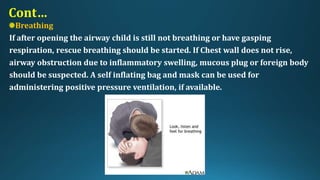
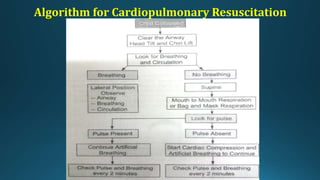
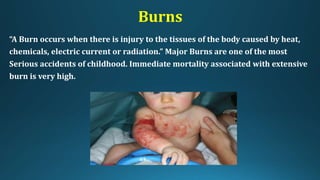
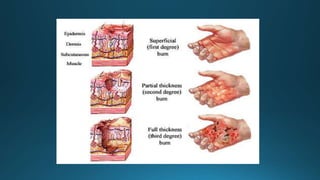
This document provides an overview of paediatric emergency management. It discusses cardiopulmonary resuscitation procedures for children and outlines management of common paediatric emergencies like drowning, burns, falls, and foreign body ingestion. Specific conditions covered in more depth include near-drowning, burn classifications and estimations, and treatment plans for minor and major burns. The document aims to equip medical professionals with knowledge of stabilizing critically ill children and preventing long-term complications from emergency situations.