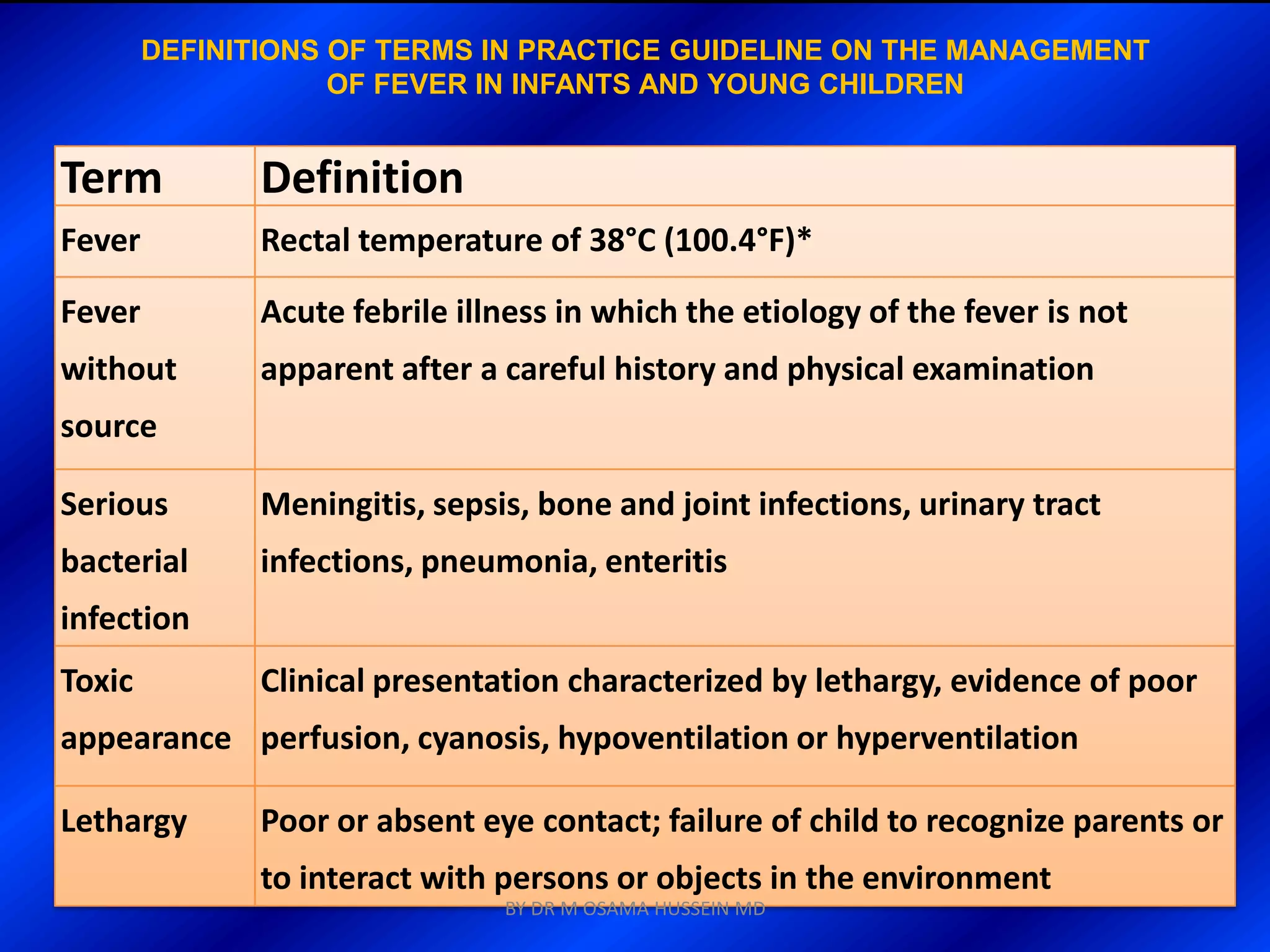
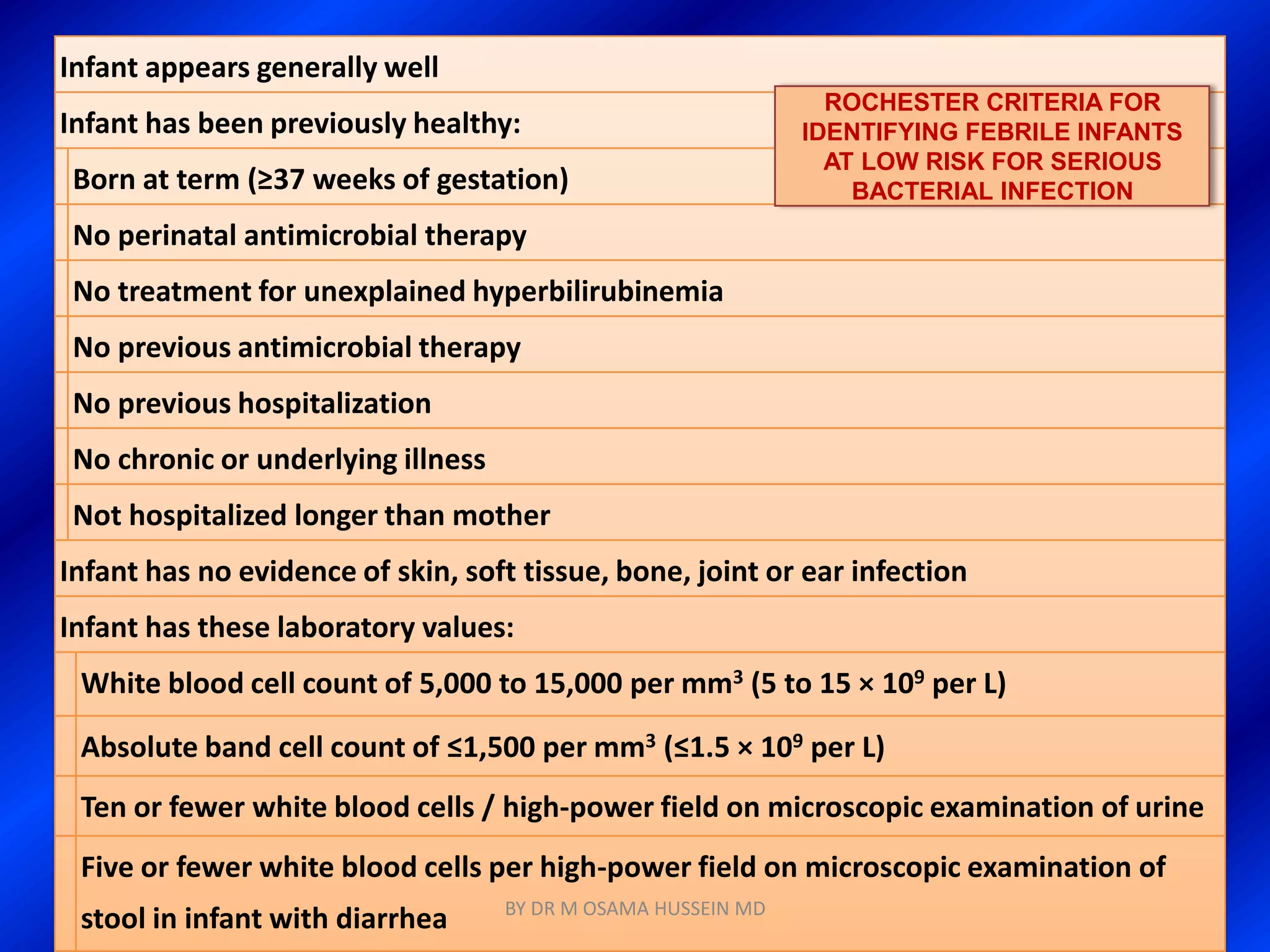
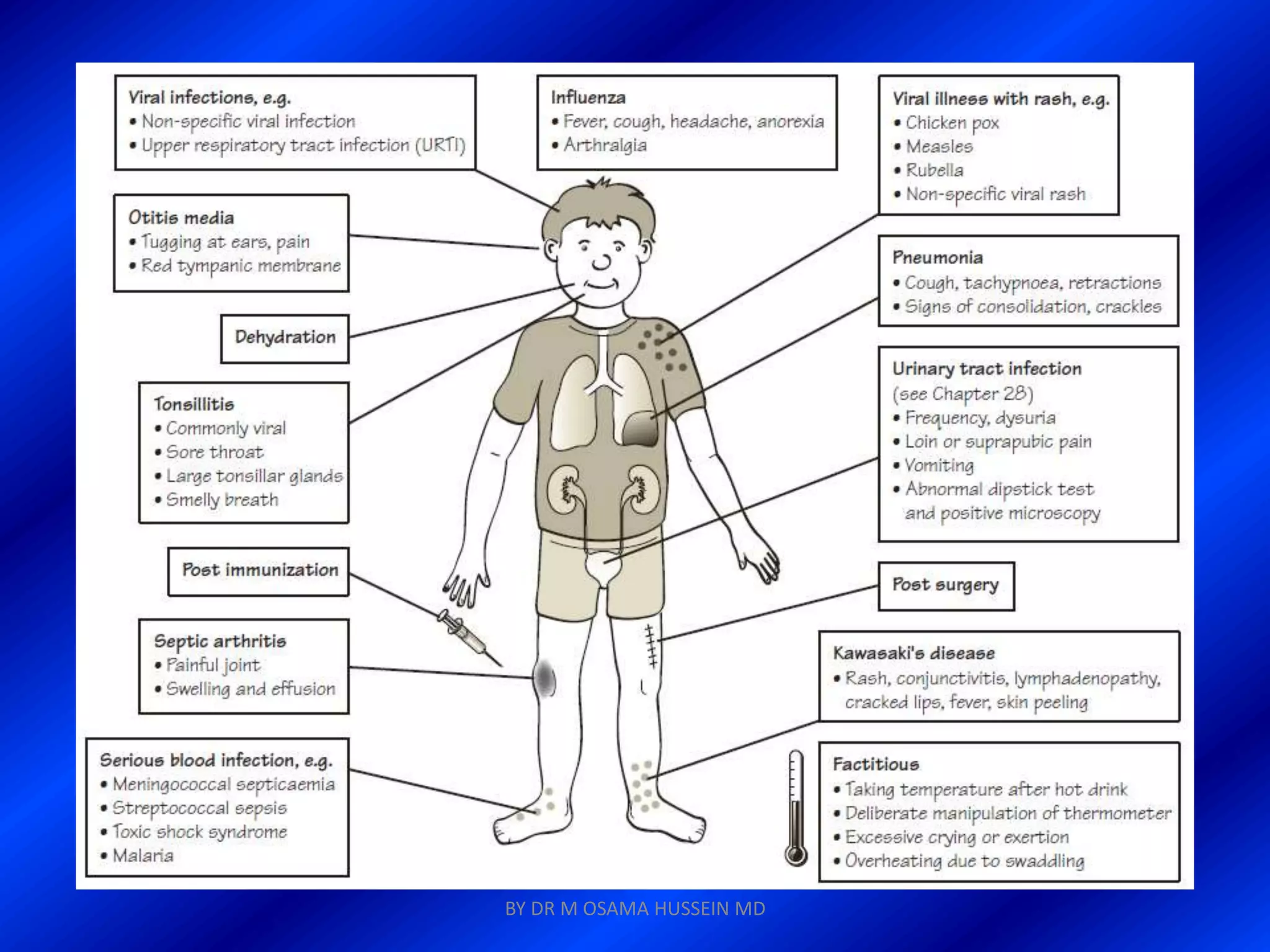
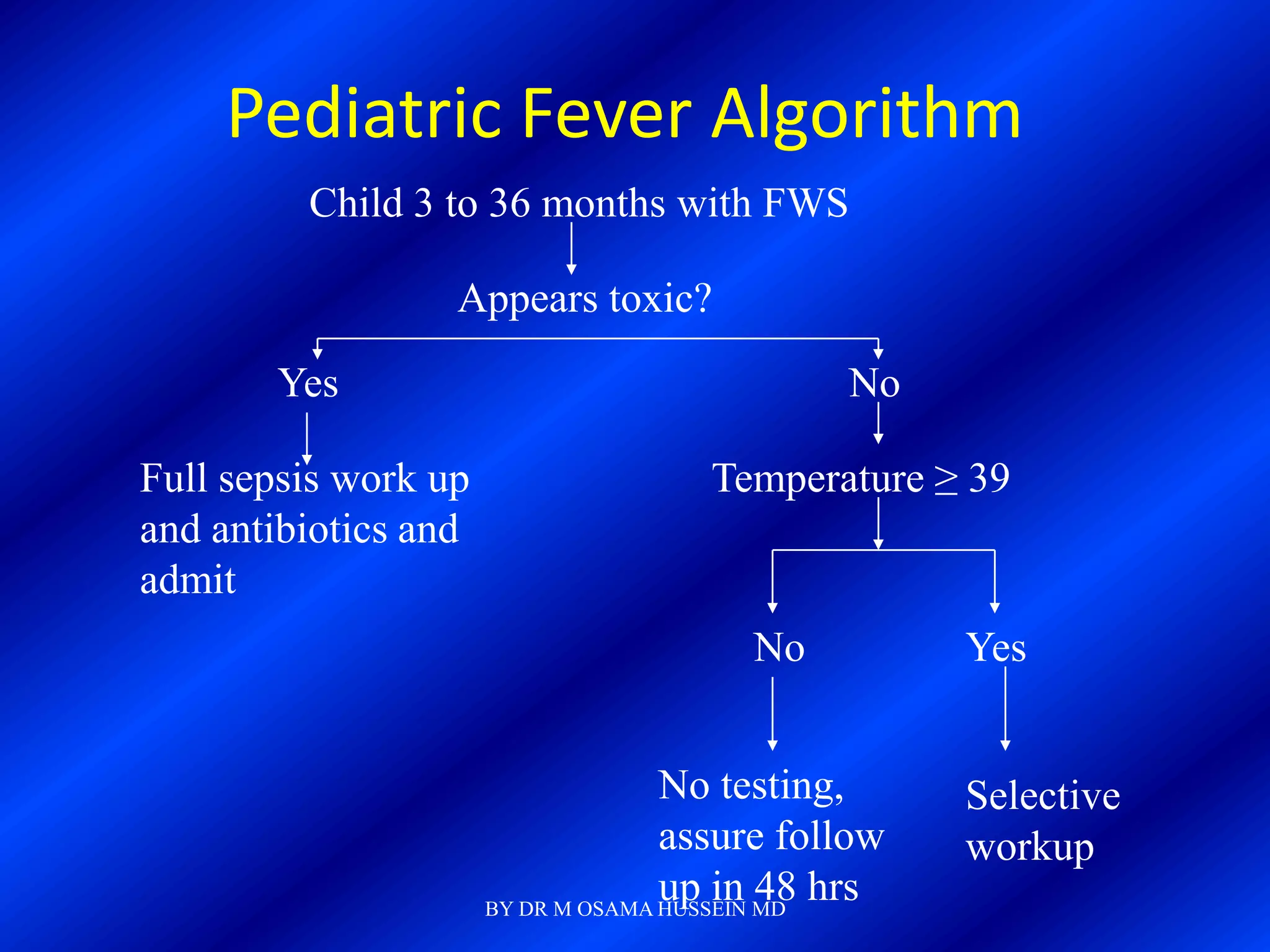
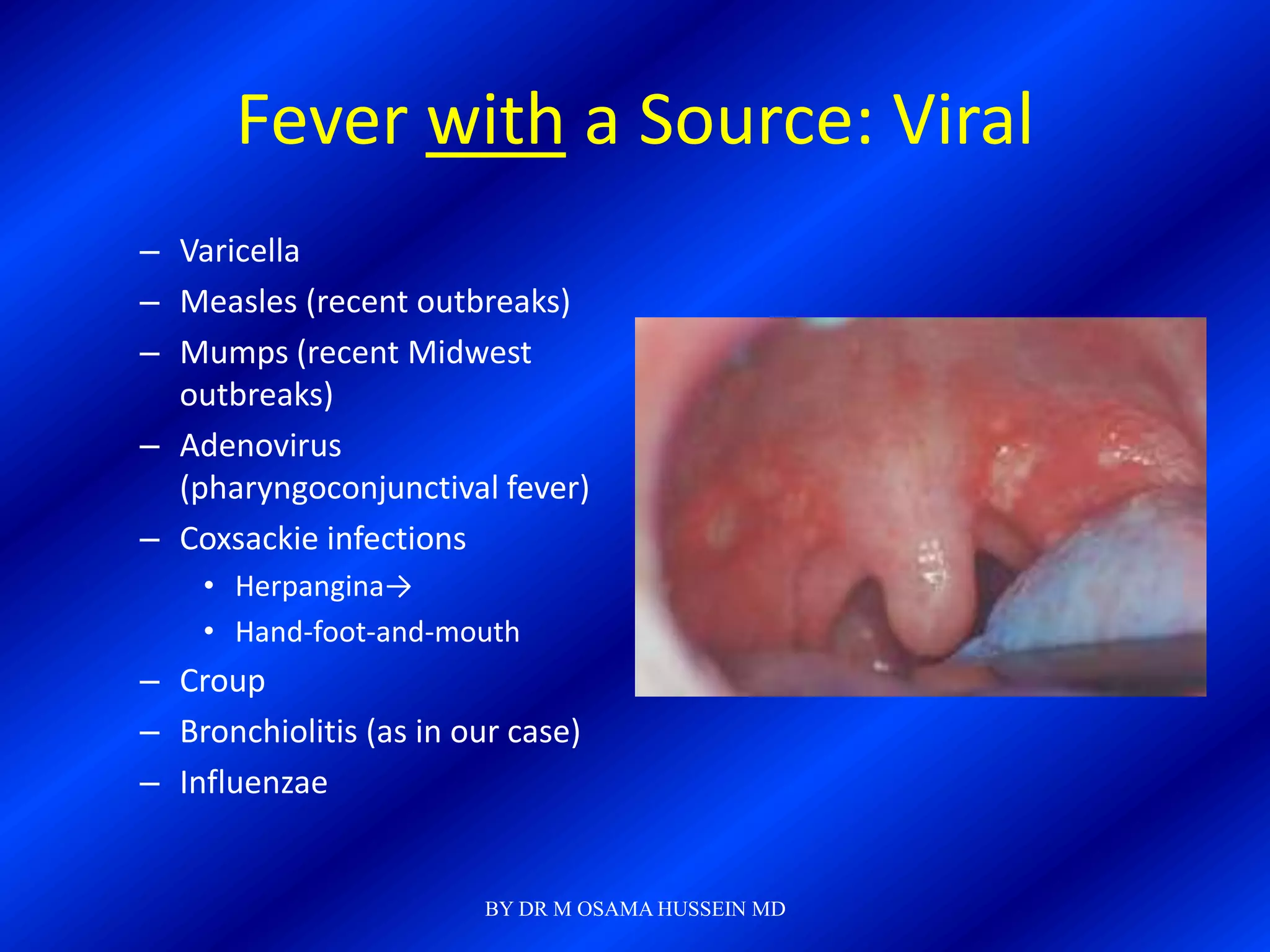
