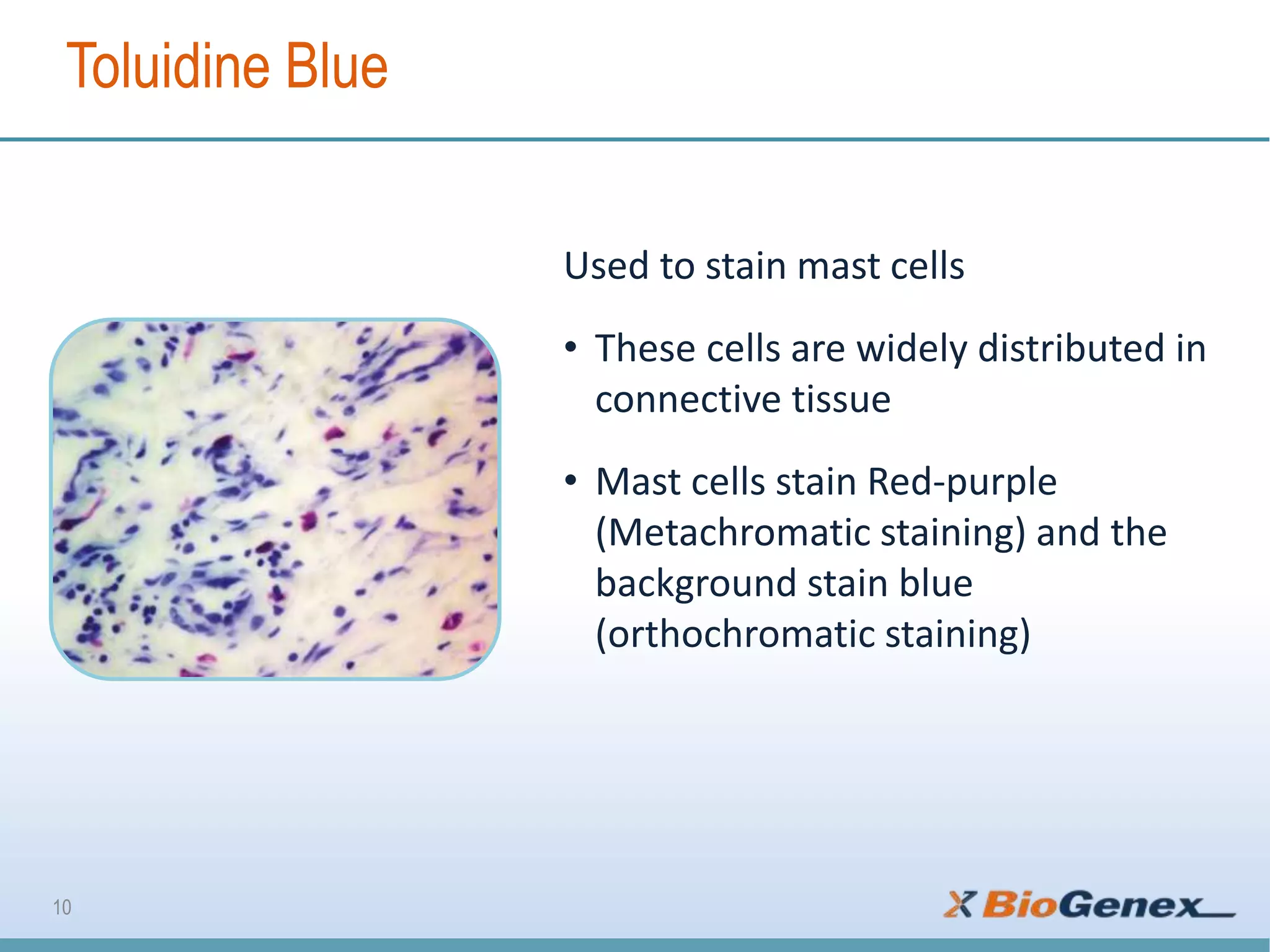
