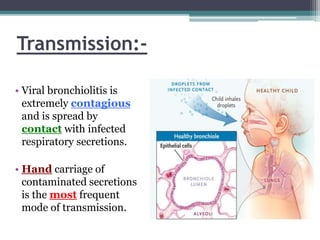
1. Bronchiolitis is most commonly caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in infants and young children, causing inflammation in the small airways.
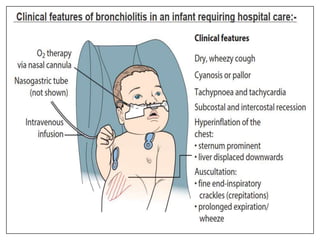
2. It typically presents with cough, wheezing, nasal congestion and difficulty breathing. Chest radiographs may show hyperinflation of the lungs.
3. Treatment is supportive with oxygen and monitoring since most cases resolve on their own. Hospitalization is needed for moderate to severe distress, hypoxemia or apnea. While recurrence is common, bronchiolitis often improves within a week.