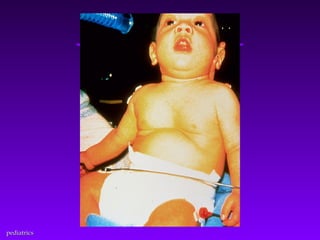
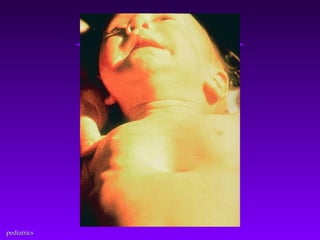
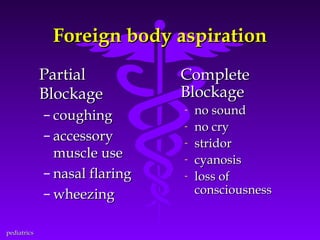
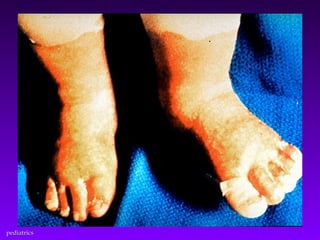
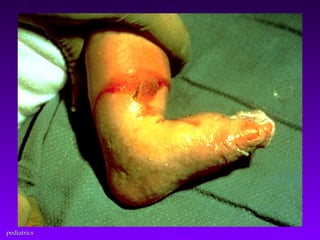
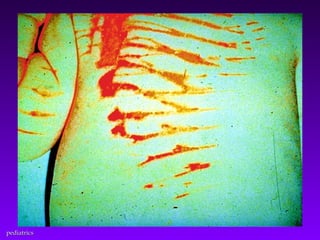
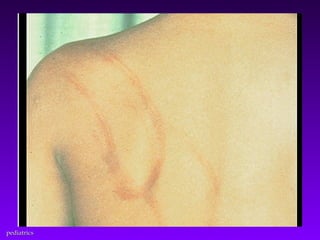
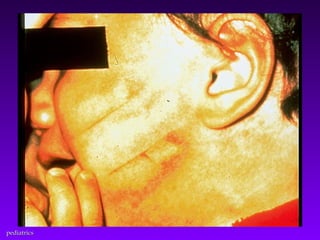
This document discusses several common pediatric emergencies including fever, febrile seizures, dehydration, airway obstruction from croup, epiglottitis or foreign body aspiration, asthma, meningitis, submersion injury, poisoning, sudden infant death syndrome, and child abuse. For each condition, the document outlines signs and symptoms and recommended emergency care focusing on the ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation), passive cooling, oxygen administration, positioning, and transport as needed. Respiratory arrest is identified as the most frequent cause of cardiac arrest in pediatrics.