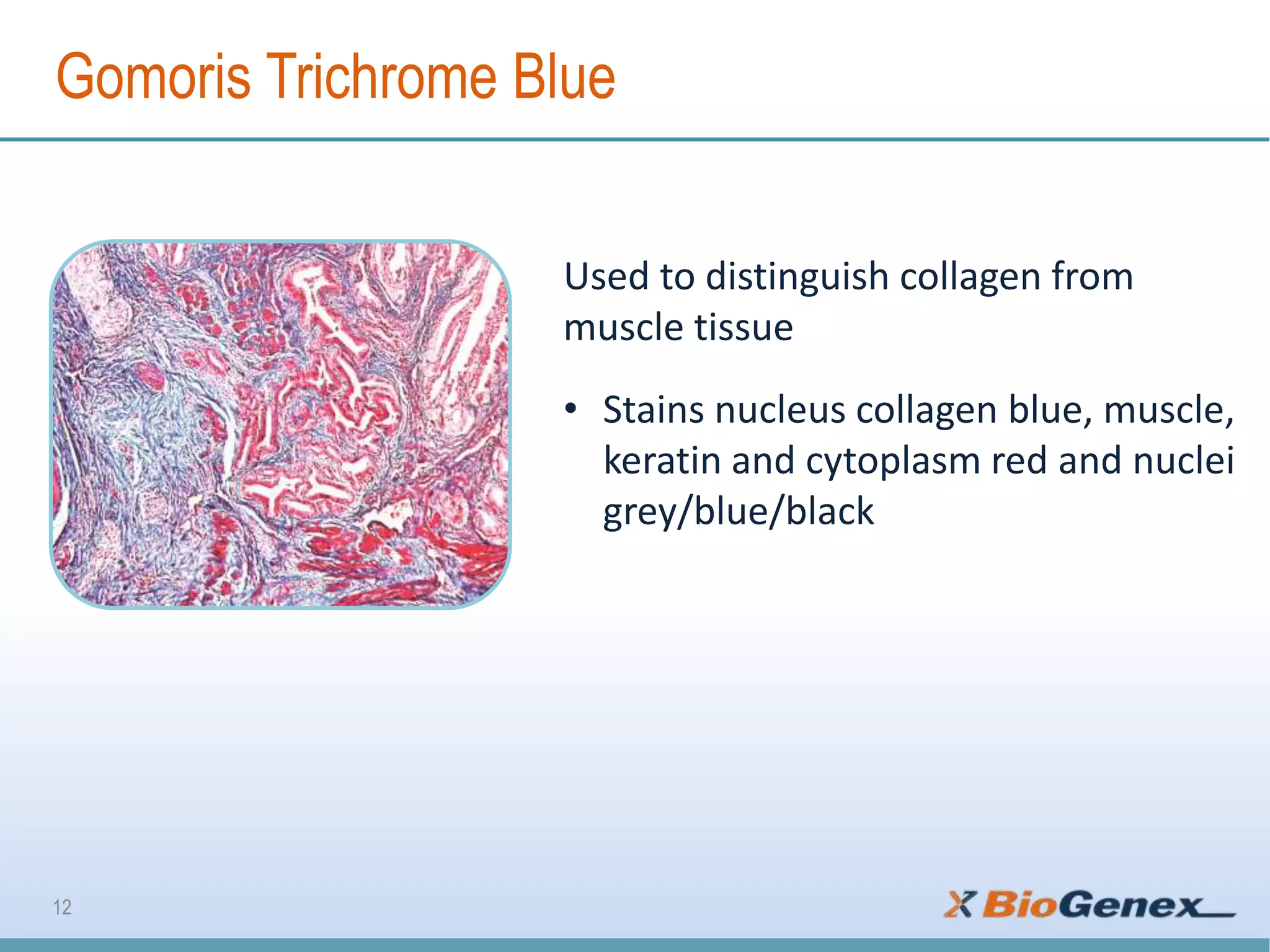
