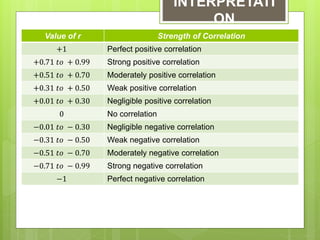
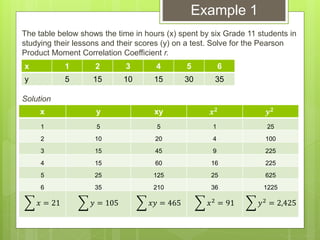
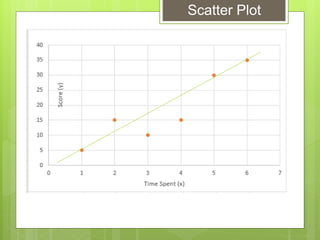
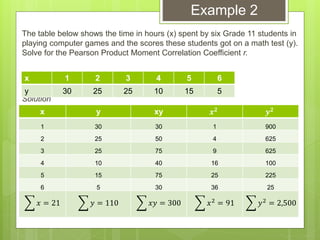
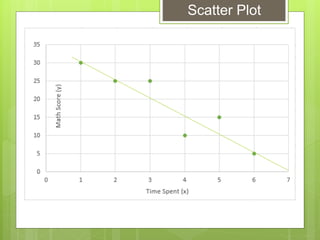
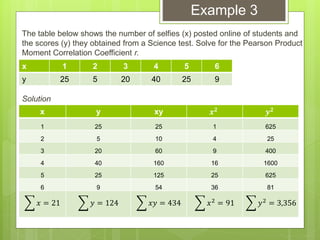
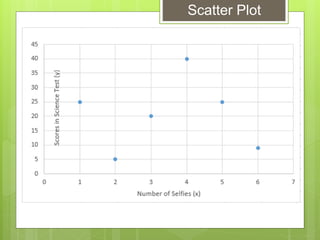
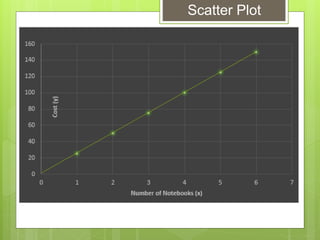
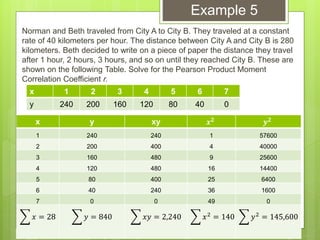
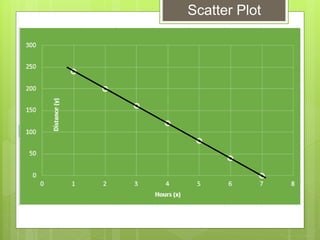
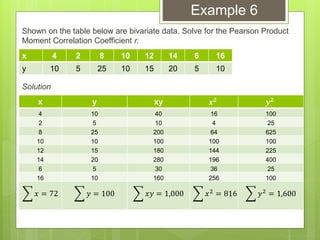
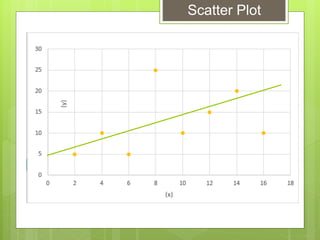
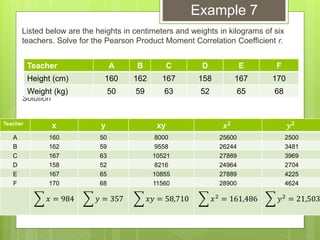
The document provides examples for calculating the Pearson Product Moment Correlation Coefficient (r) from bivariate data. It defines r as a measure of the strength of the linear relationship between two variables. Several fully worked examples are shown calculating r from tables of paired data and interpreting the resulting r value based on established thresholds for strength of correlation. Formulas and steps for calculating r are demonstrated throughout.