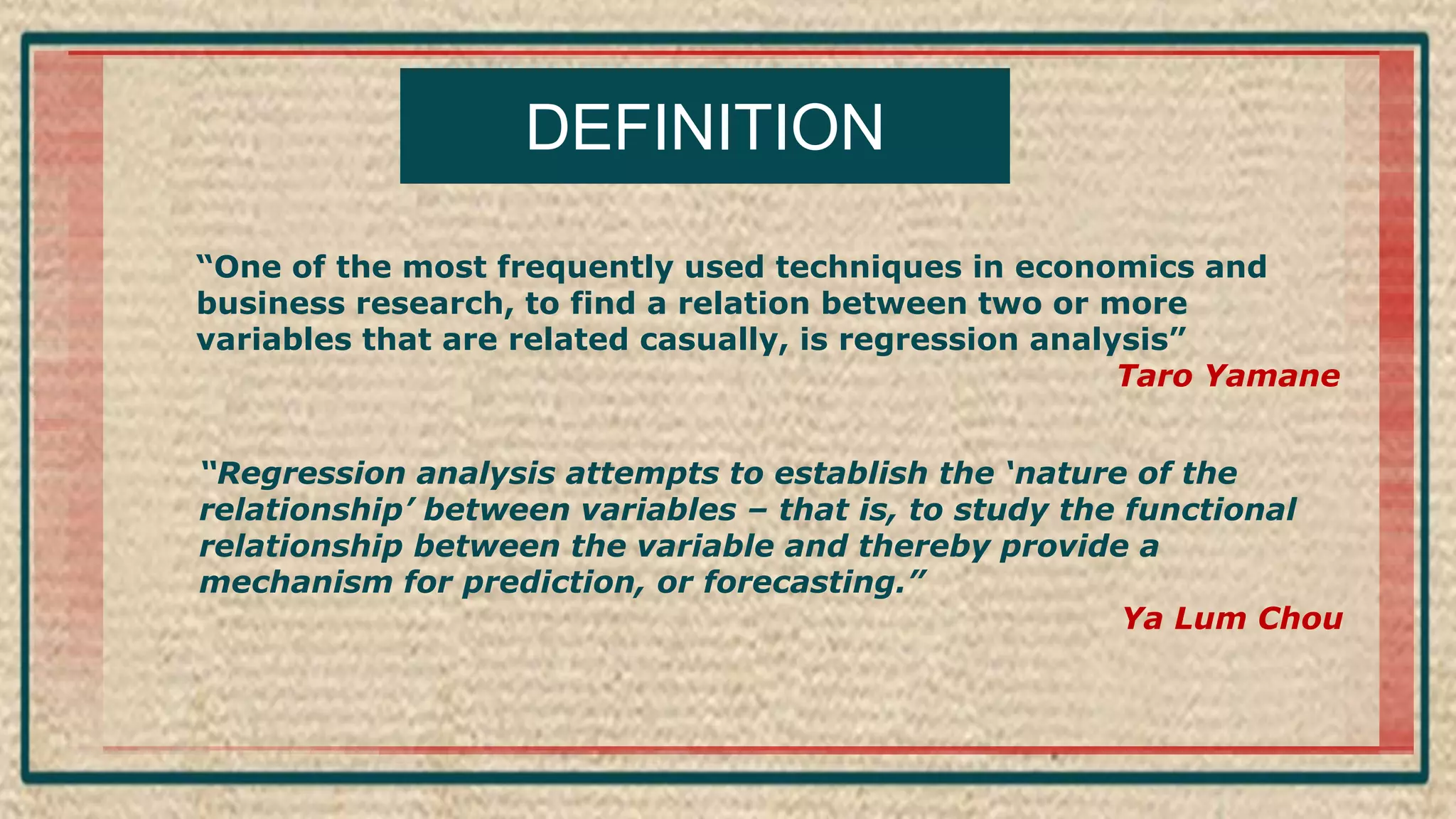
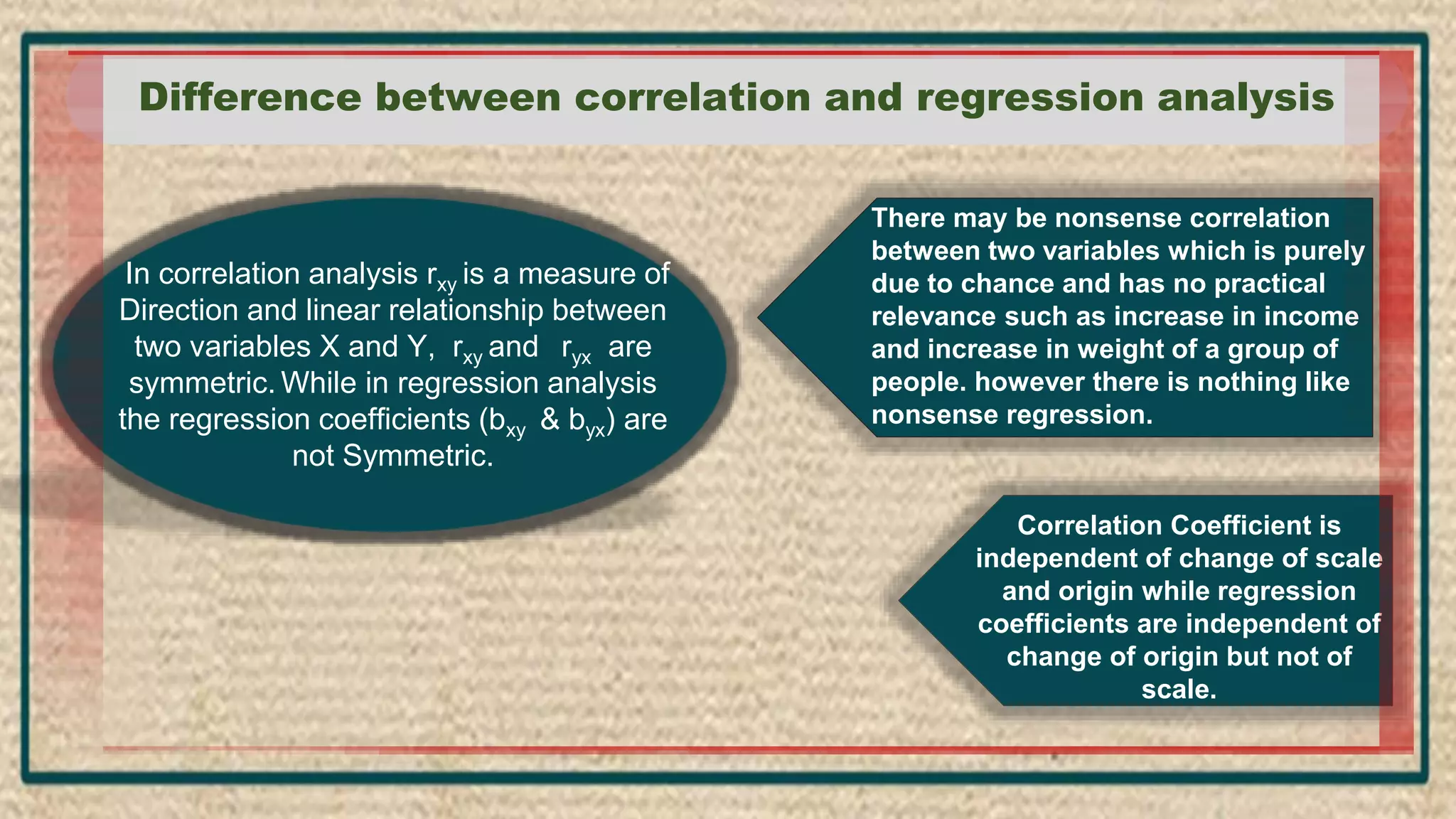
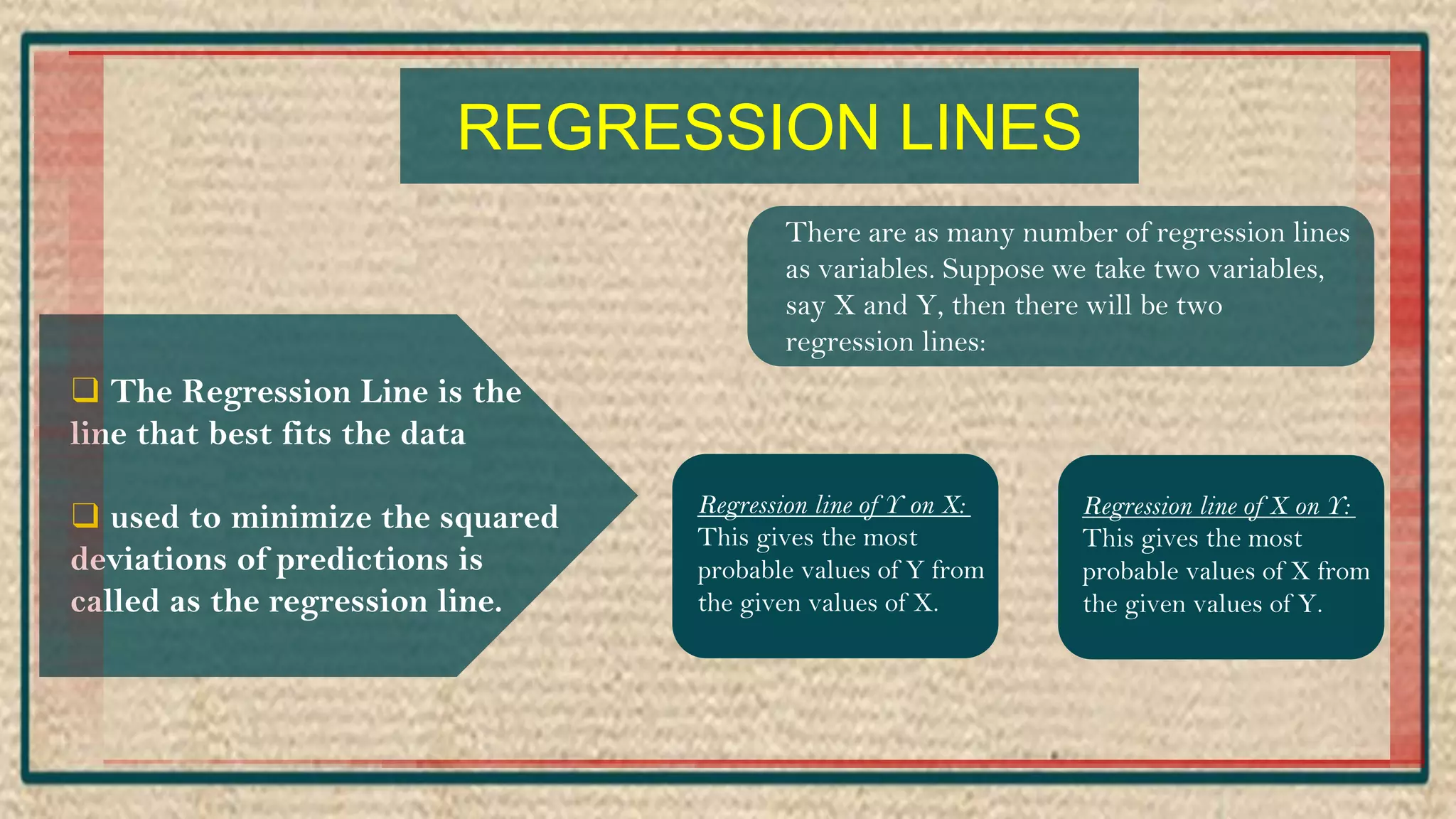