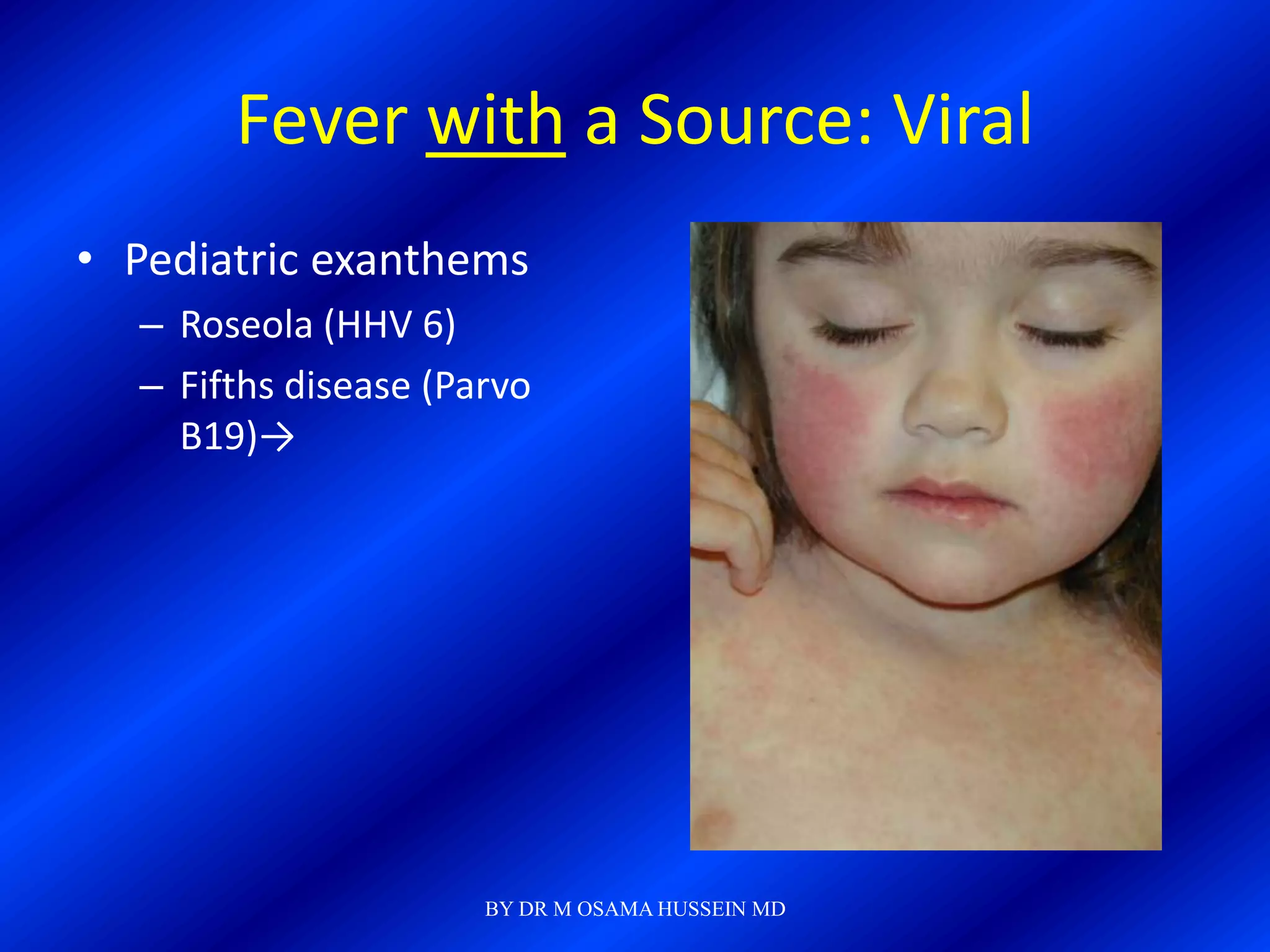
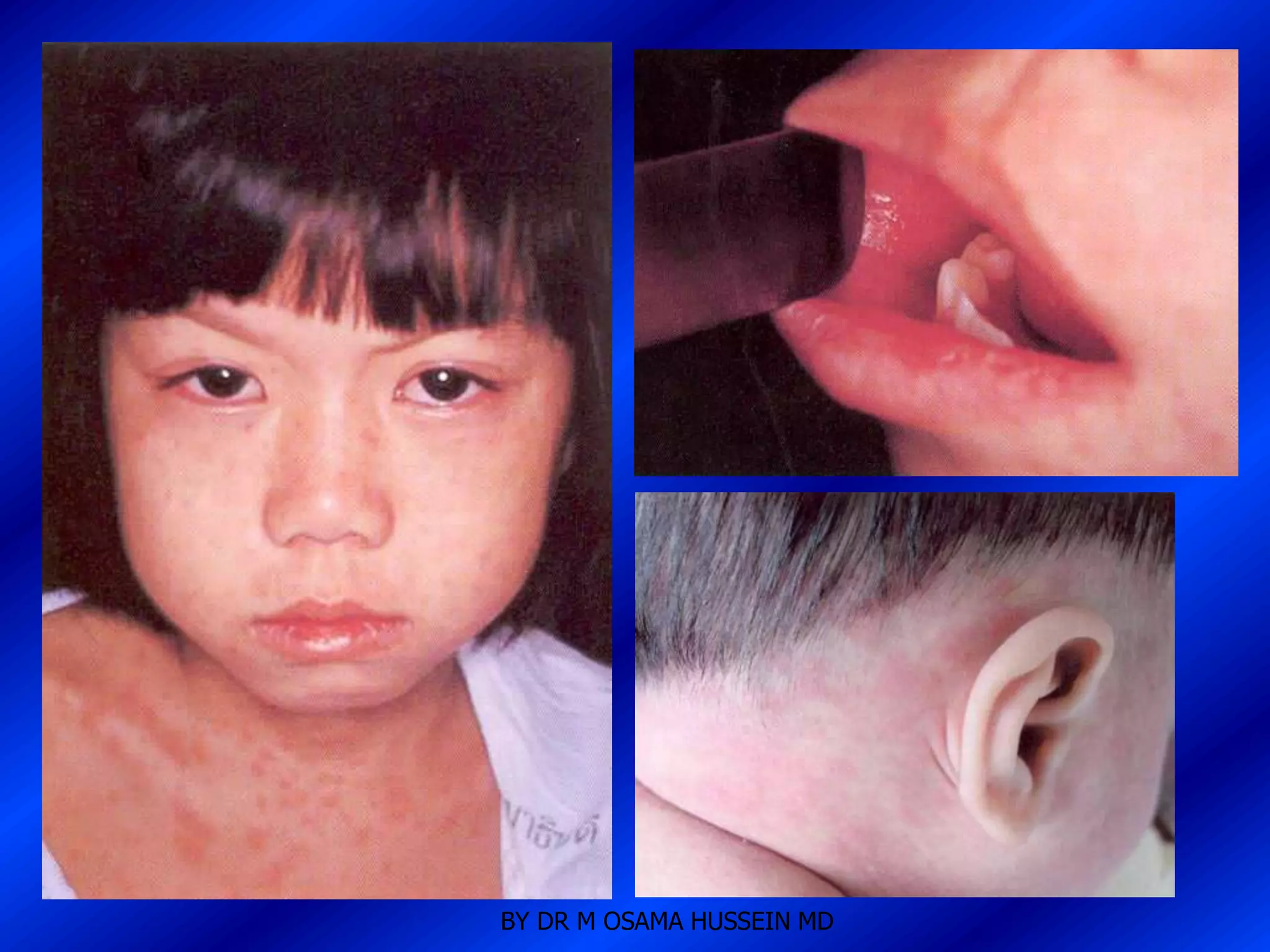
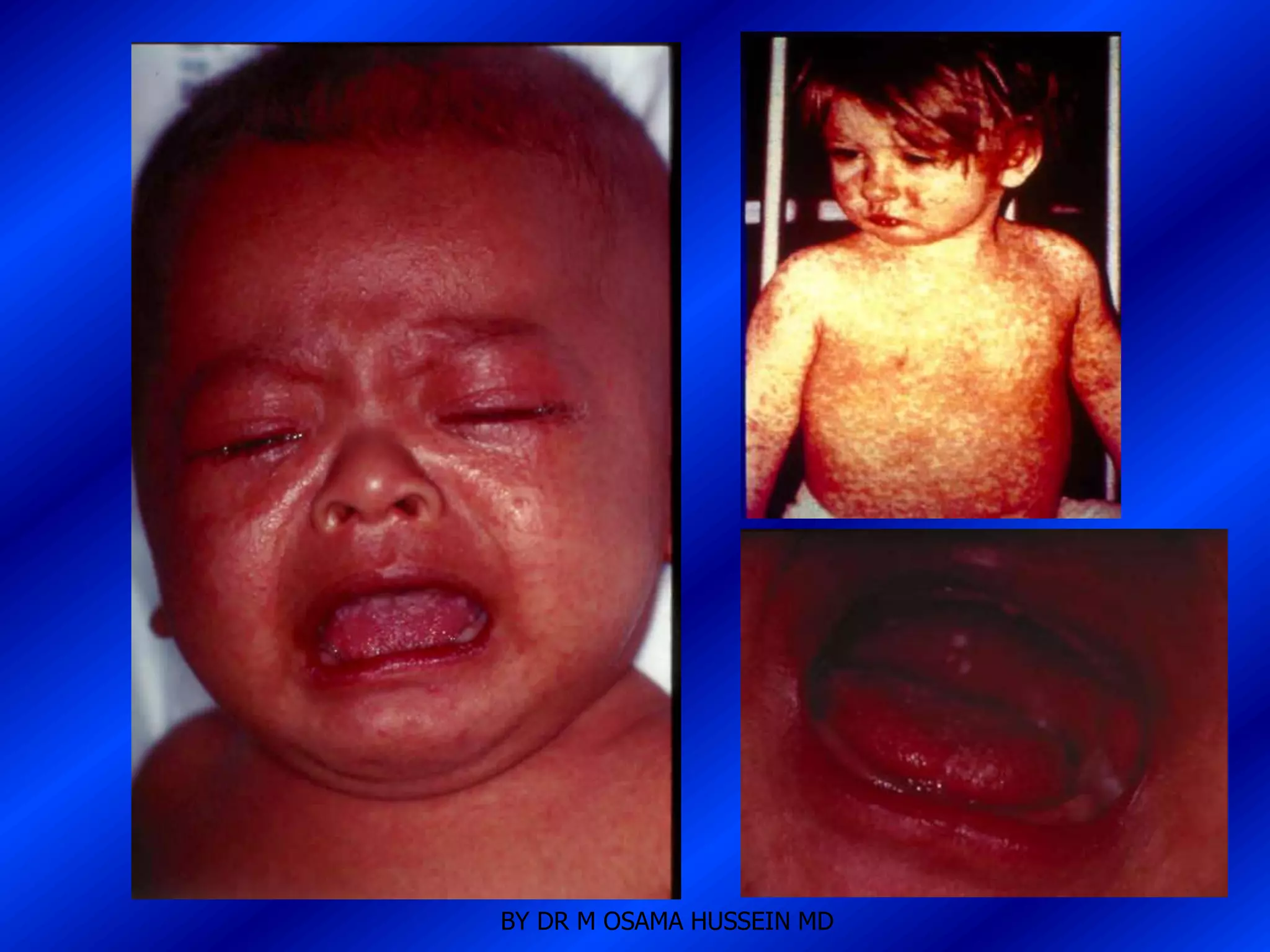
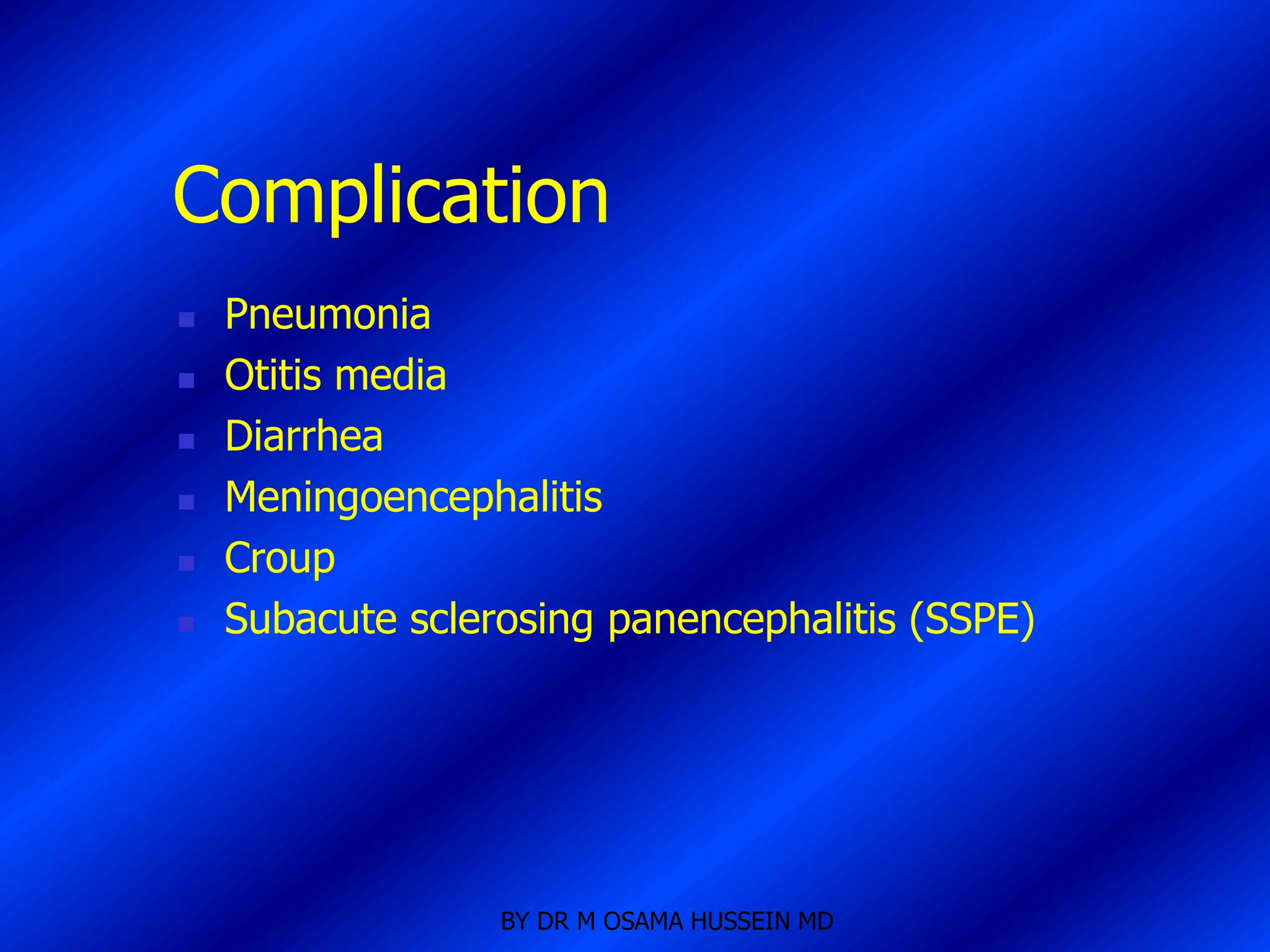