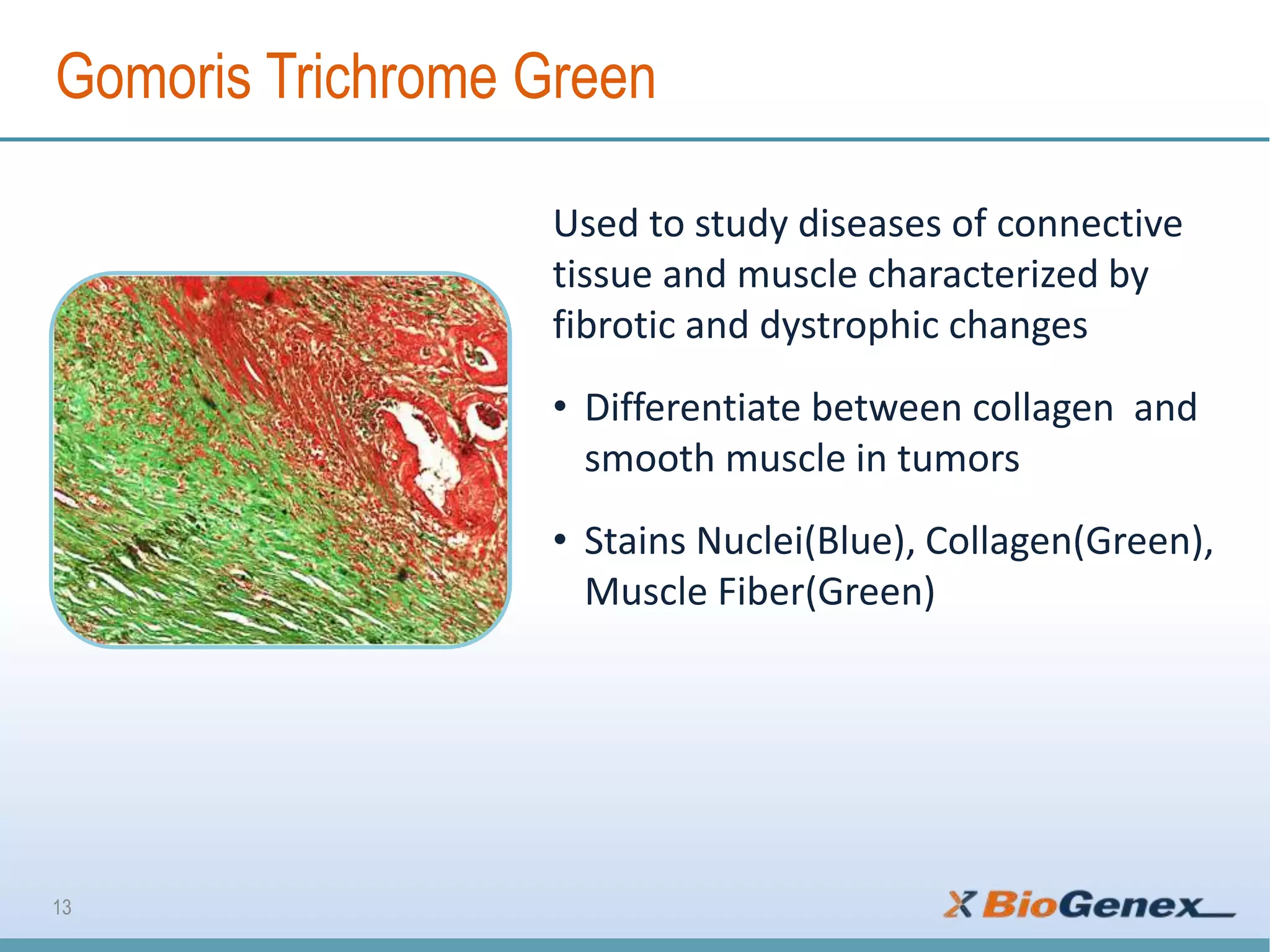
