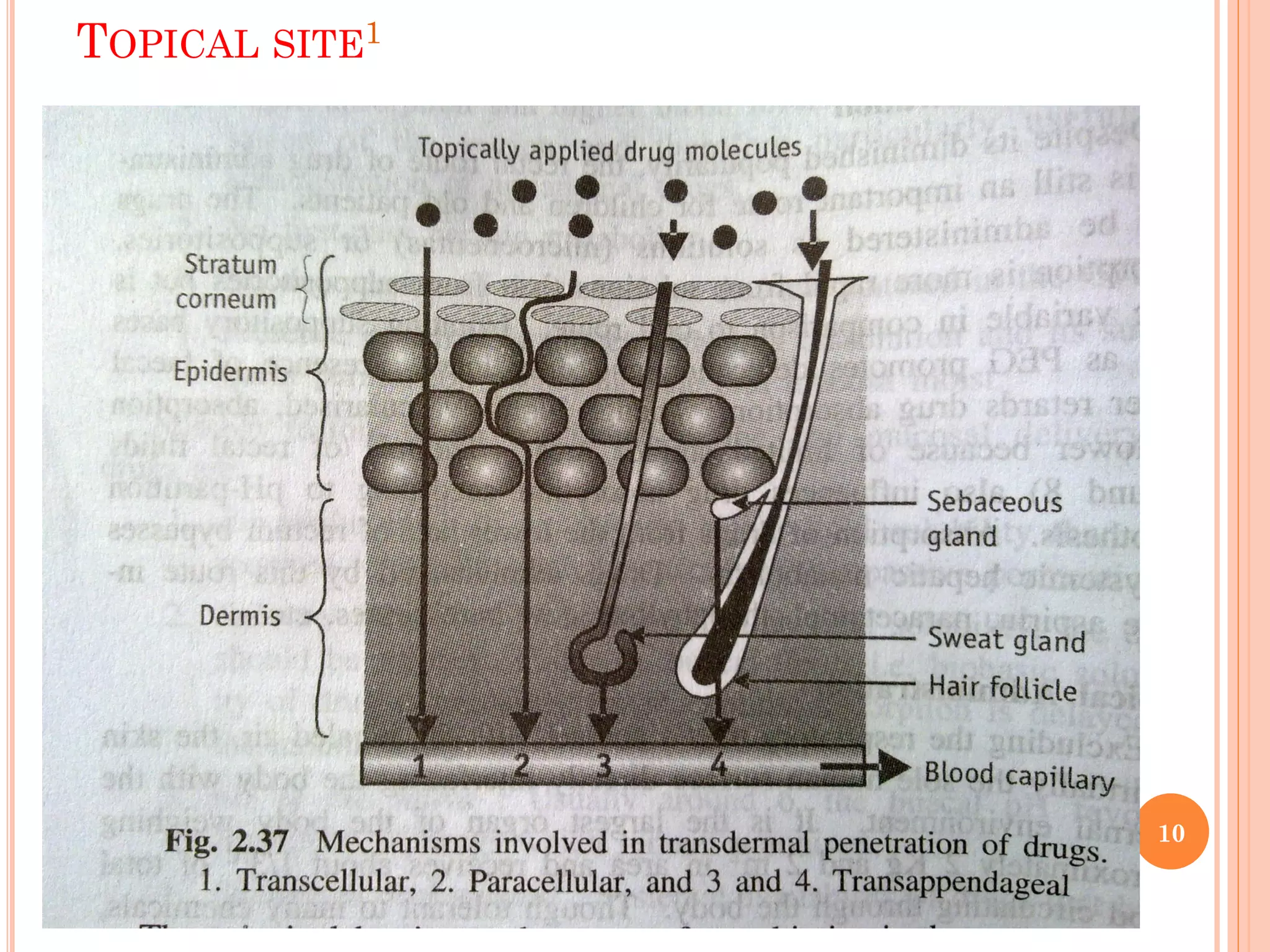
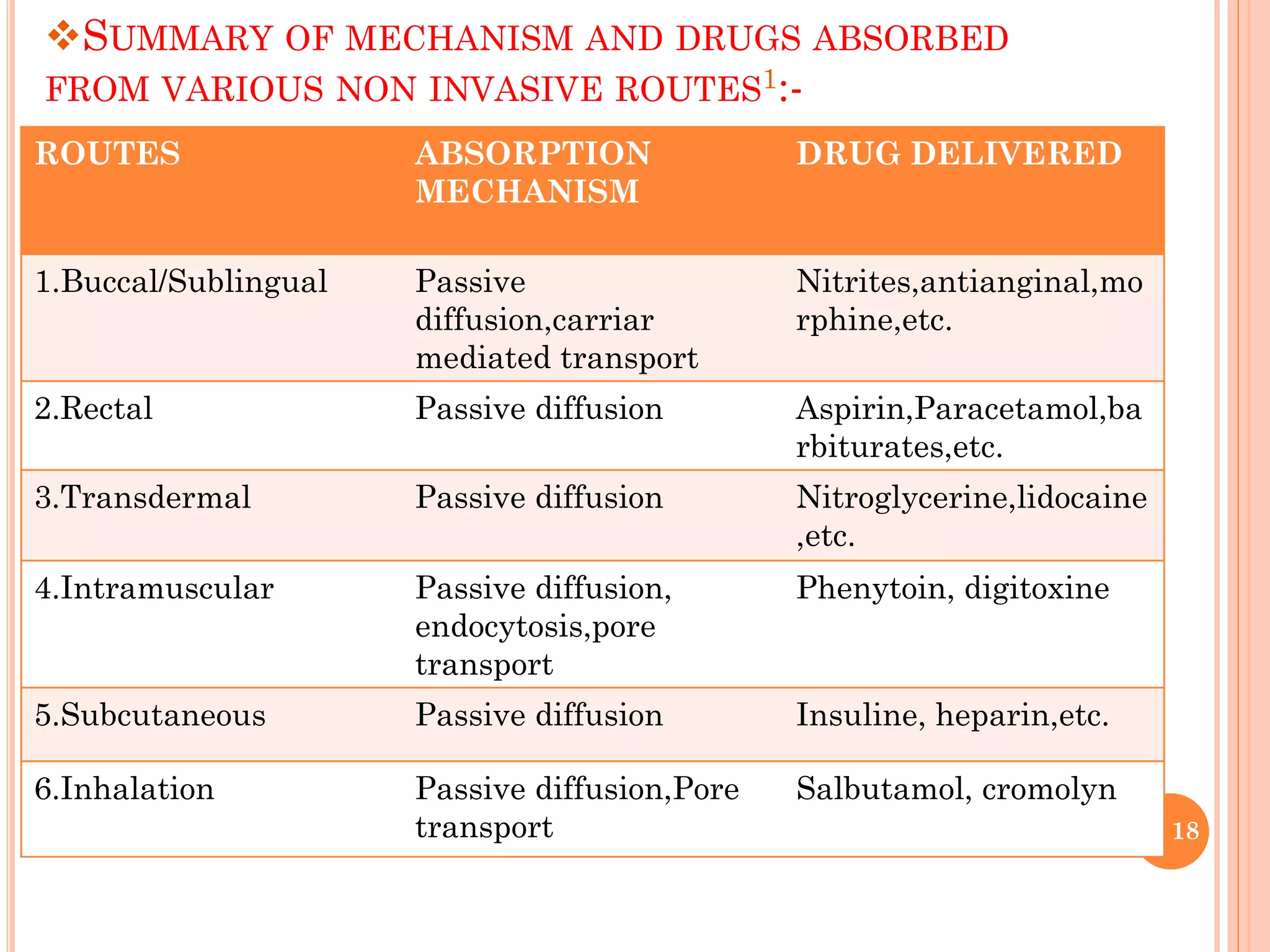
Non-oral routes of drug administration provide advantages over oral routes by bypassing the gastrointestinal tract and avoiding first-pass metabolism. Common non-oral routes discussed include buccal/sublingual, rectal, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, pulmonary, intranasal, intraocular, and vaginal administration. Absorption through these routes occurs primarily via passive diffusion, carrier-mediated transport, or pore transport depending on the drug properties and administration site. Non-oral routes allow for rapid drug absorption, higher bioavailability compared to oral routes, and targeted delivery for local or systemic effects.