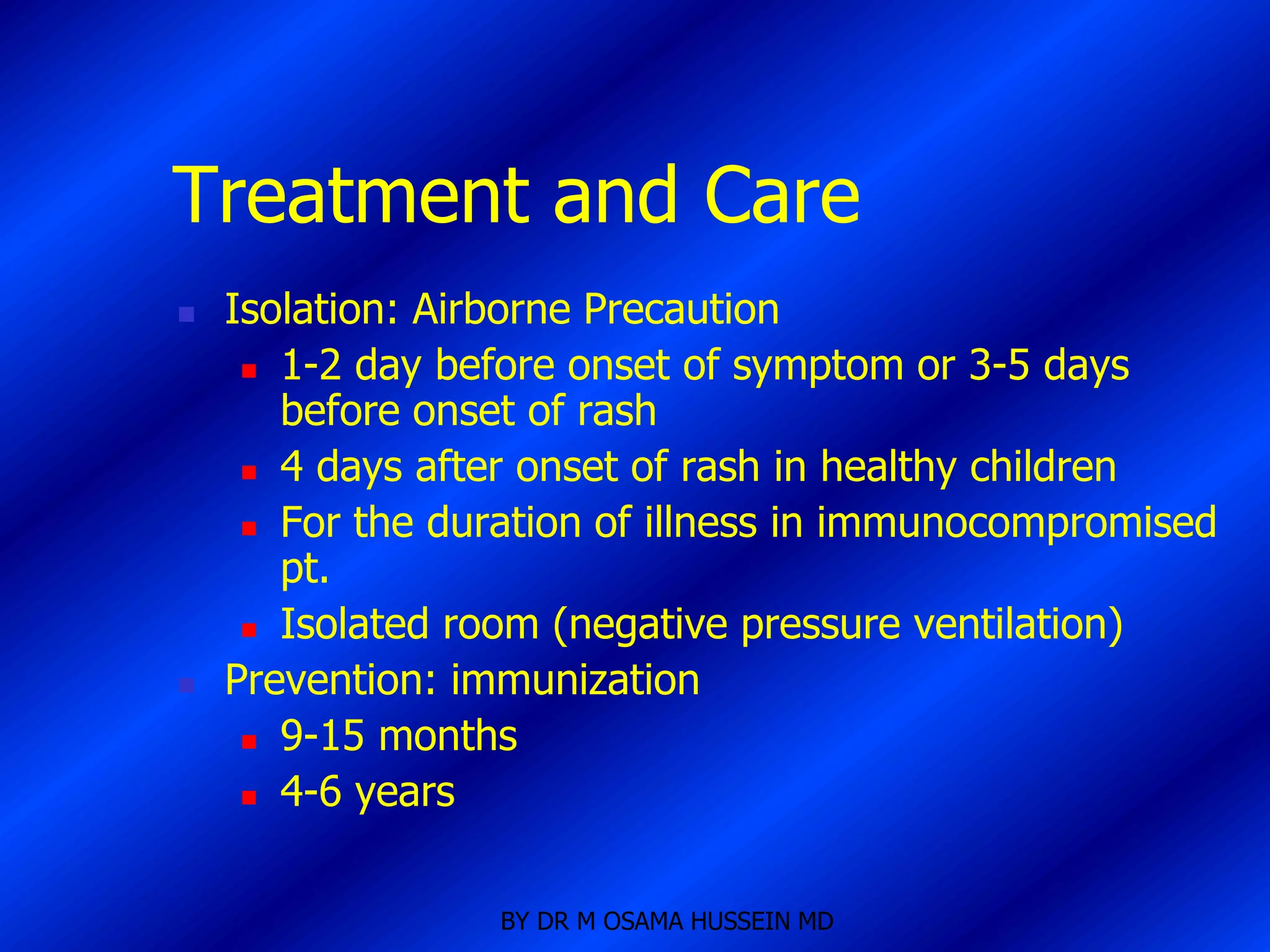
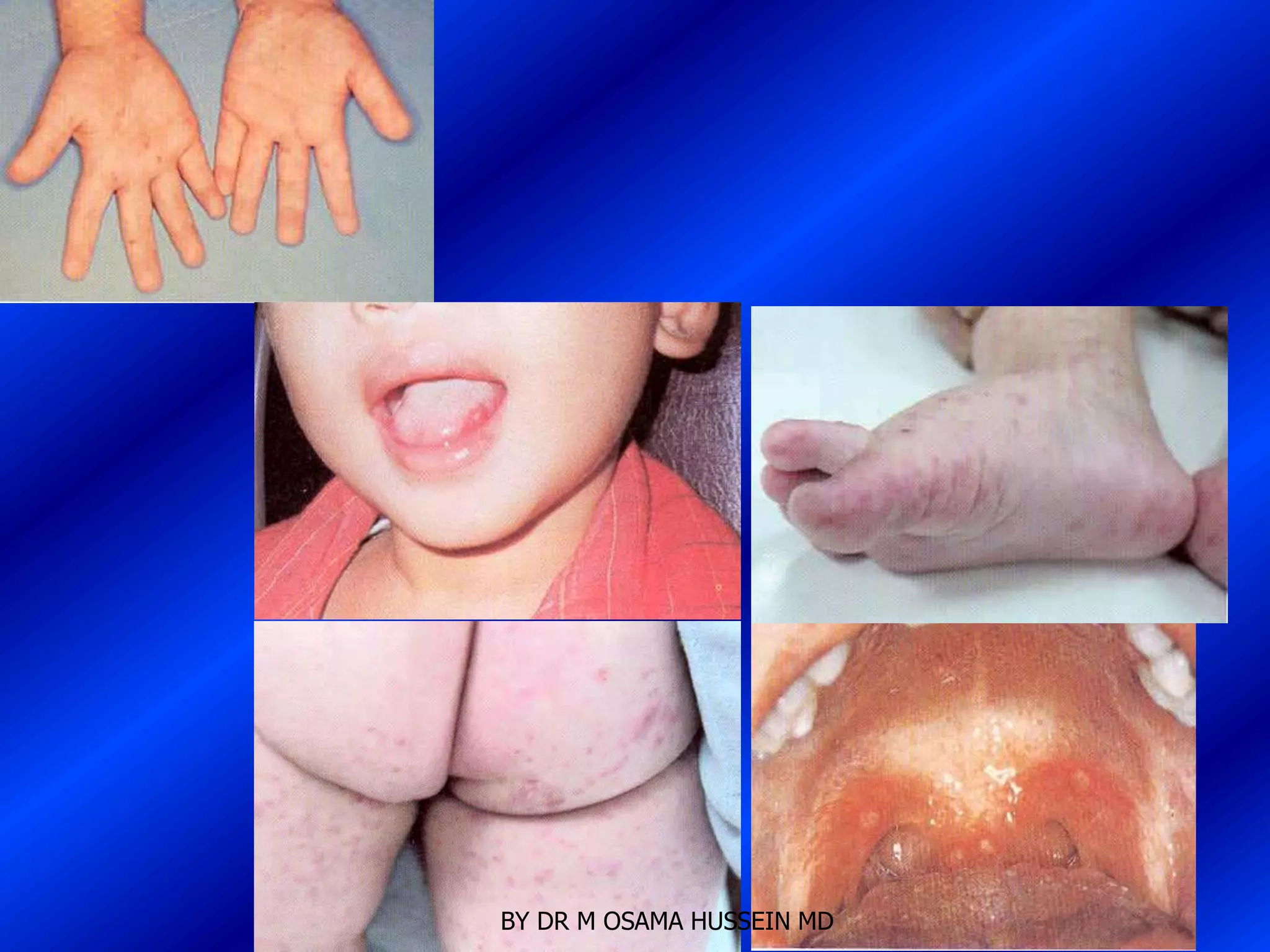
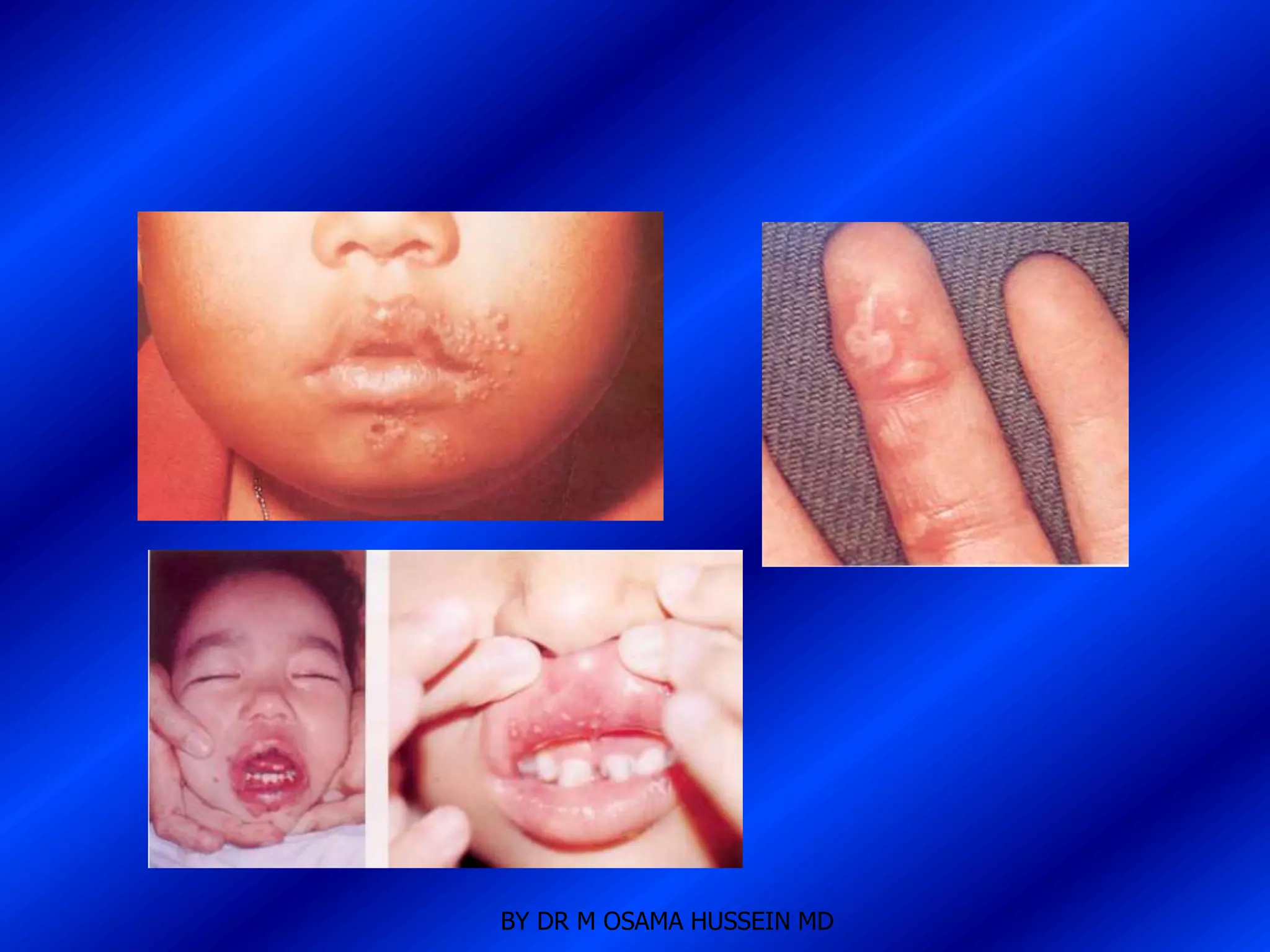
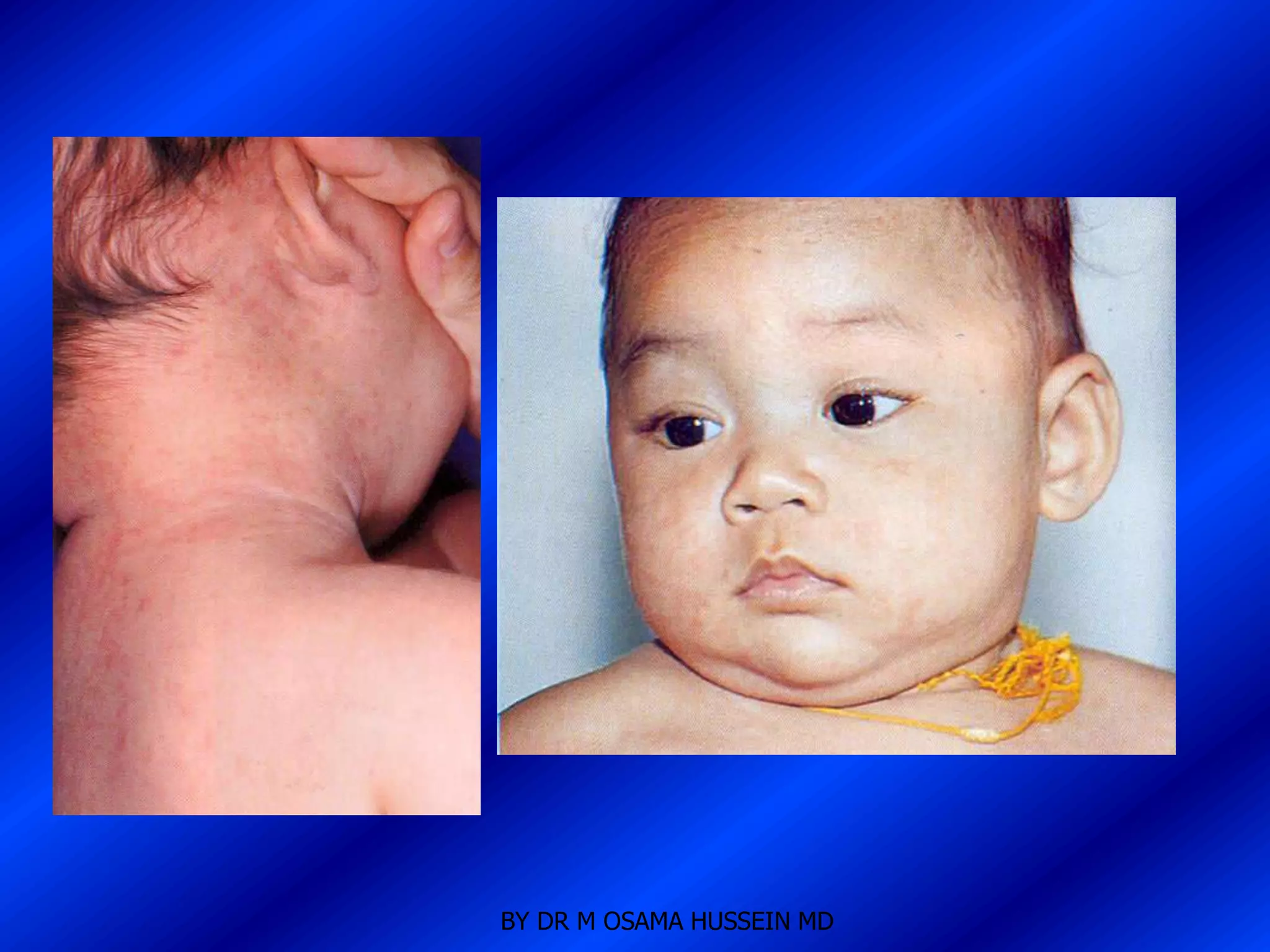
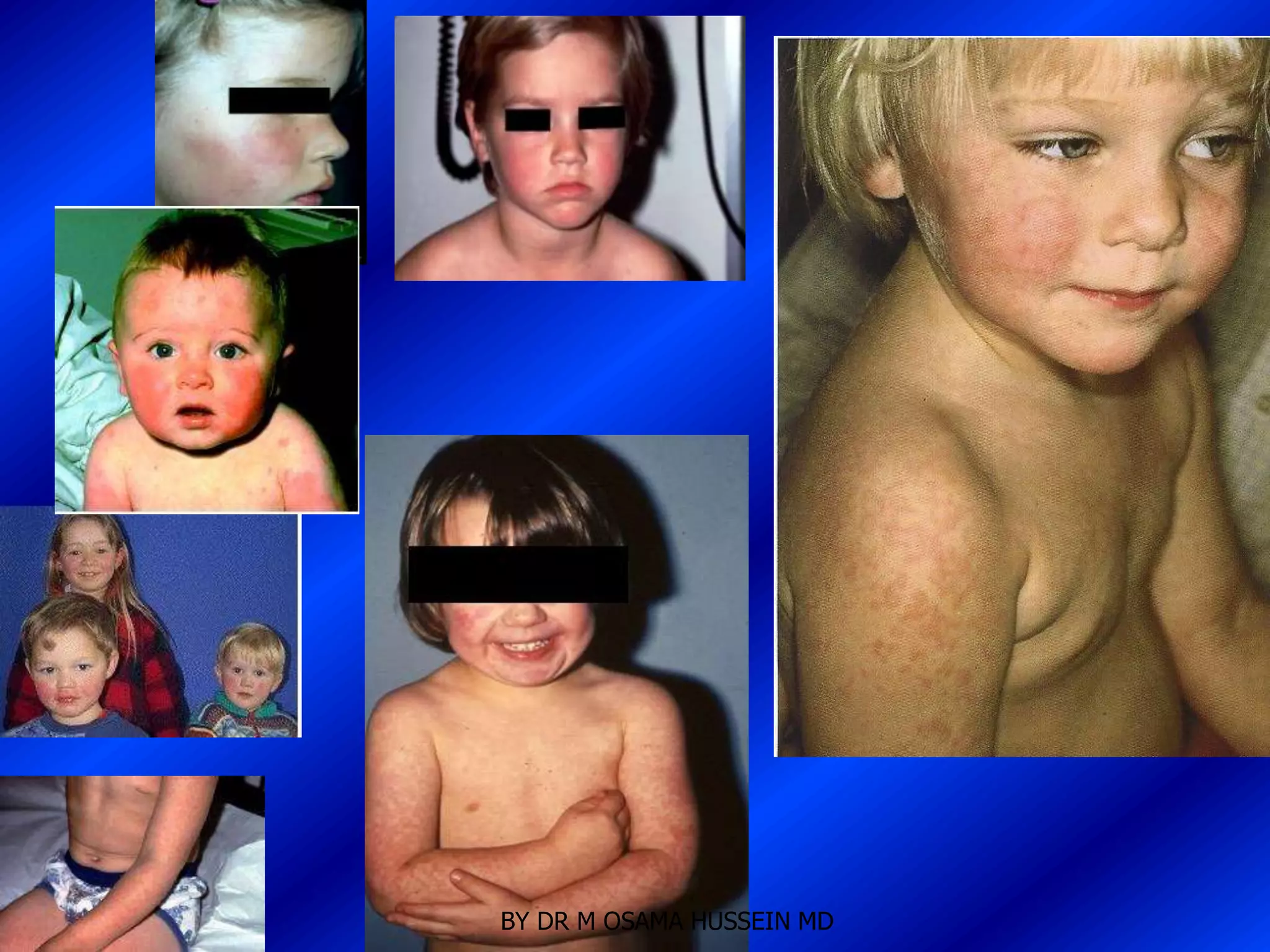
