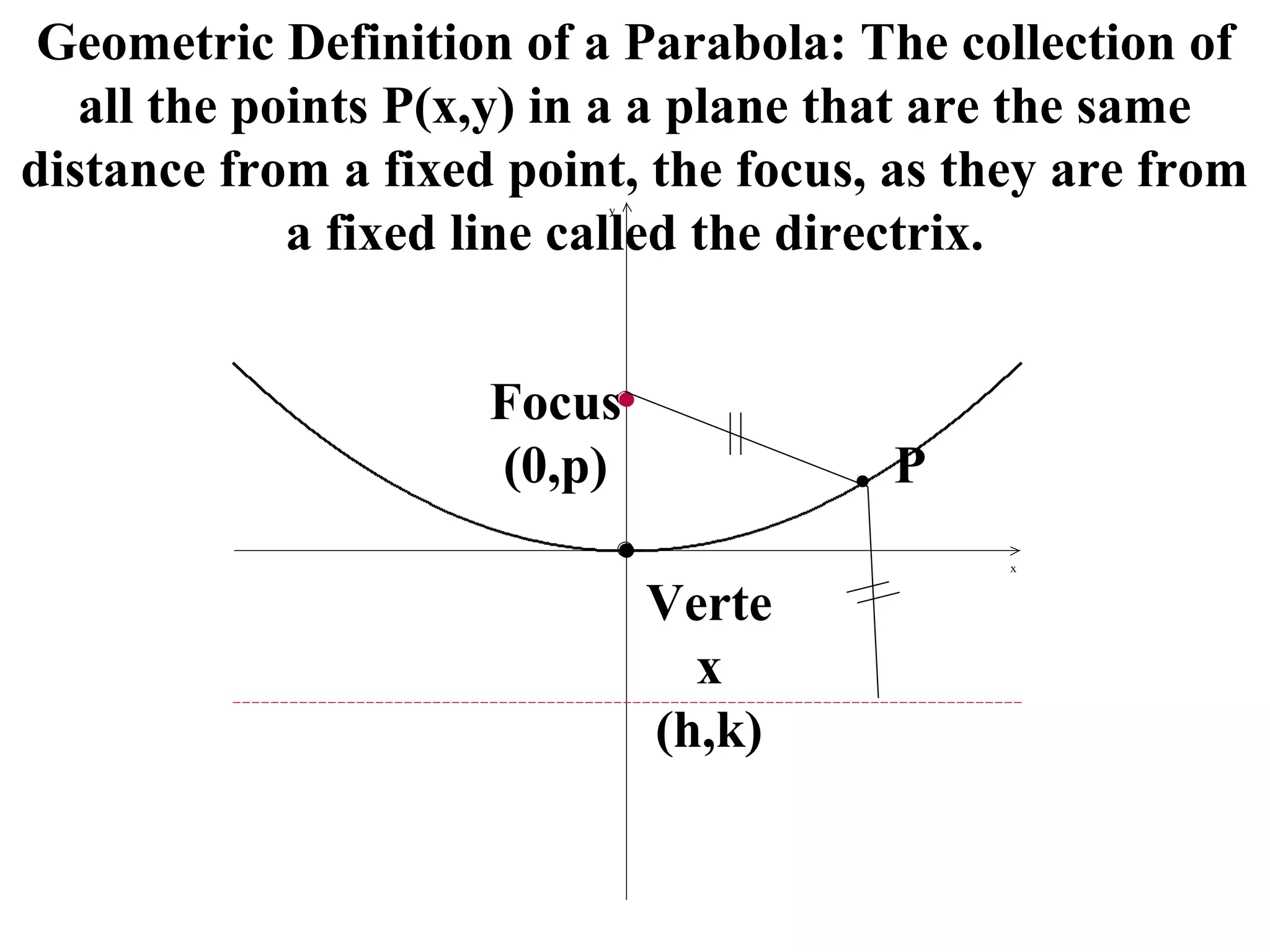
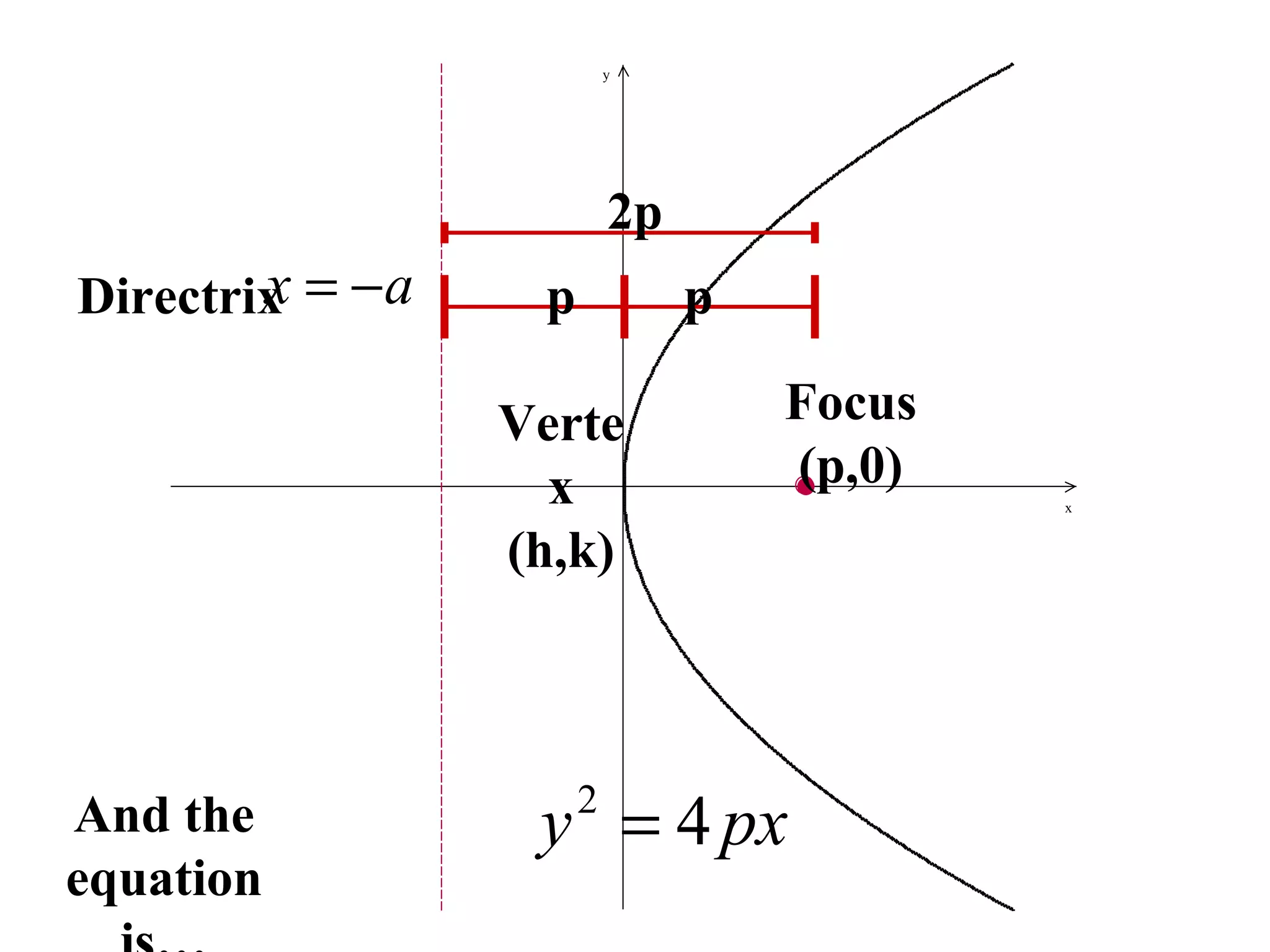
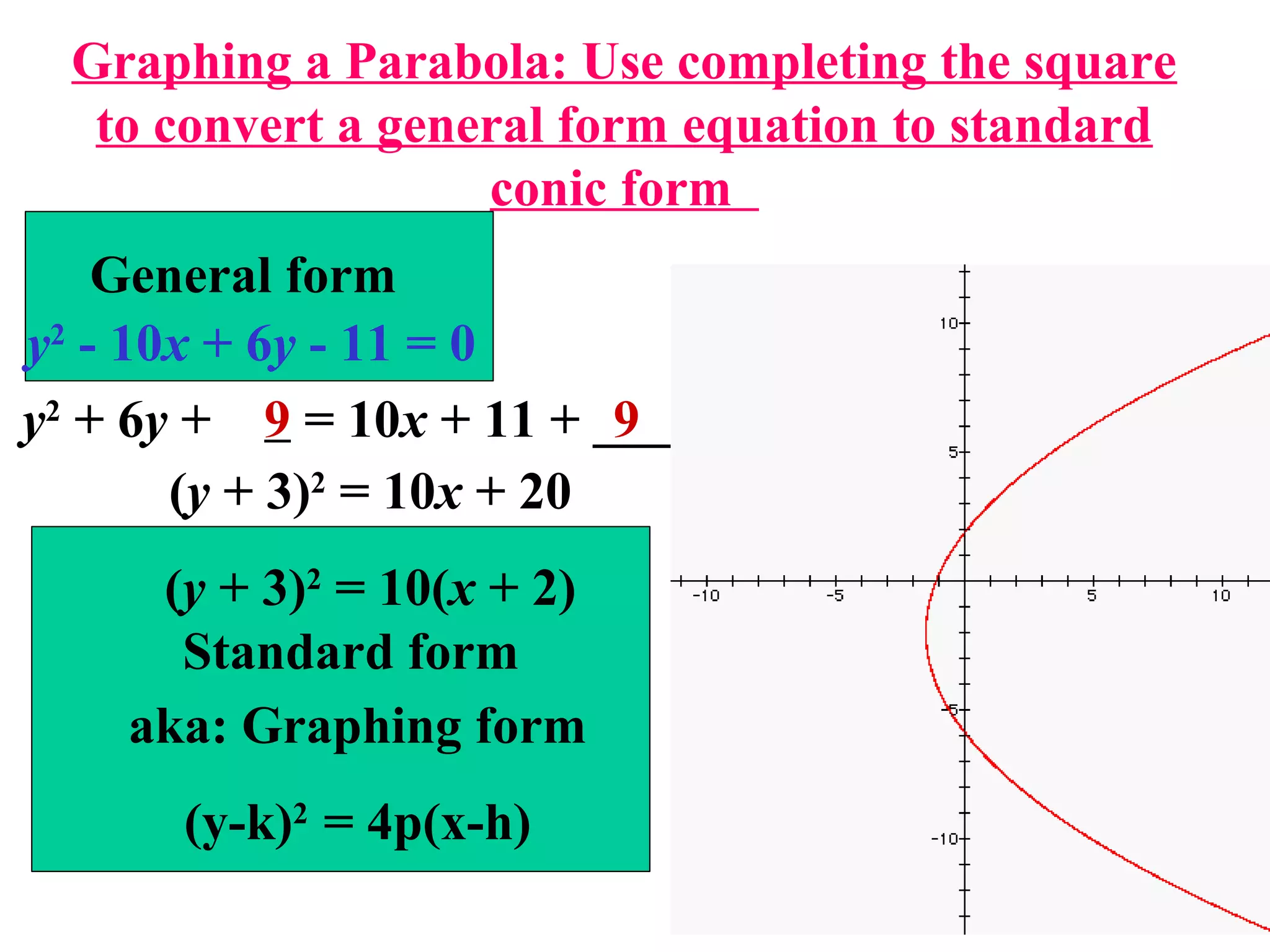
The document defines a parabola geometrically as the set of all points in a plane that are the same distance from a fixed point, called the focus, as they are from a fixed line, called the directrix. It provides examples of parabolas in standard form with the vertex at various points and opening in different directions. It also discusses how to write the standard form equation of a parabola given its focus and vertex, as well as how to find the focus and directrix of a parabola given its equation. Finally, it demonstrates how to use the method of completing the square to convert a general quadratic equation into the standard form needed for graphing a parabola.