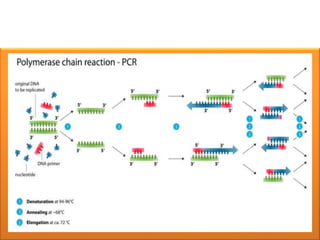
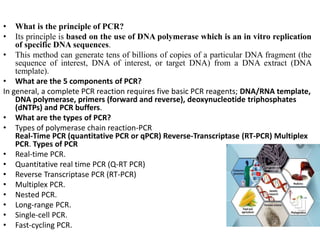
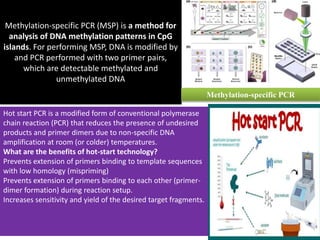
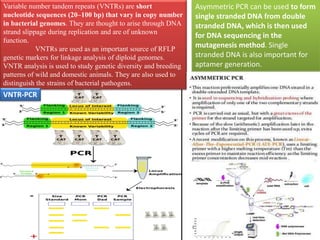
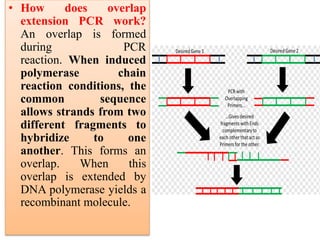
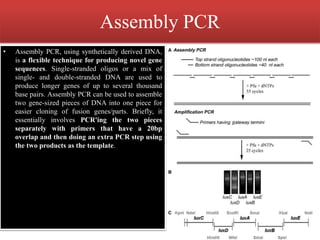
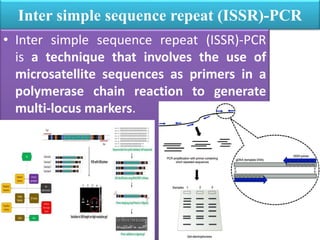
PCR is a technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences. It involves using DNA polymerase to replicate target DNA sequences across multiple temperature cycles. Key points:
1. PCR amplifies specific DNA segments through repeated cycles of heating and cooling. This allows millions of copies of the target DNA to be generated.
2. It was invented by Kary Mullis in 1983 and revolutionized molecular biology. Mullis shared the 1993 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his invention.
3. PCR has many applications including pathogen detection, genetic testing, forensics, and molecular cloning. It is a core technique in molecular biology and genetics research.