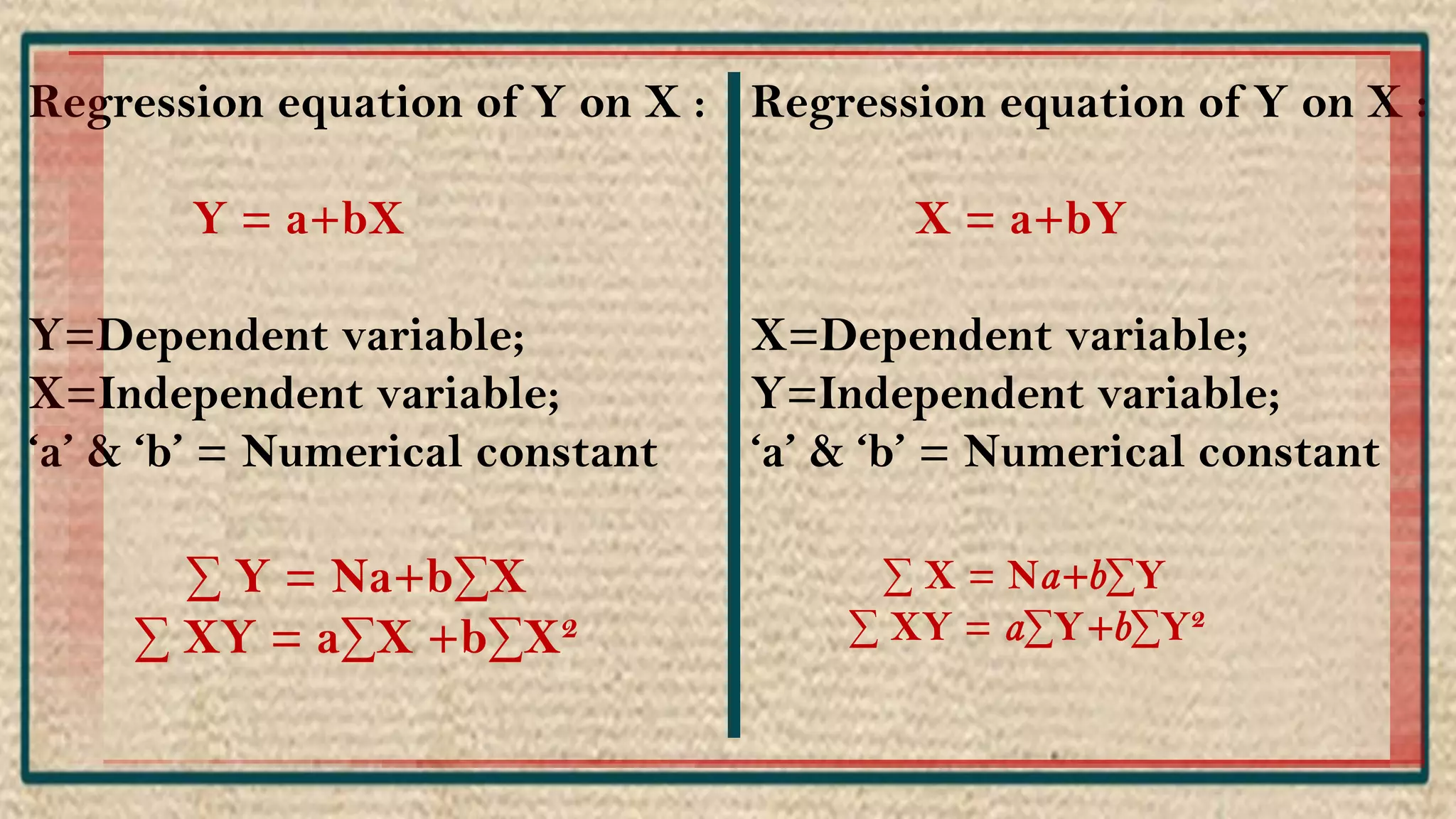
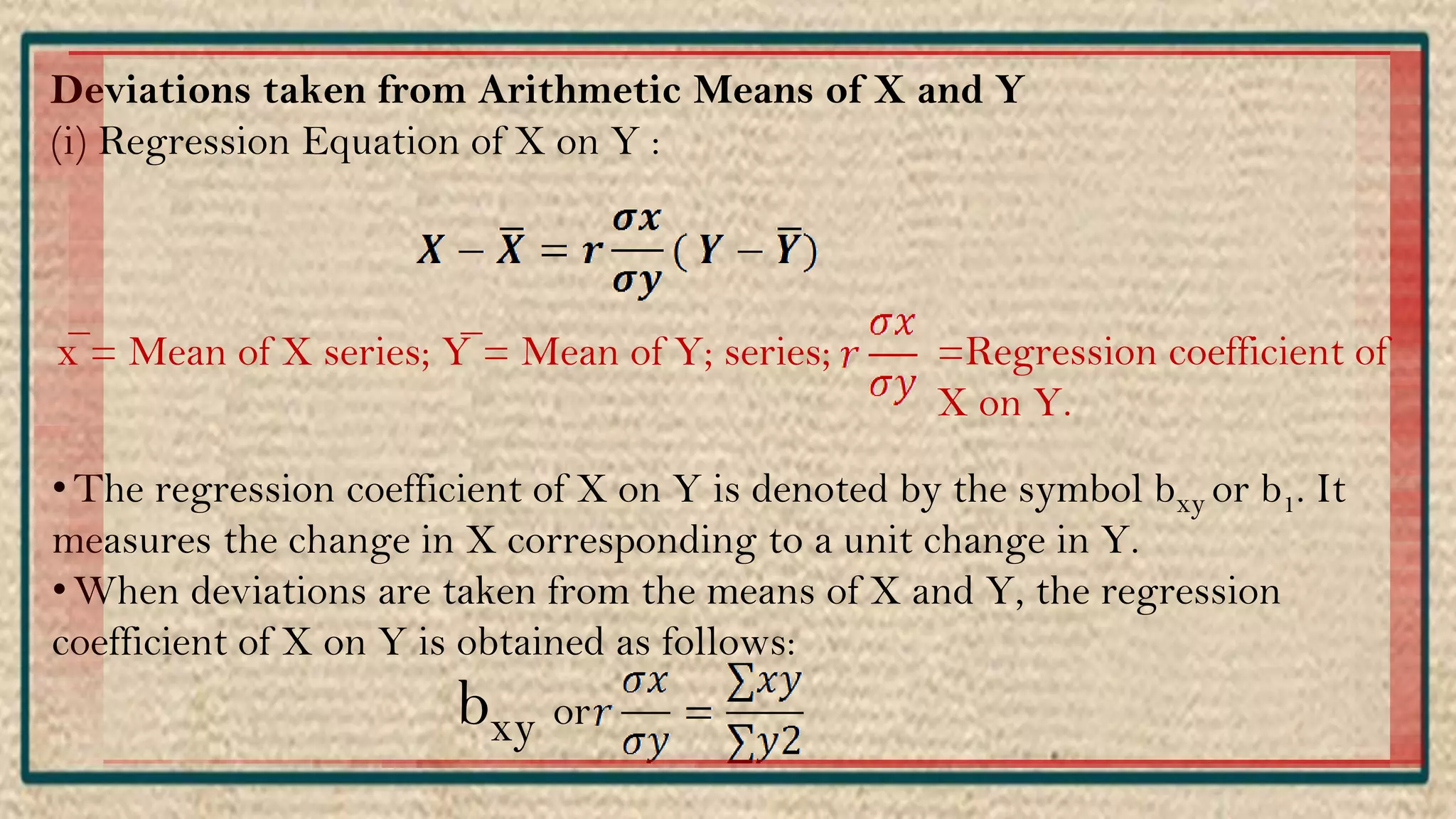
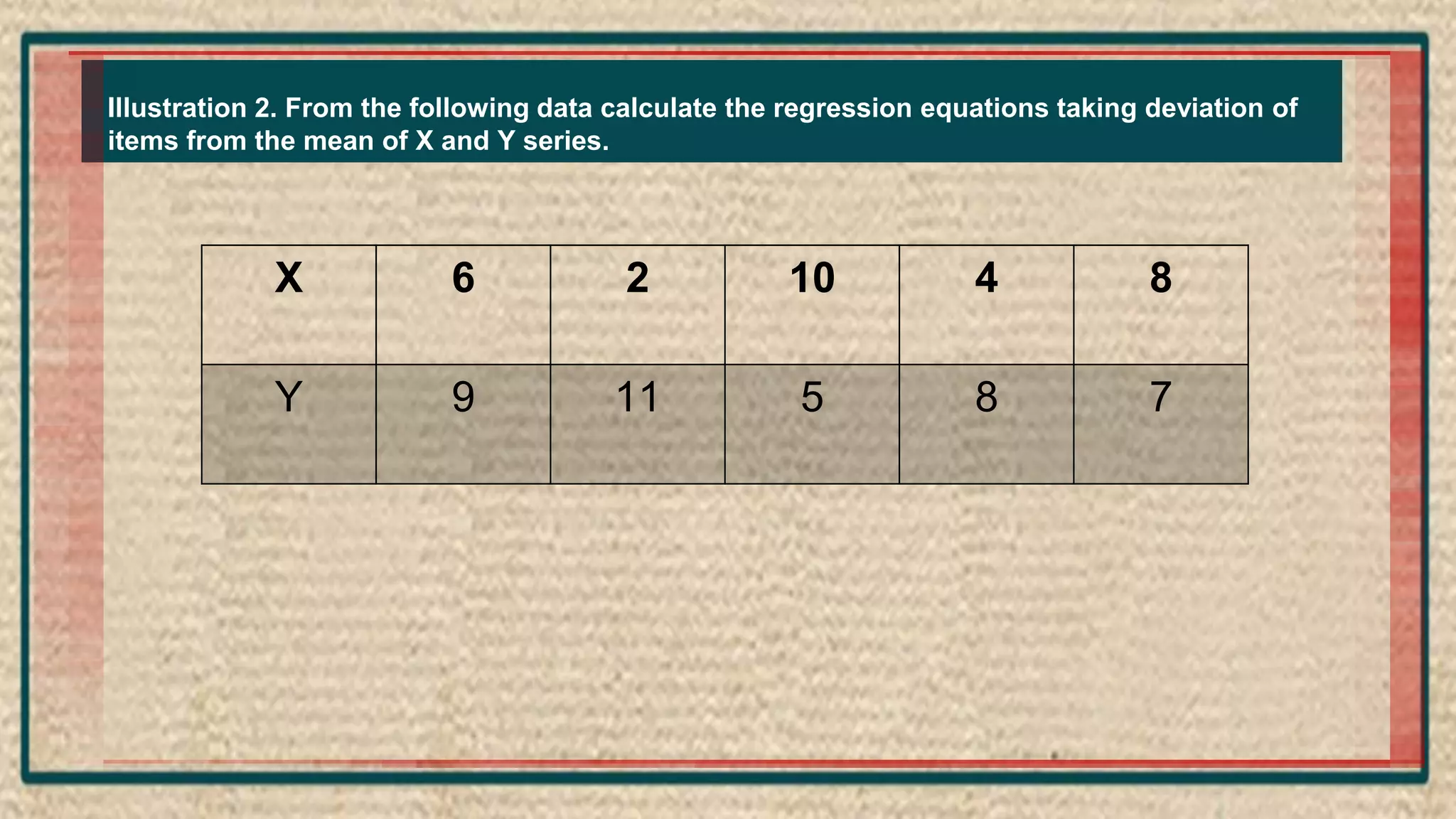
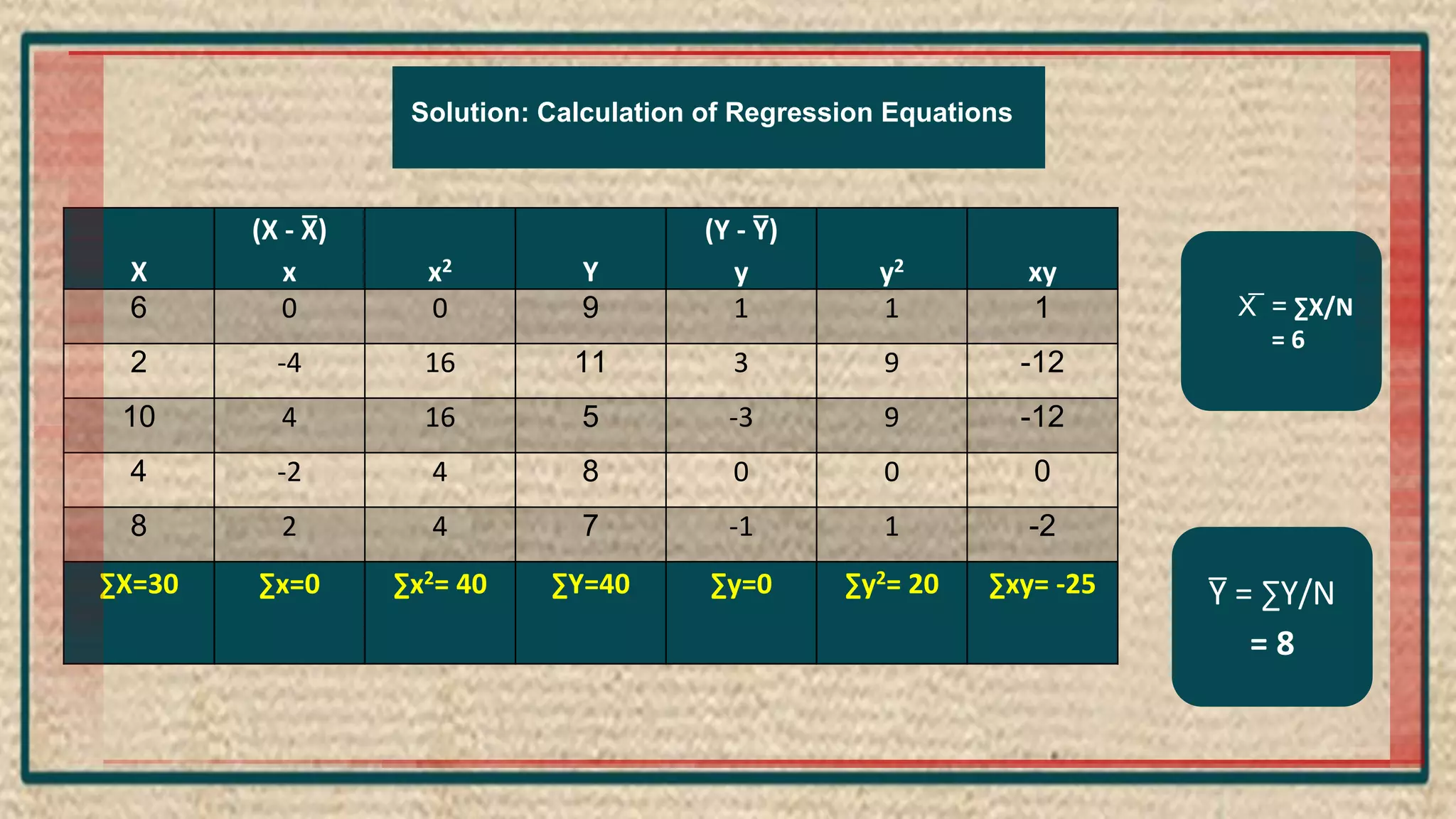