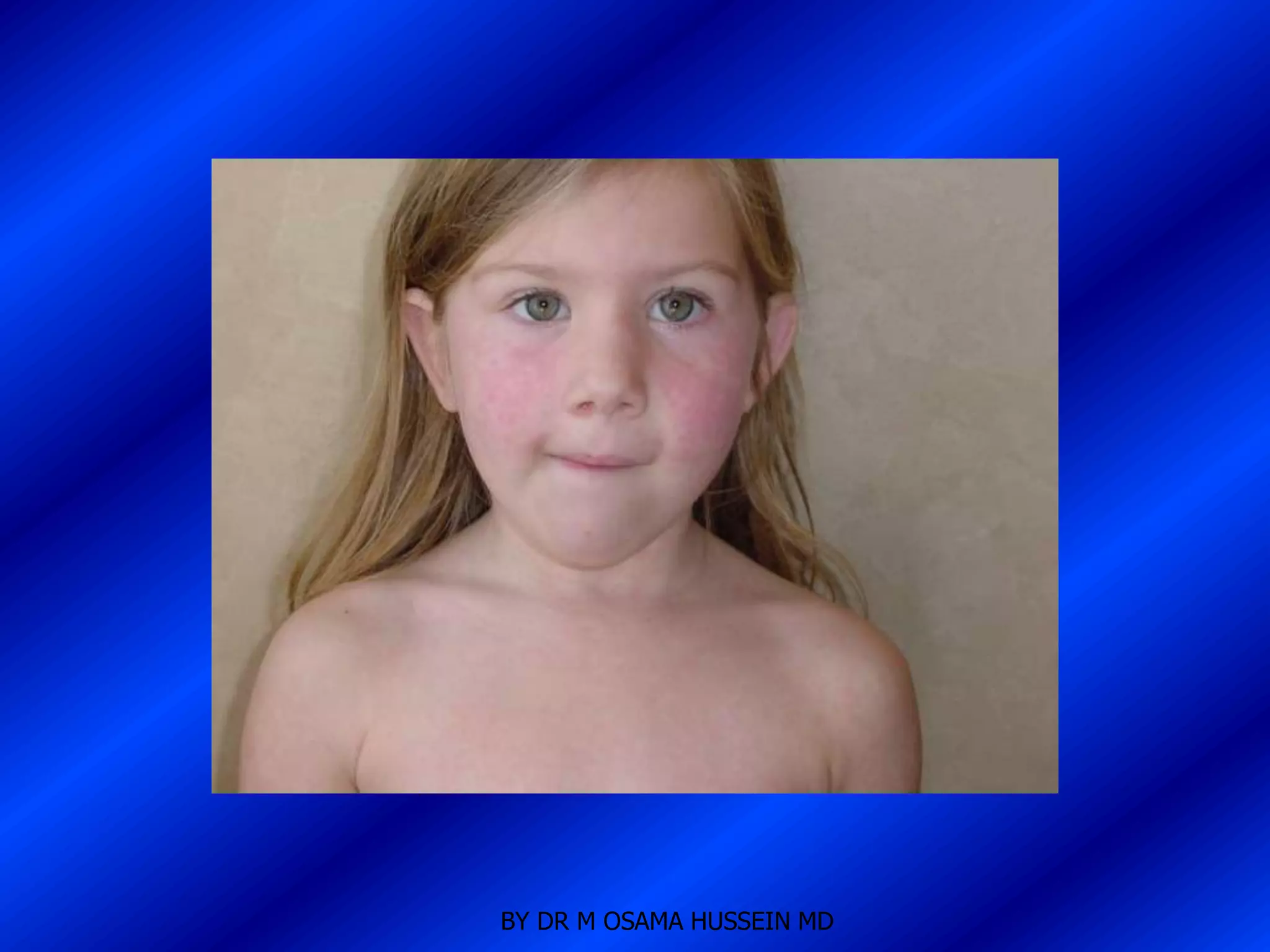
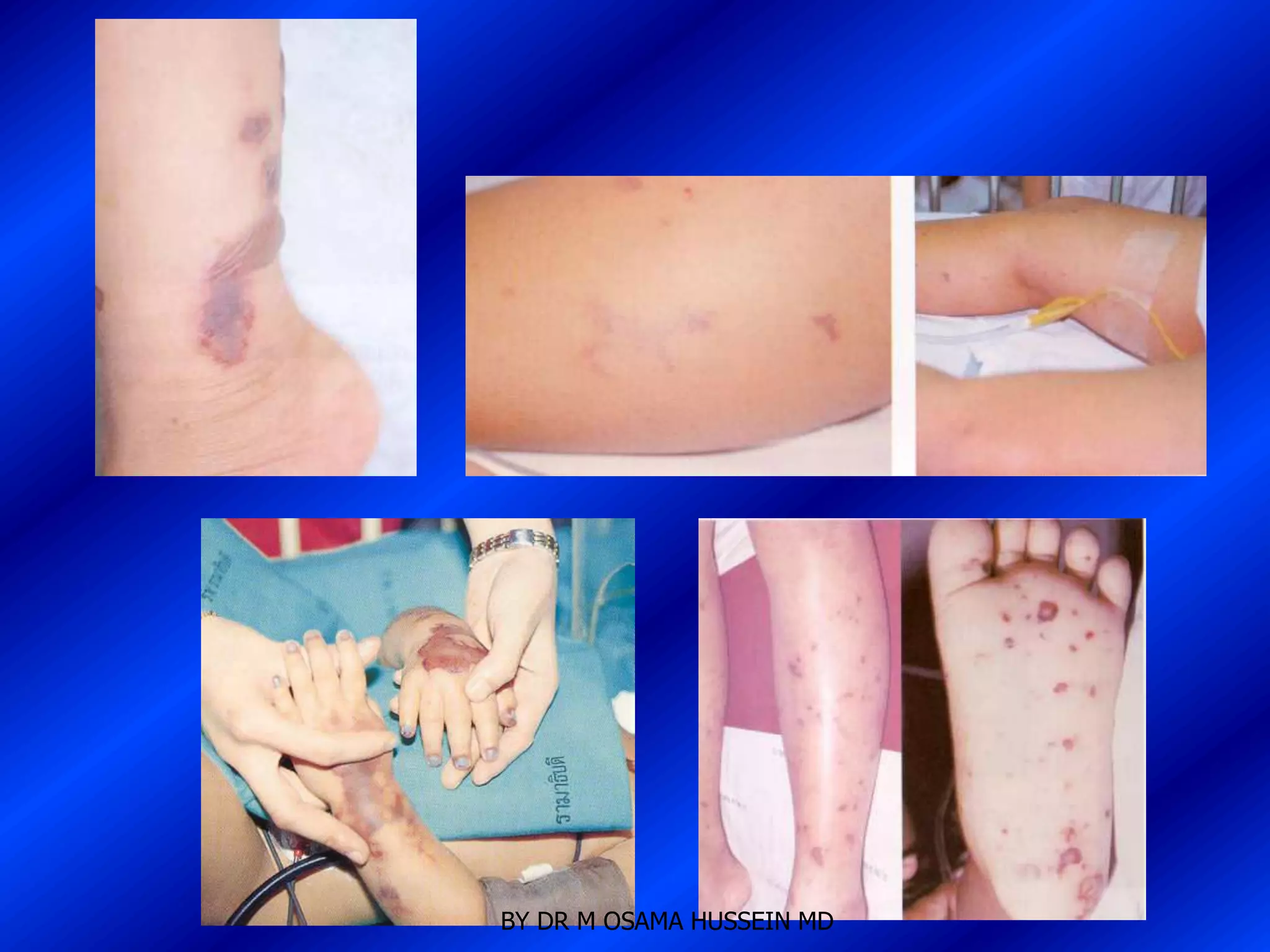
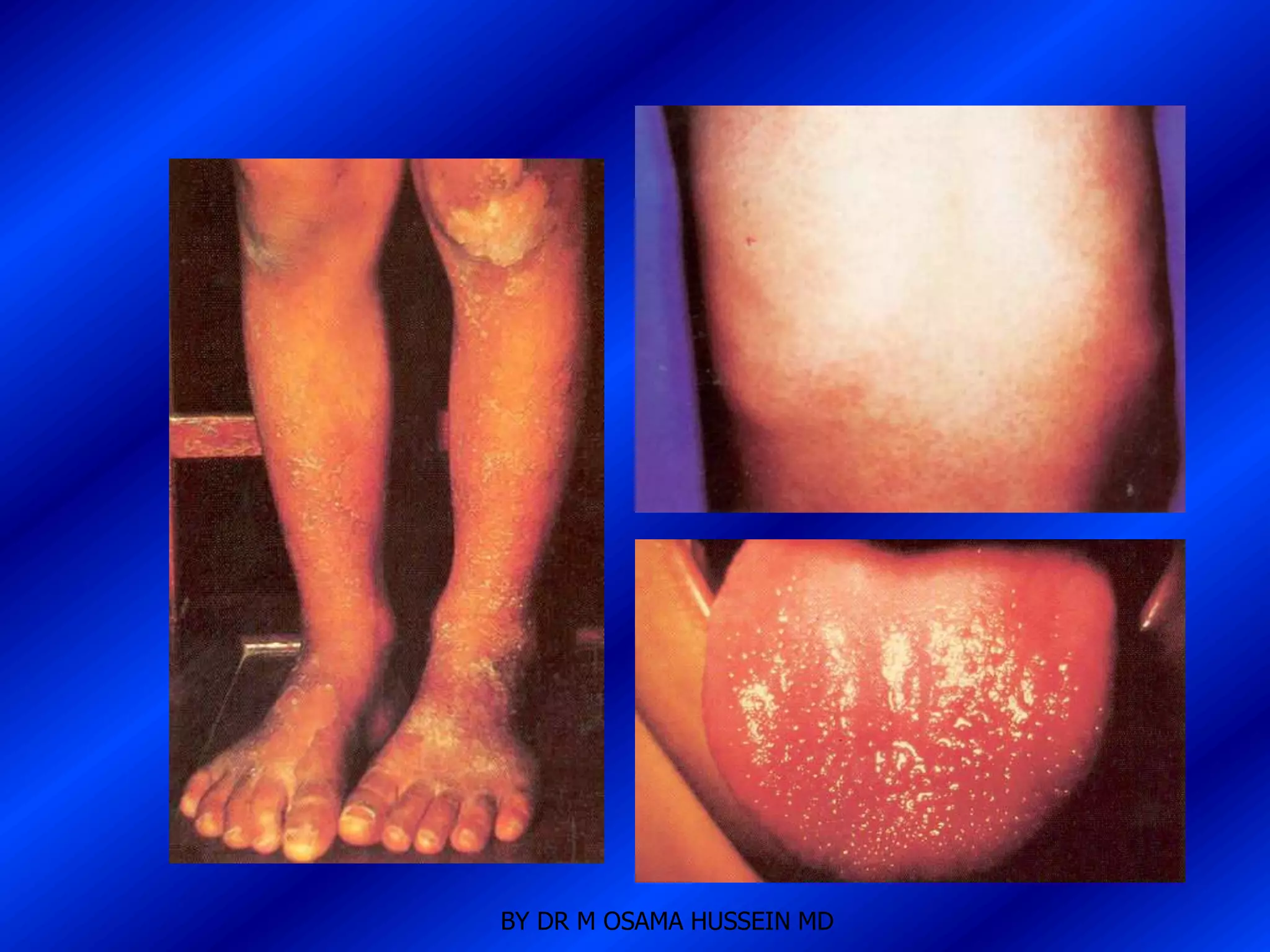
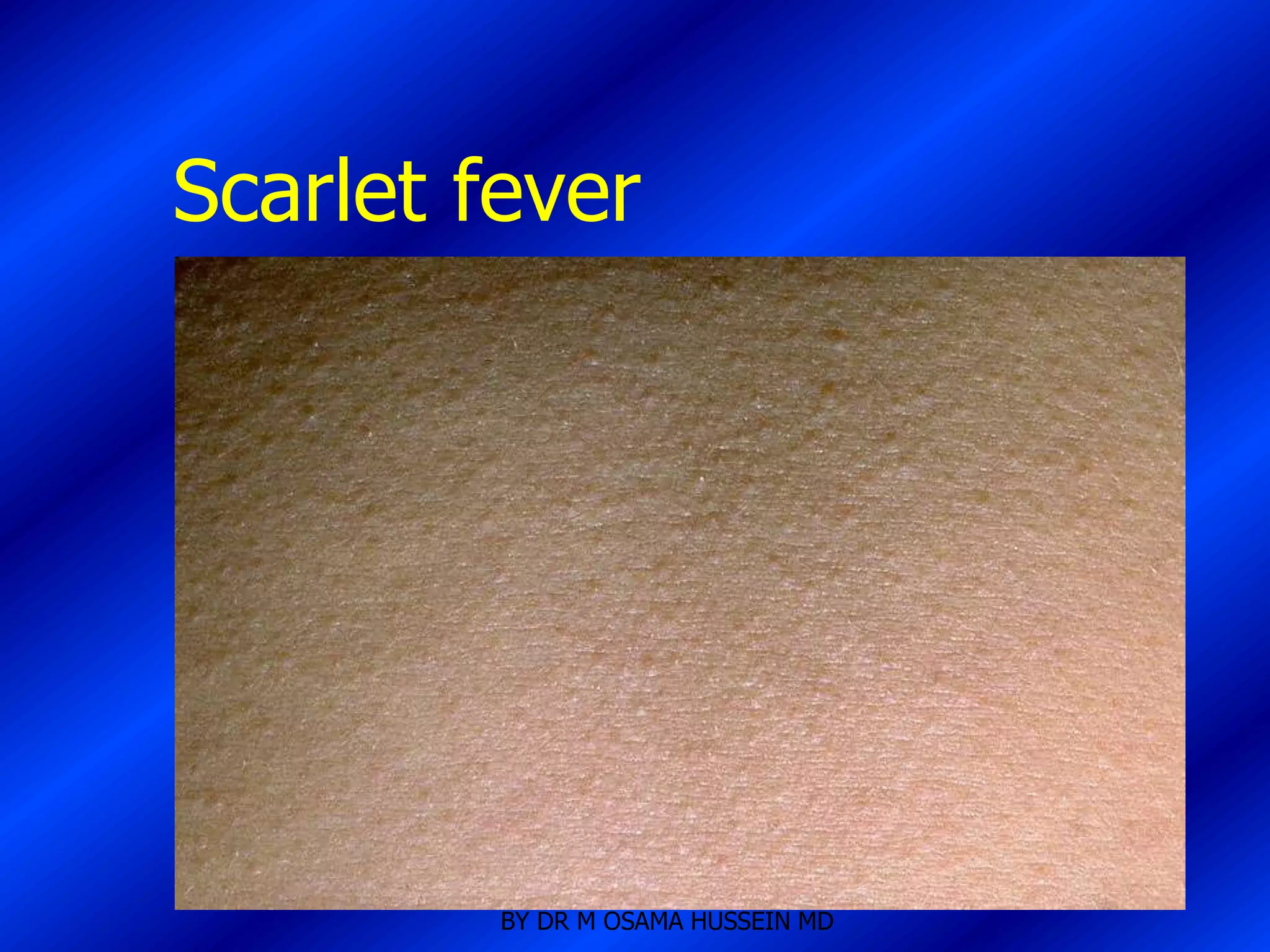