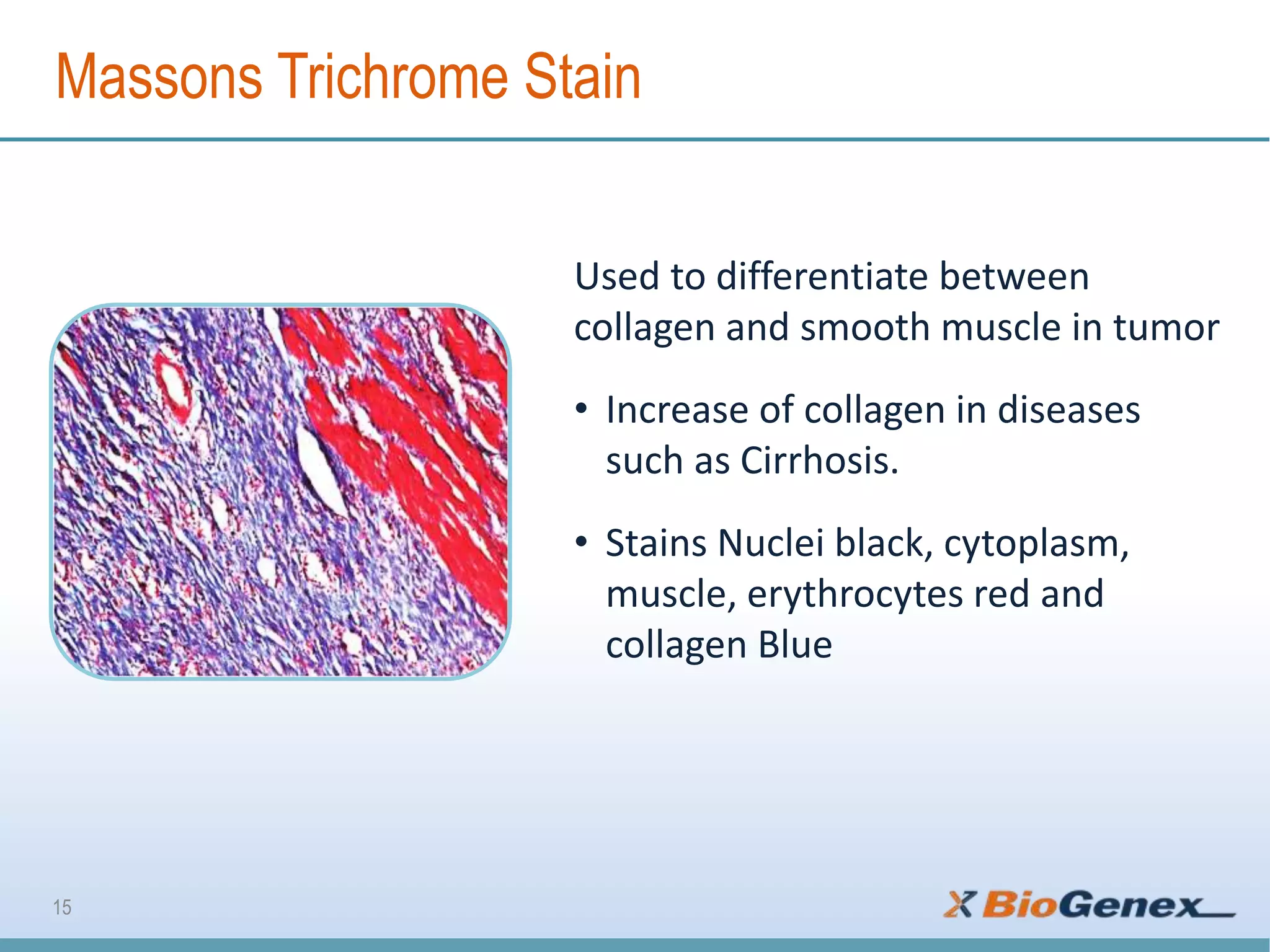