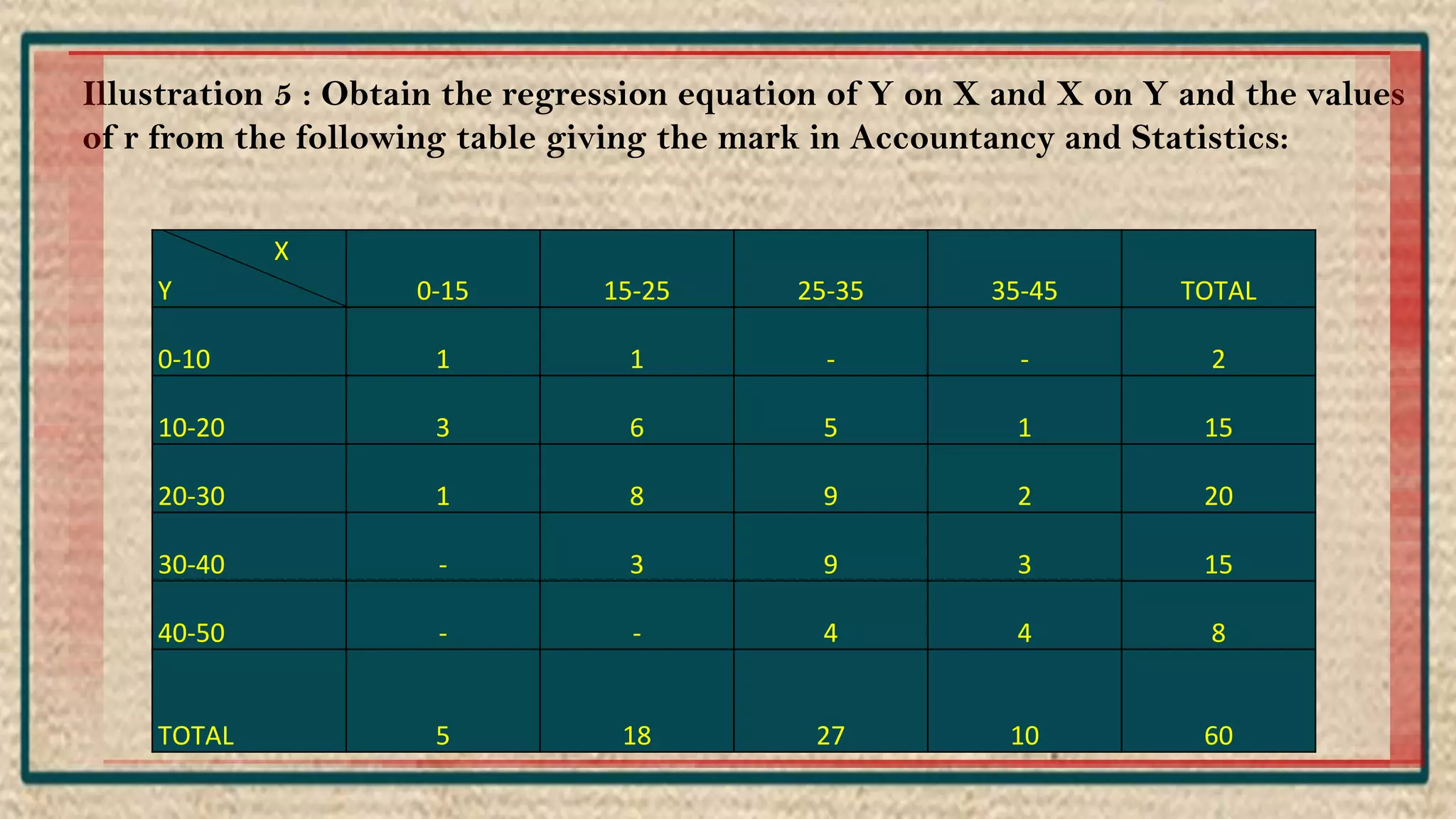
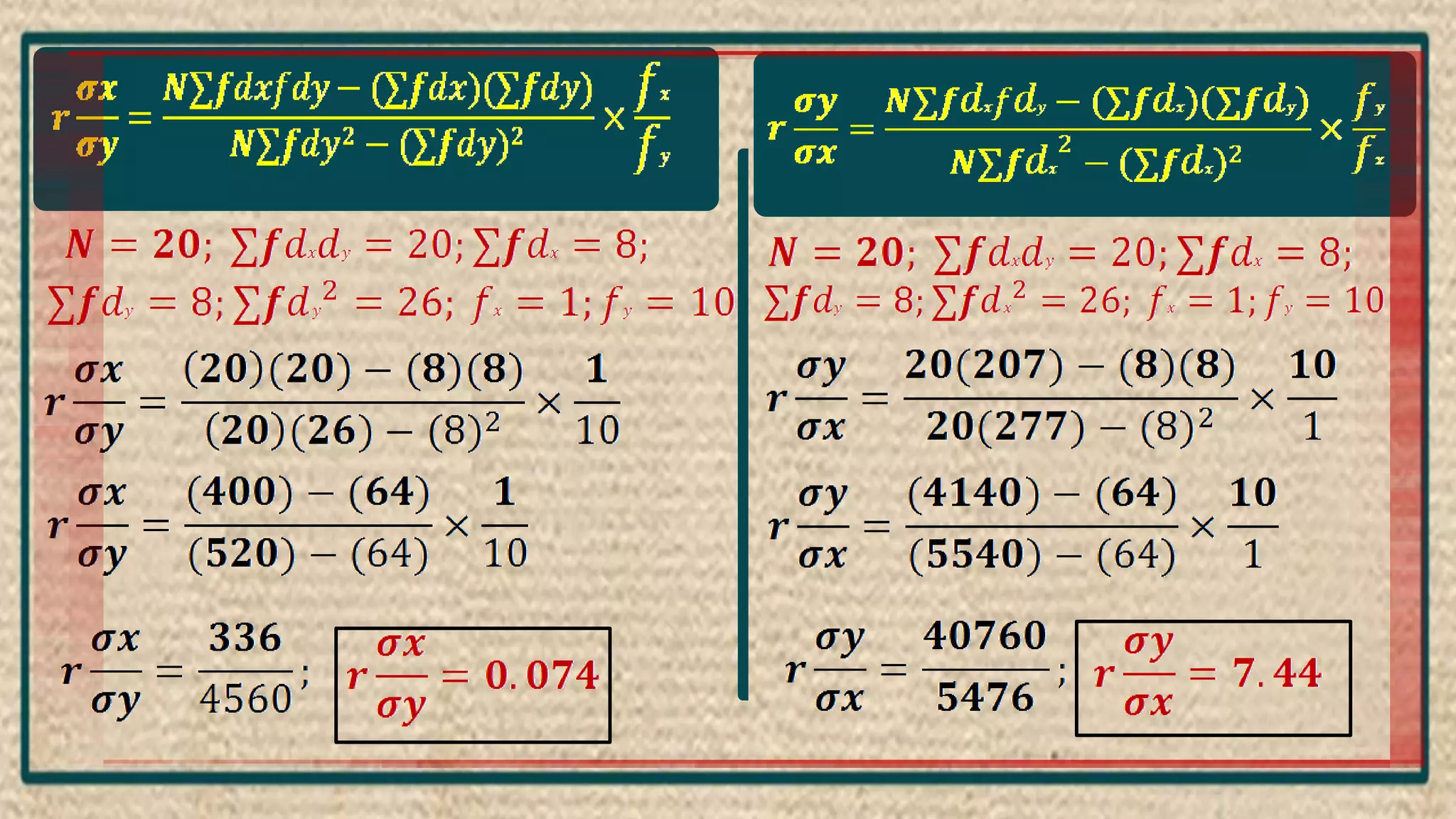
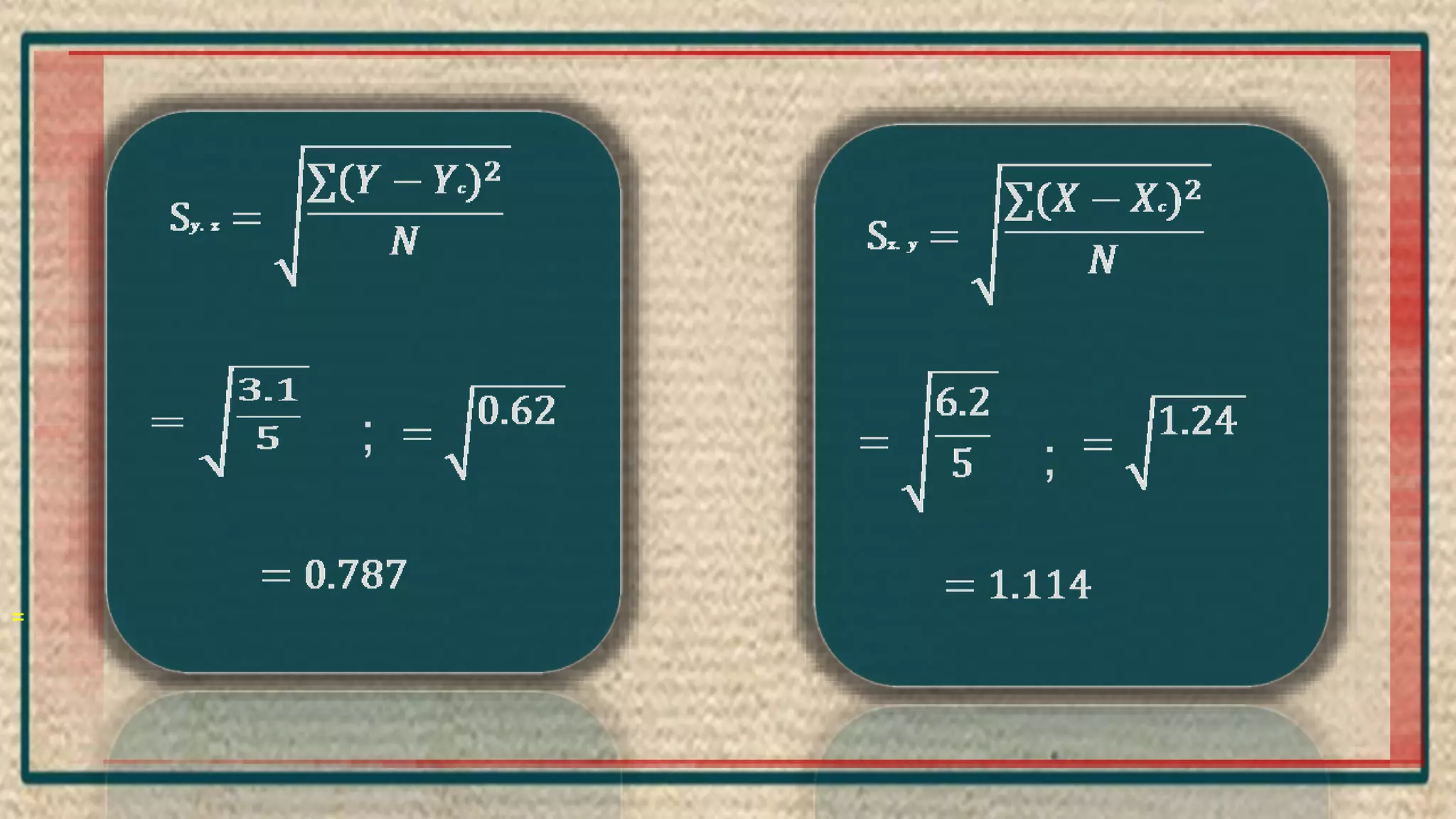
