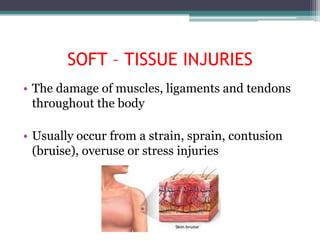
This document summarizes 5 common medical emergencies: cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, airway obstruction, burns, and soft-tissue injuries. It provides details on the symptoms and treatment for each emergency. Key points include that cardiac arrest results from an electrical disturbance and stops heart function/blood flow, respiratory arrest occurs when breathing ceases, airway obstruction can block breathing, burns are classified by degree of skin damage, and soft-tissue injuries involve muscle/tendon damage. Proper treatment may involve CPR, intubation, cooling burns, or RICE therapy depending on the emergency type. Automated external defibrillators can treat cardiac arrhythmias through defibrillation.