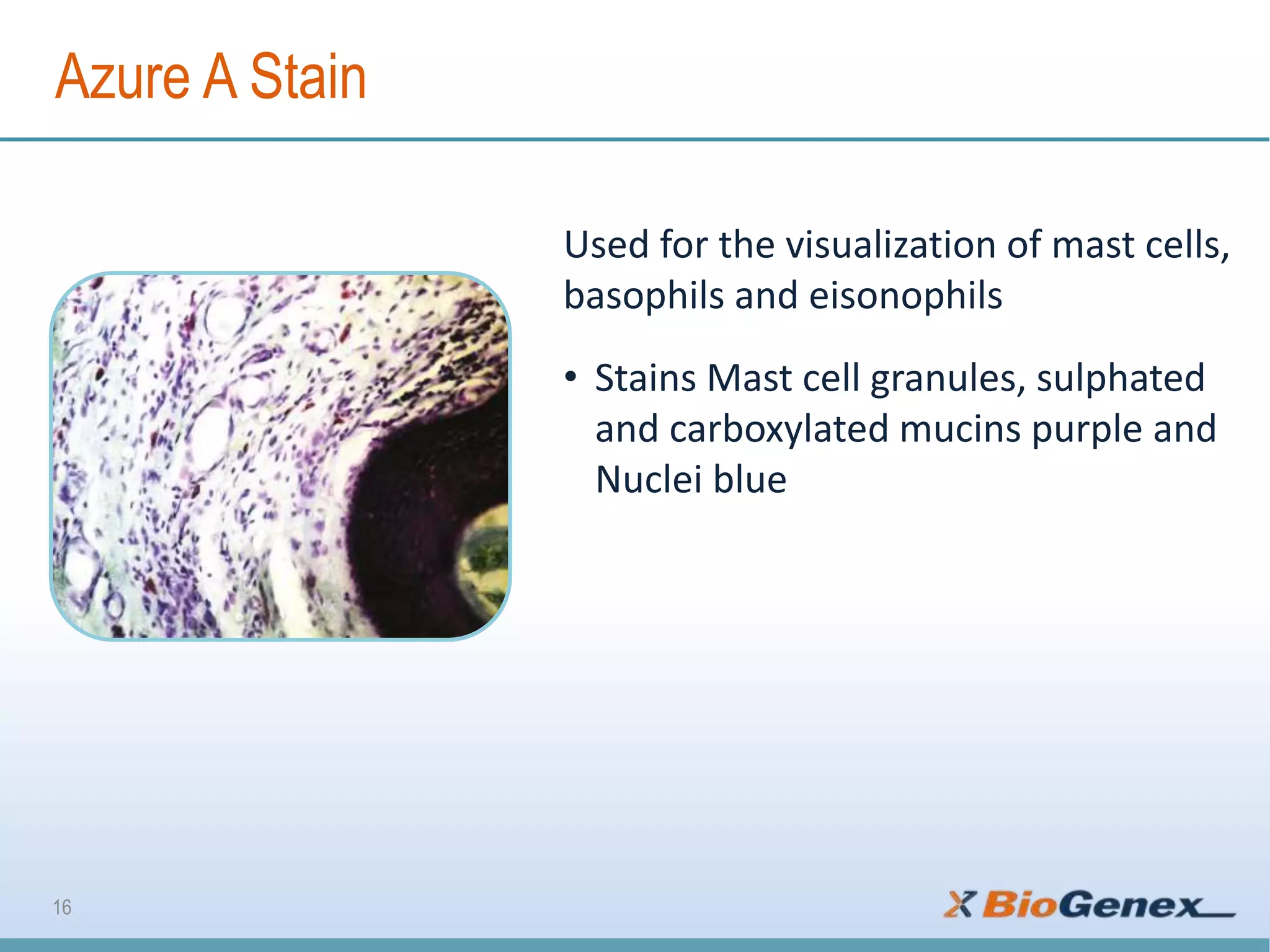