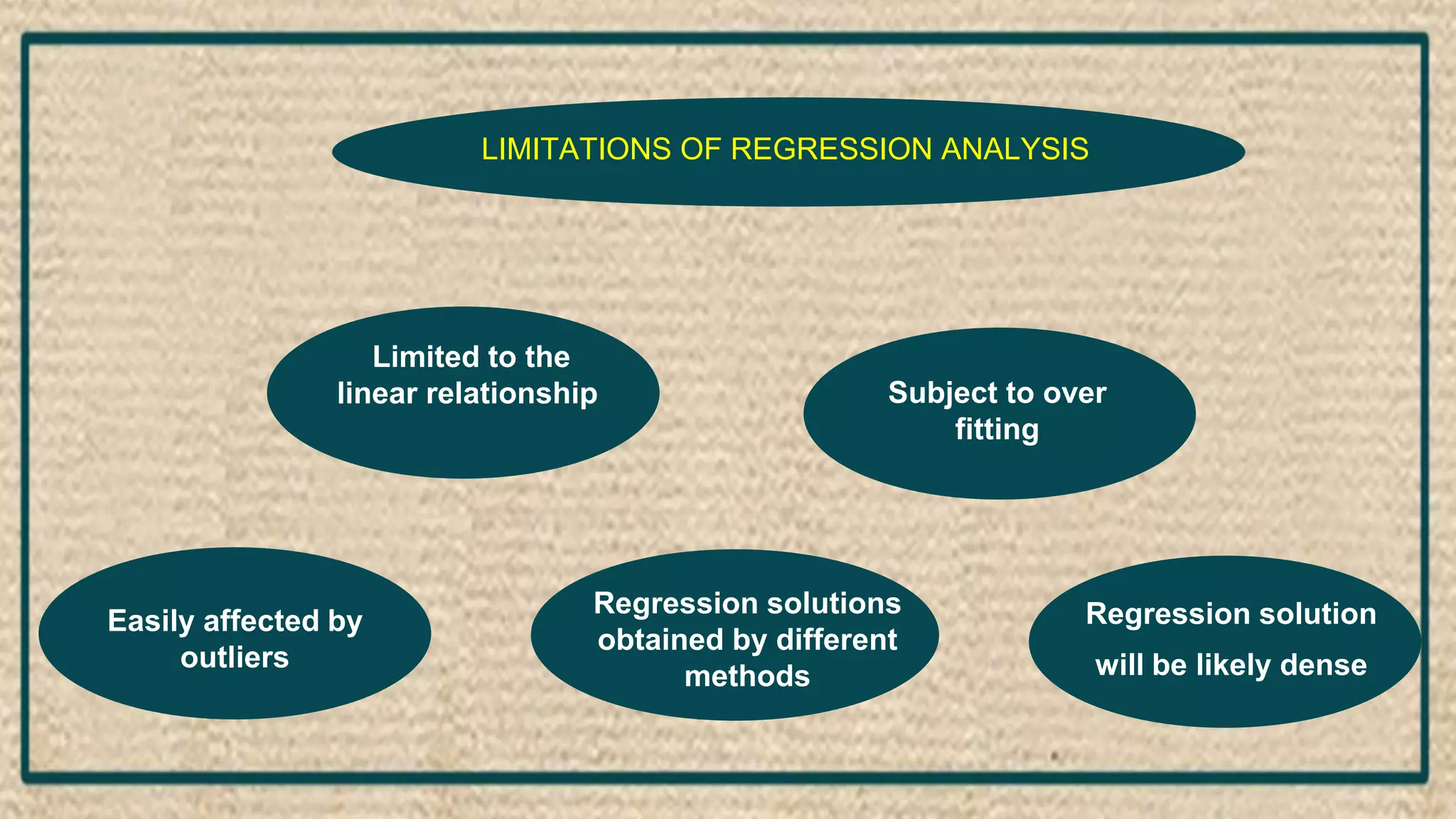
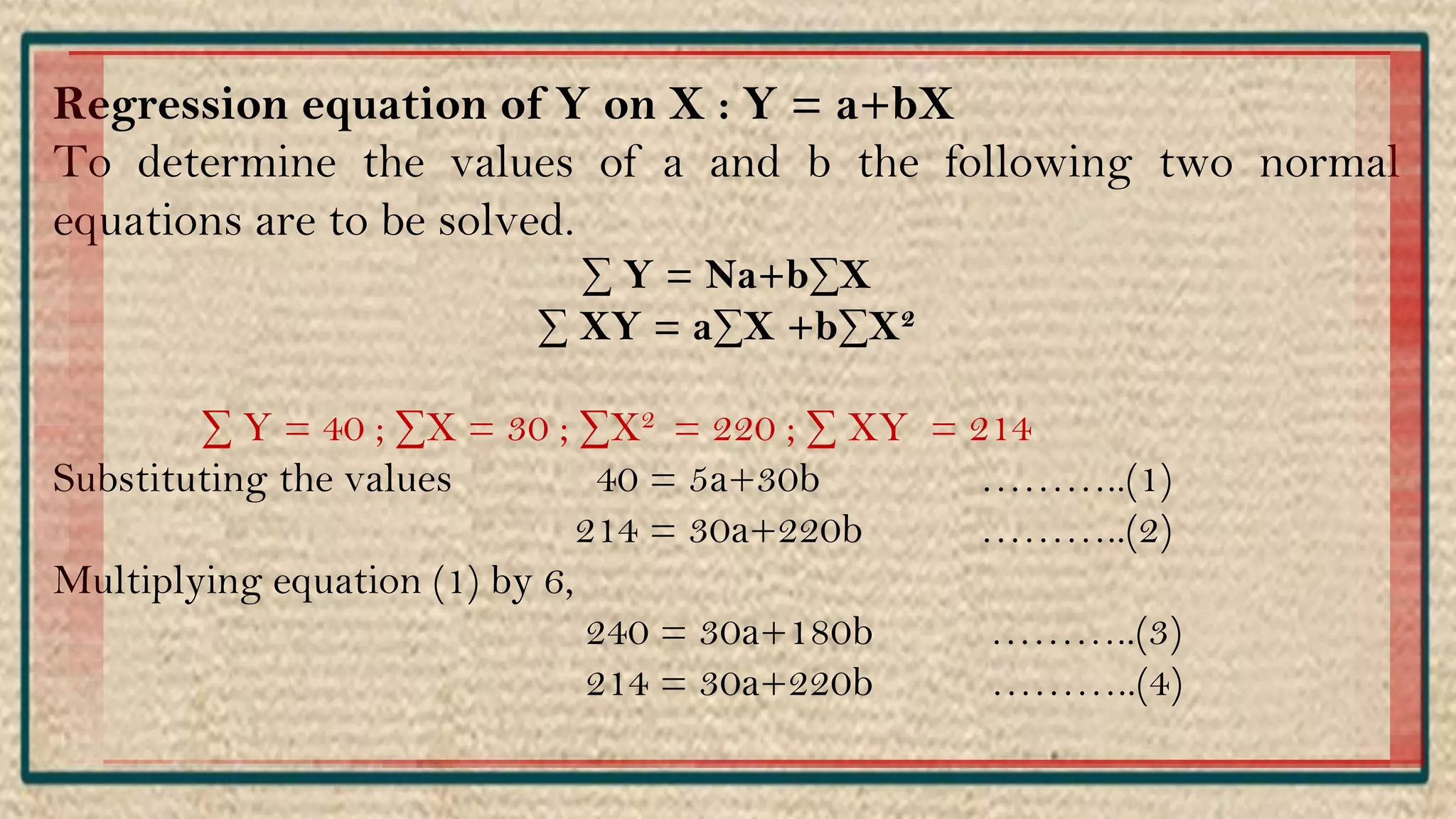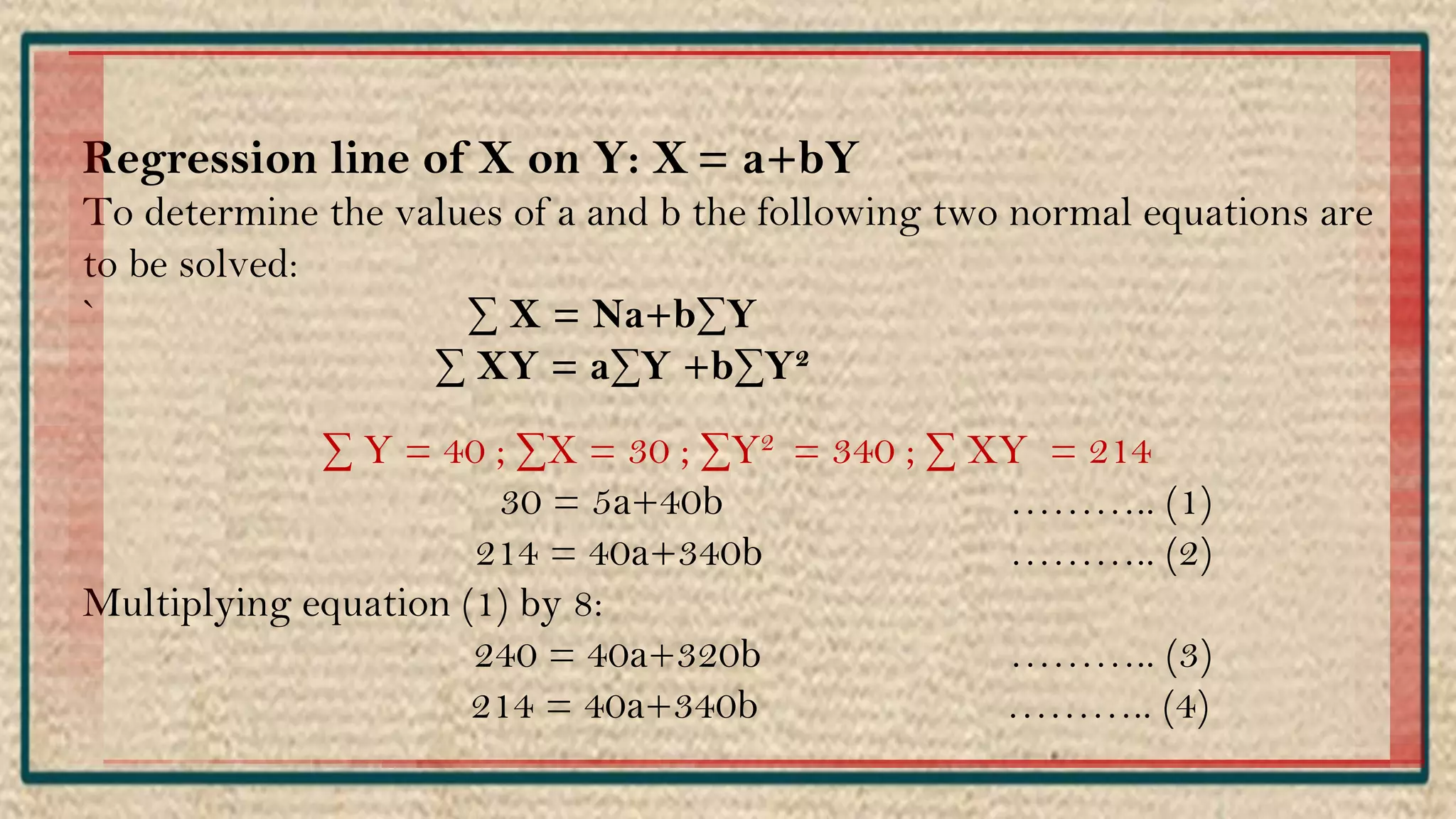