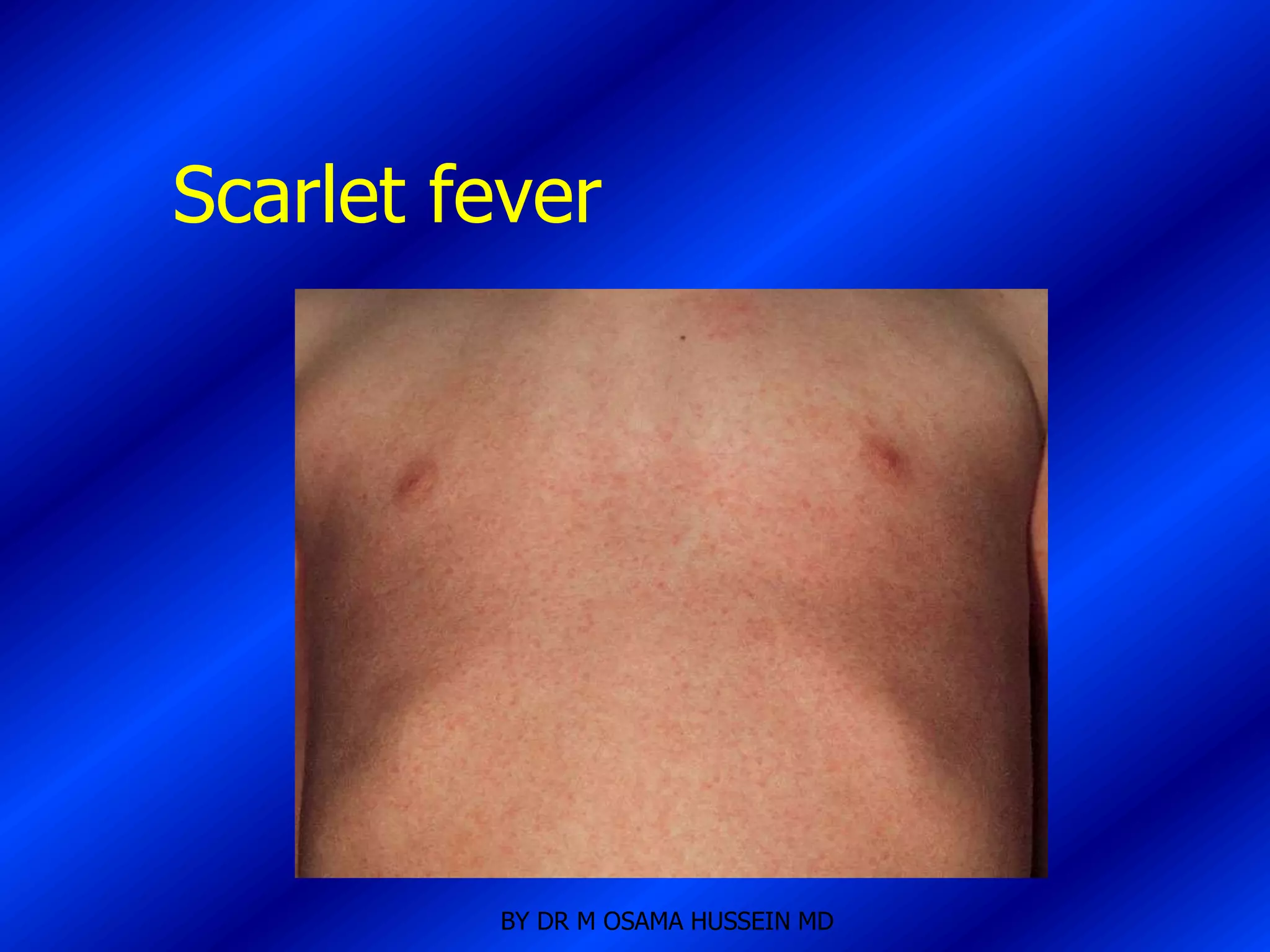
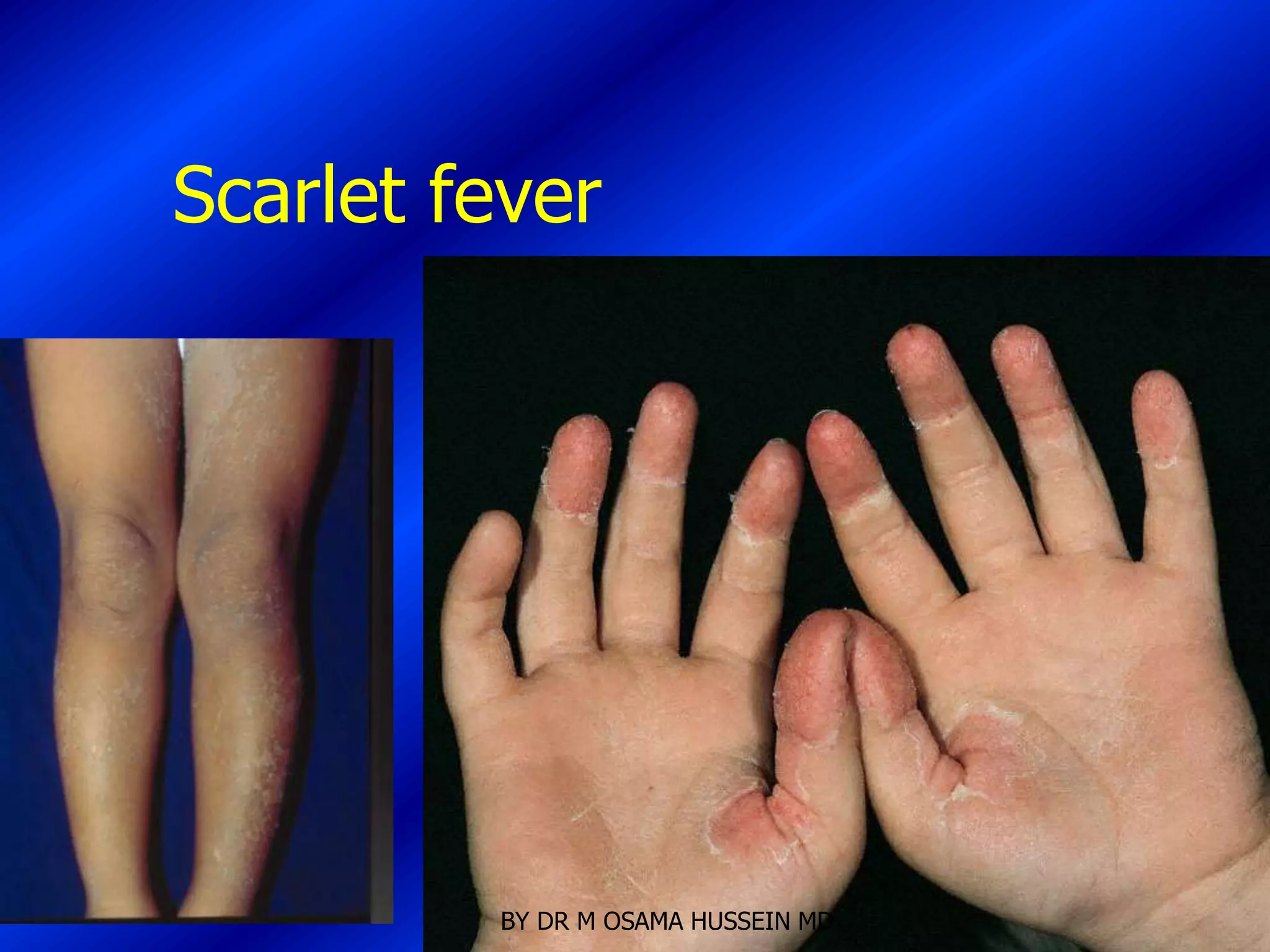
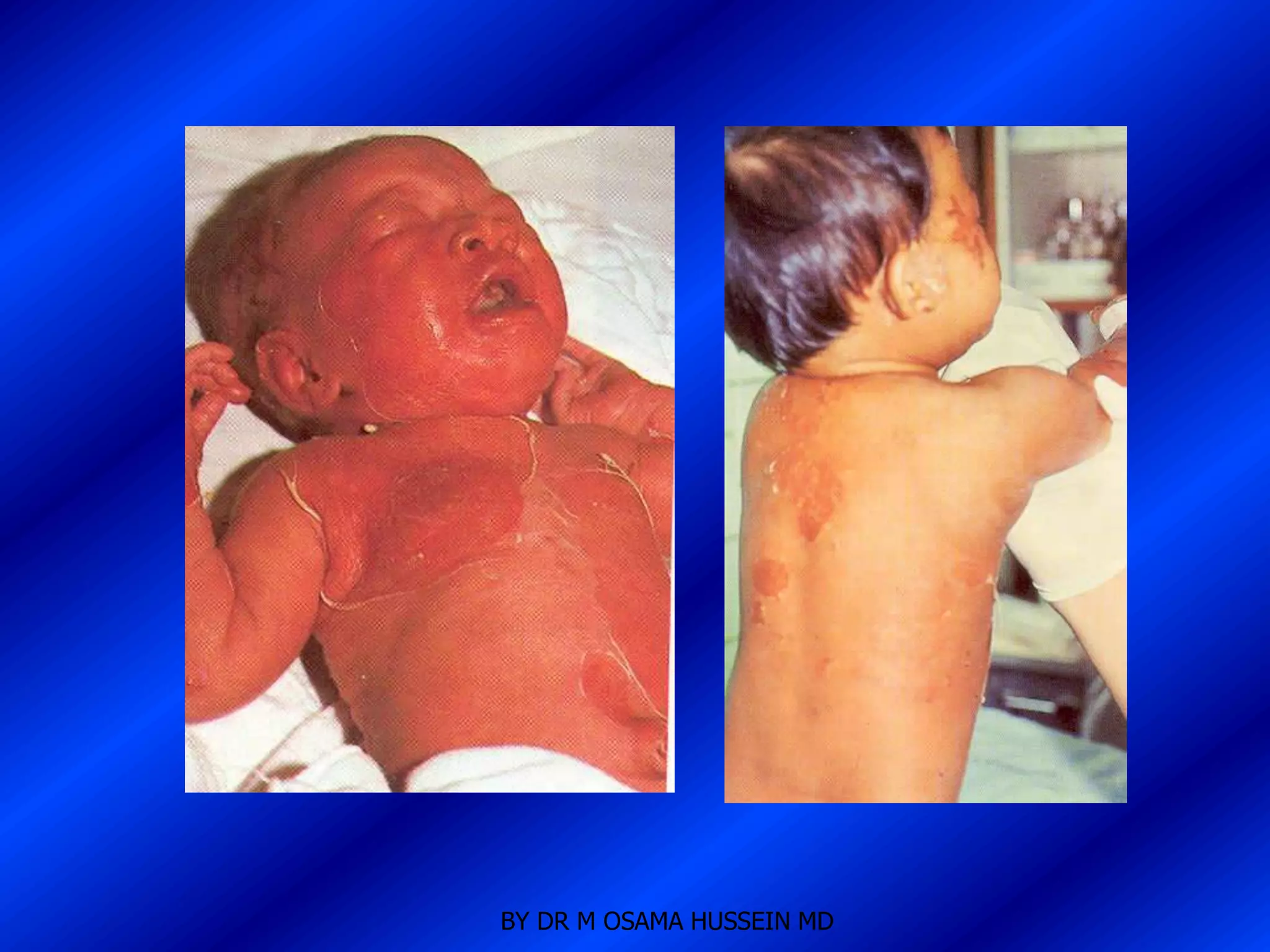
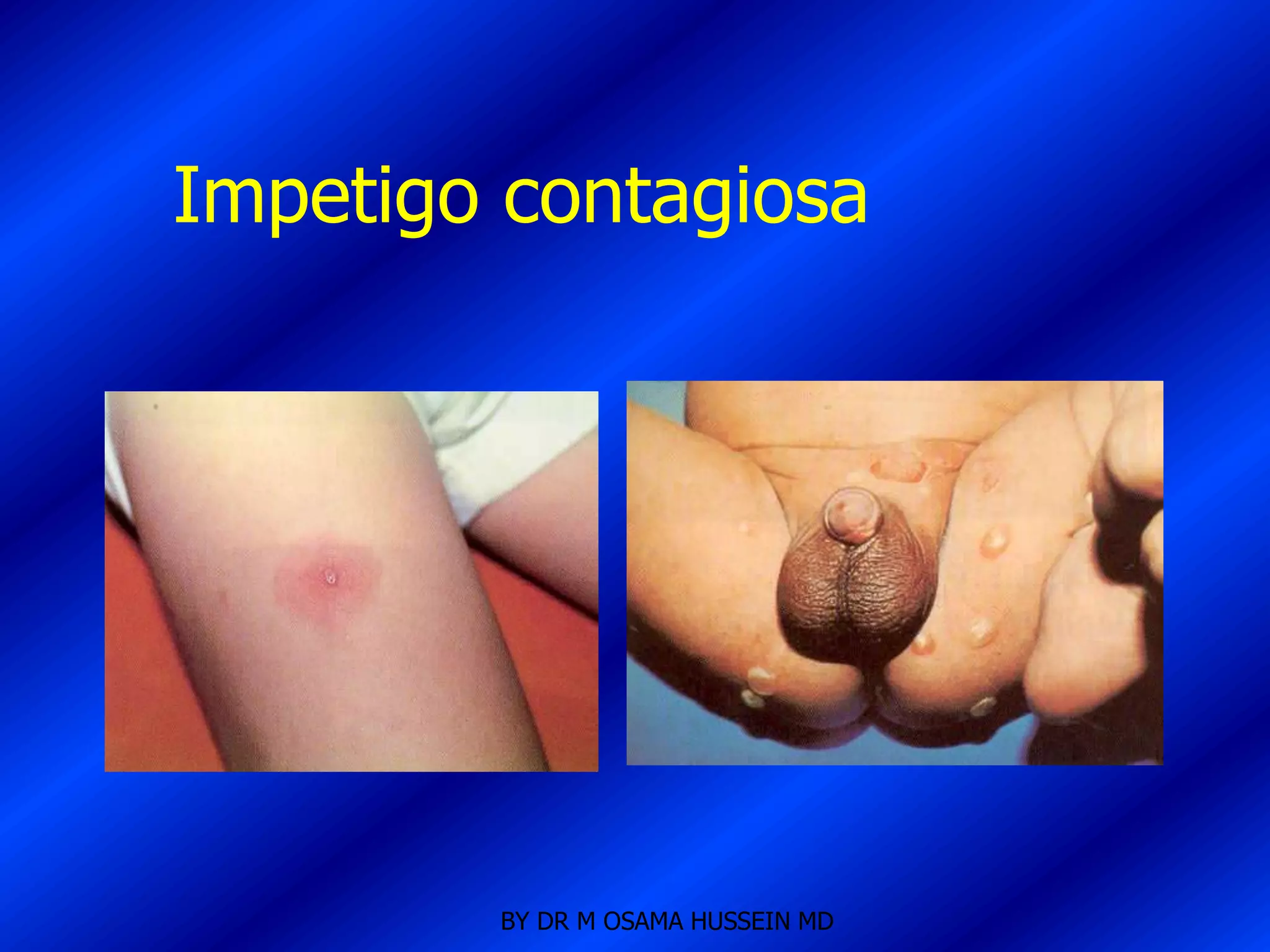
This document discusses the management of fever in infants and young children. It defines key terms like fever and serious bacterial infection. It provides guidelines for identifying febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infection. It discusses the approach to fever without a source and outlines testing and treatment recommendations based on a child's age. The document also reviews specific considerations for viral and bacterial causes of fever, appropriate use of antipyretics, and how to manage conditions like Kawasaki's disease and febrile seizures.