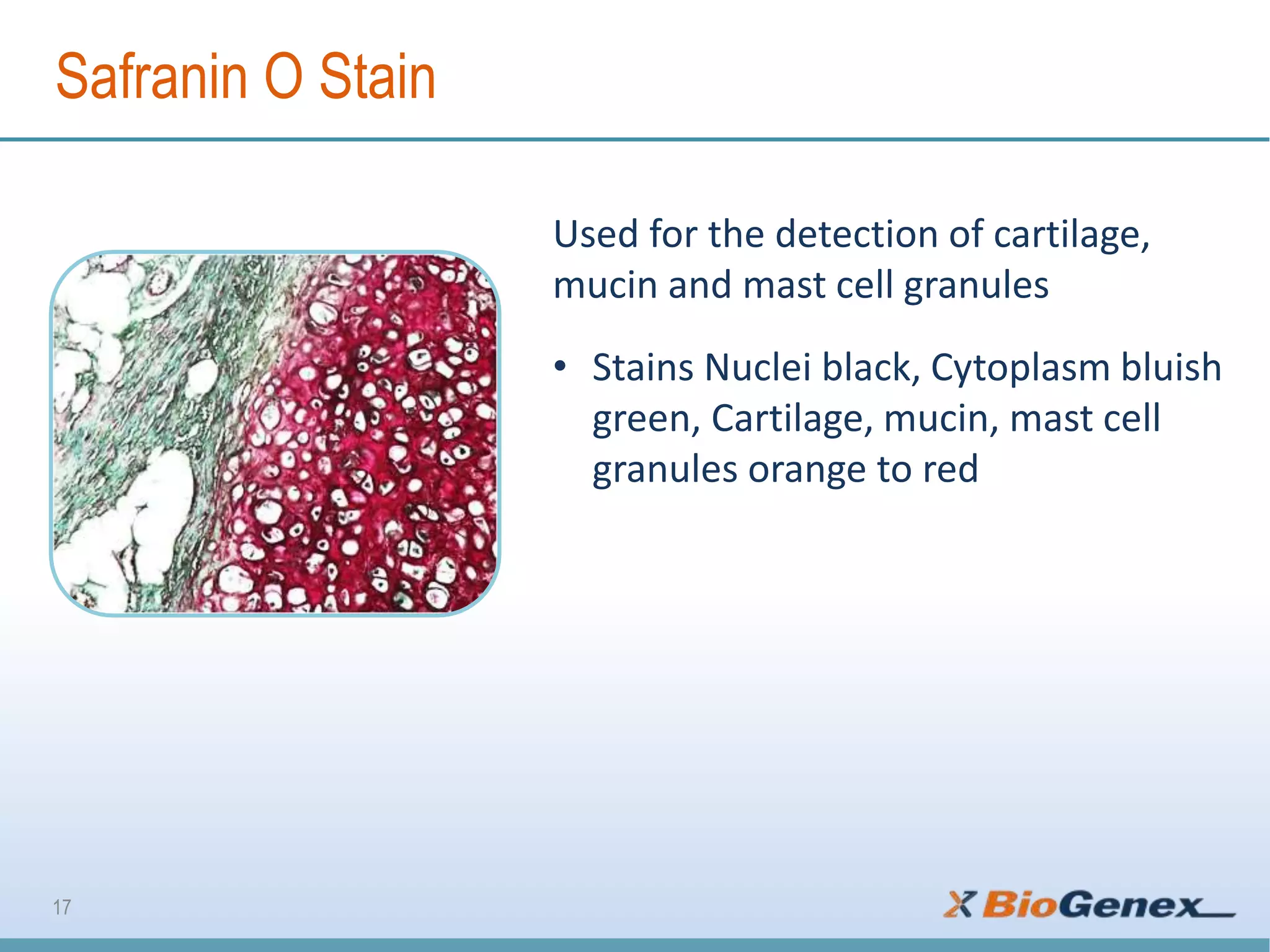