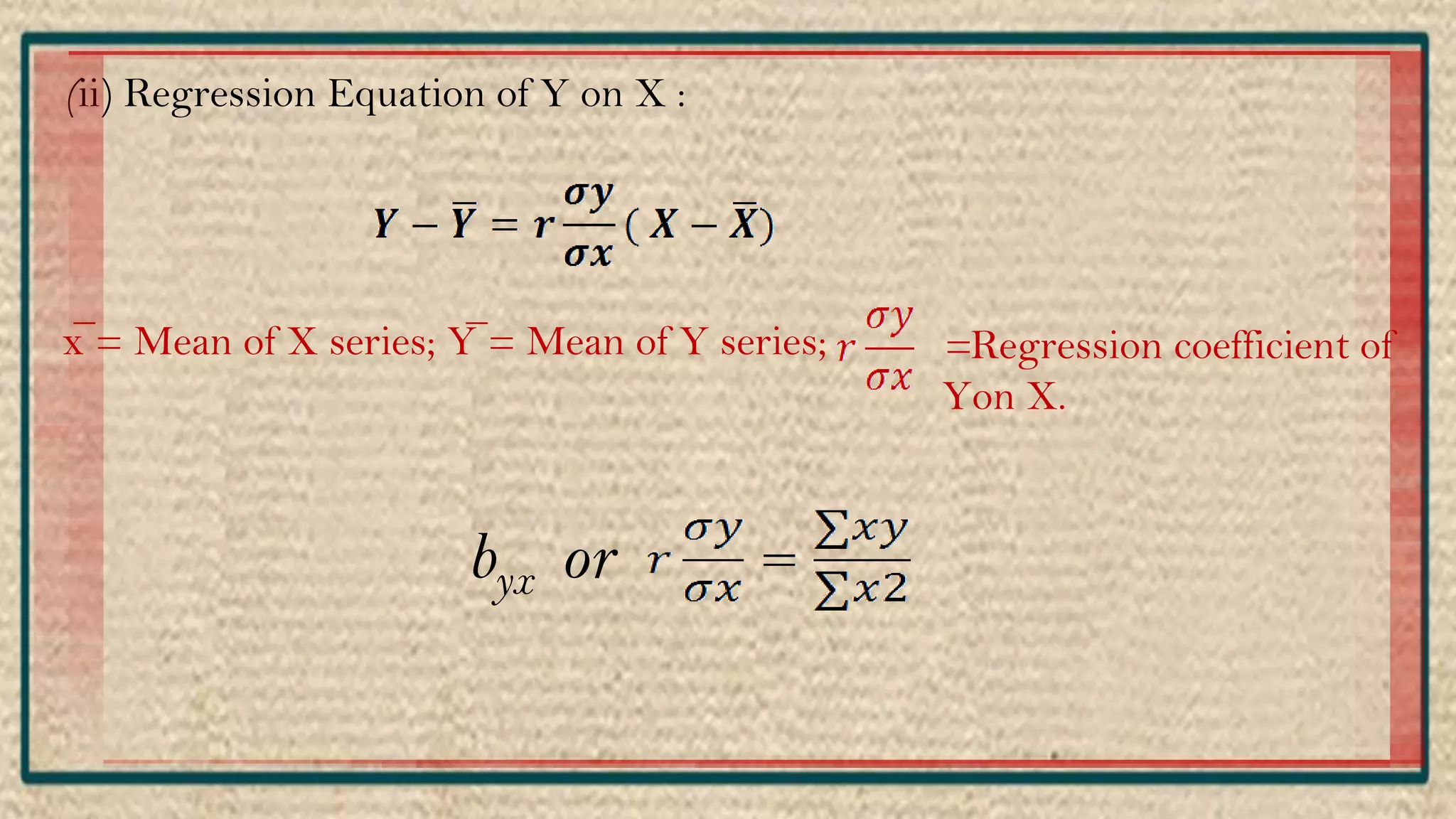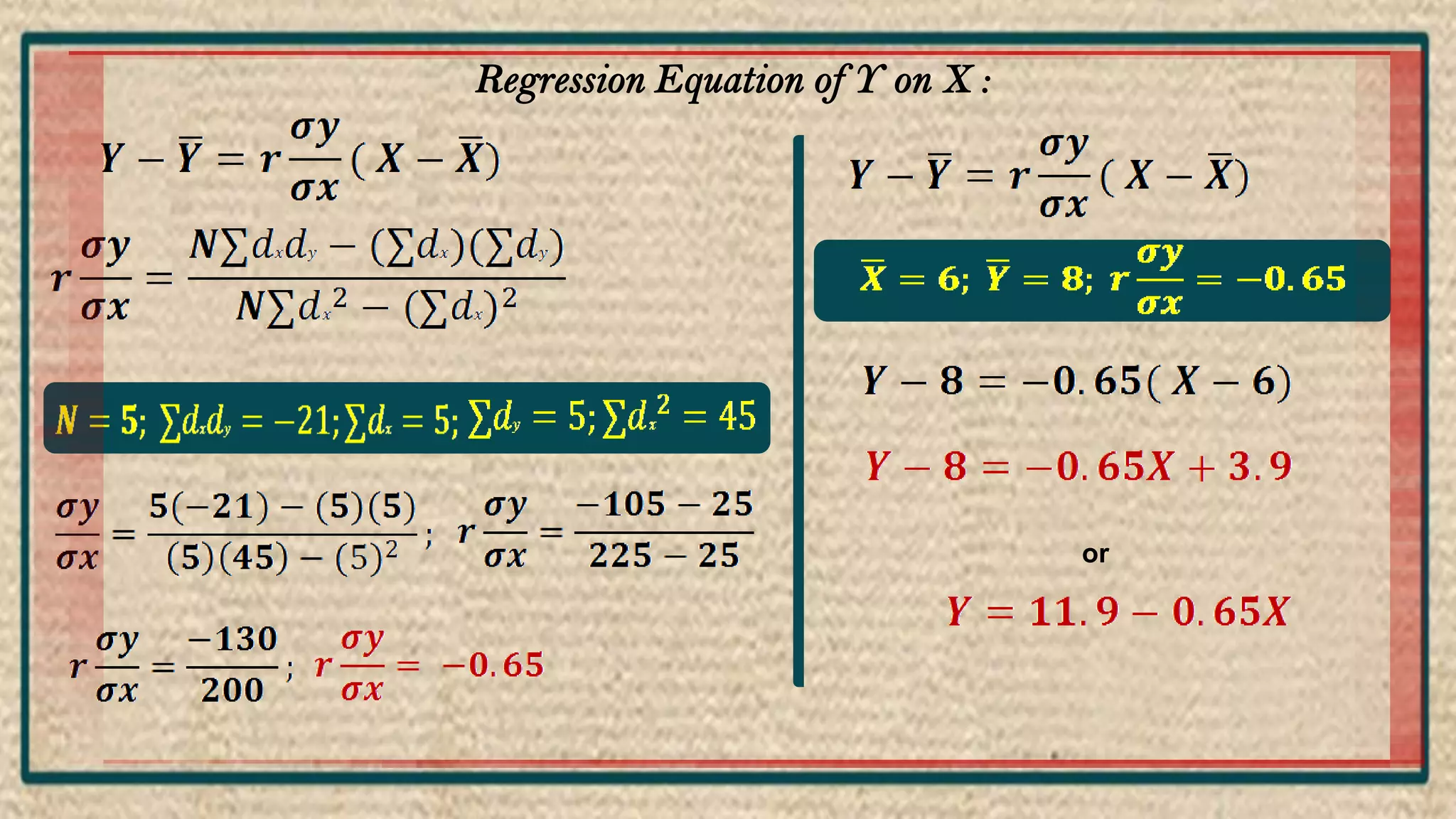The document discusses regression analysis, including definitions, uses, calculating regression equations from data, graphing regression lines, the standard error of estimate, and limitations. Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to understand the relationship between variables and allow for predictions. The document provides examples of calculating regression equations from various data sets and determining the standard error of estimate.