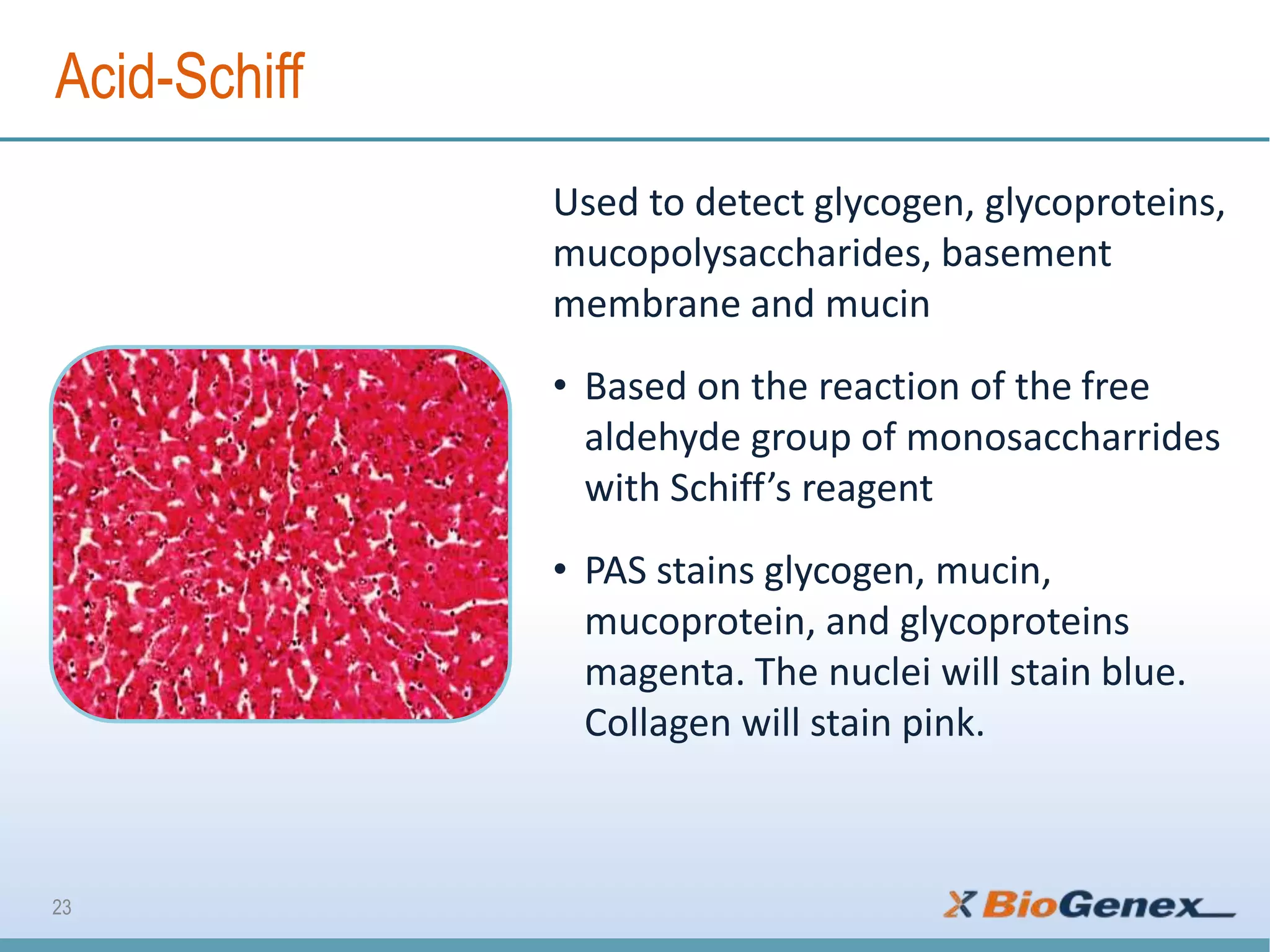
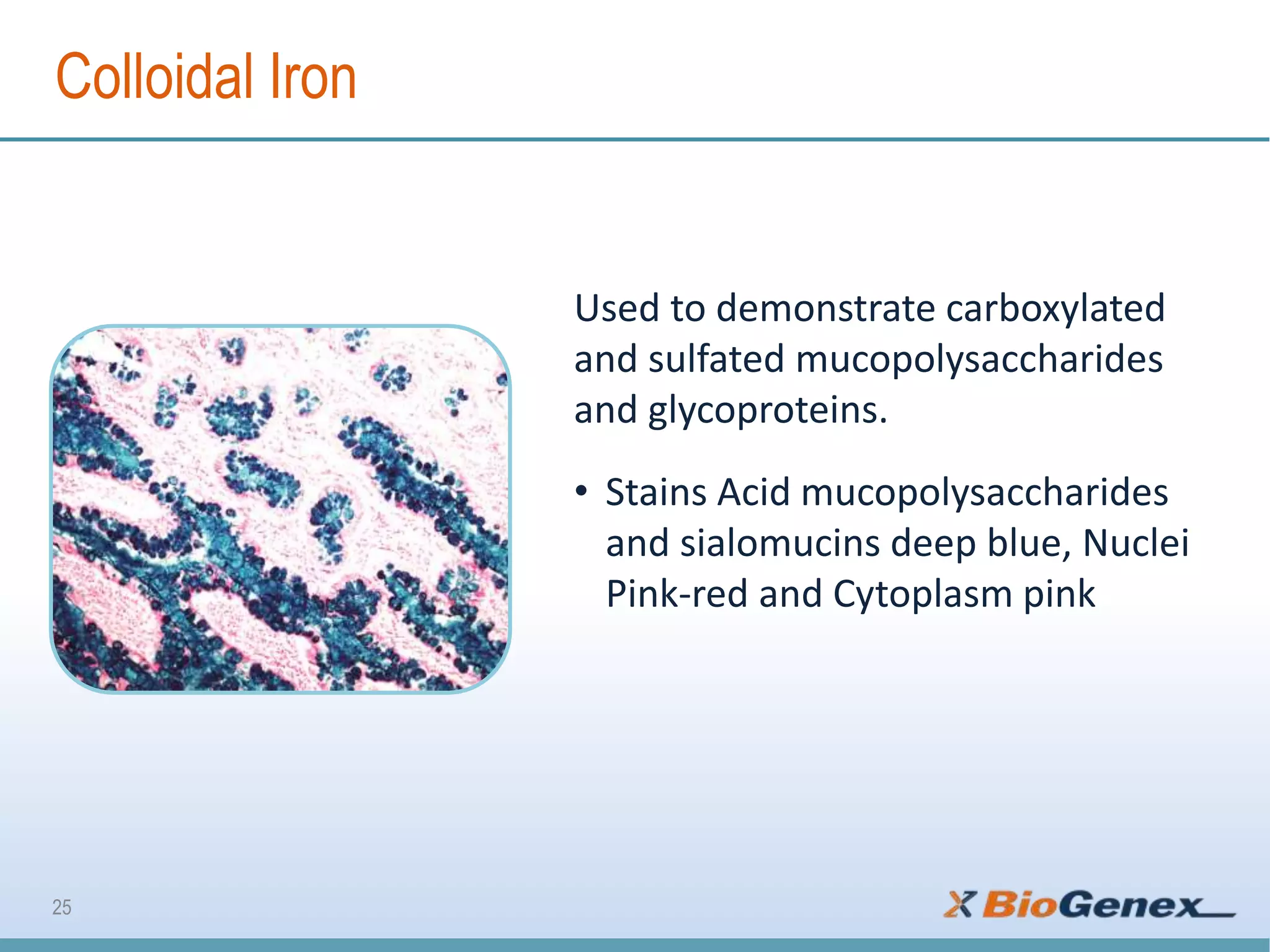
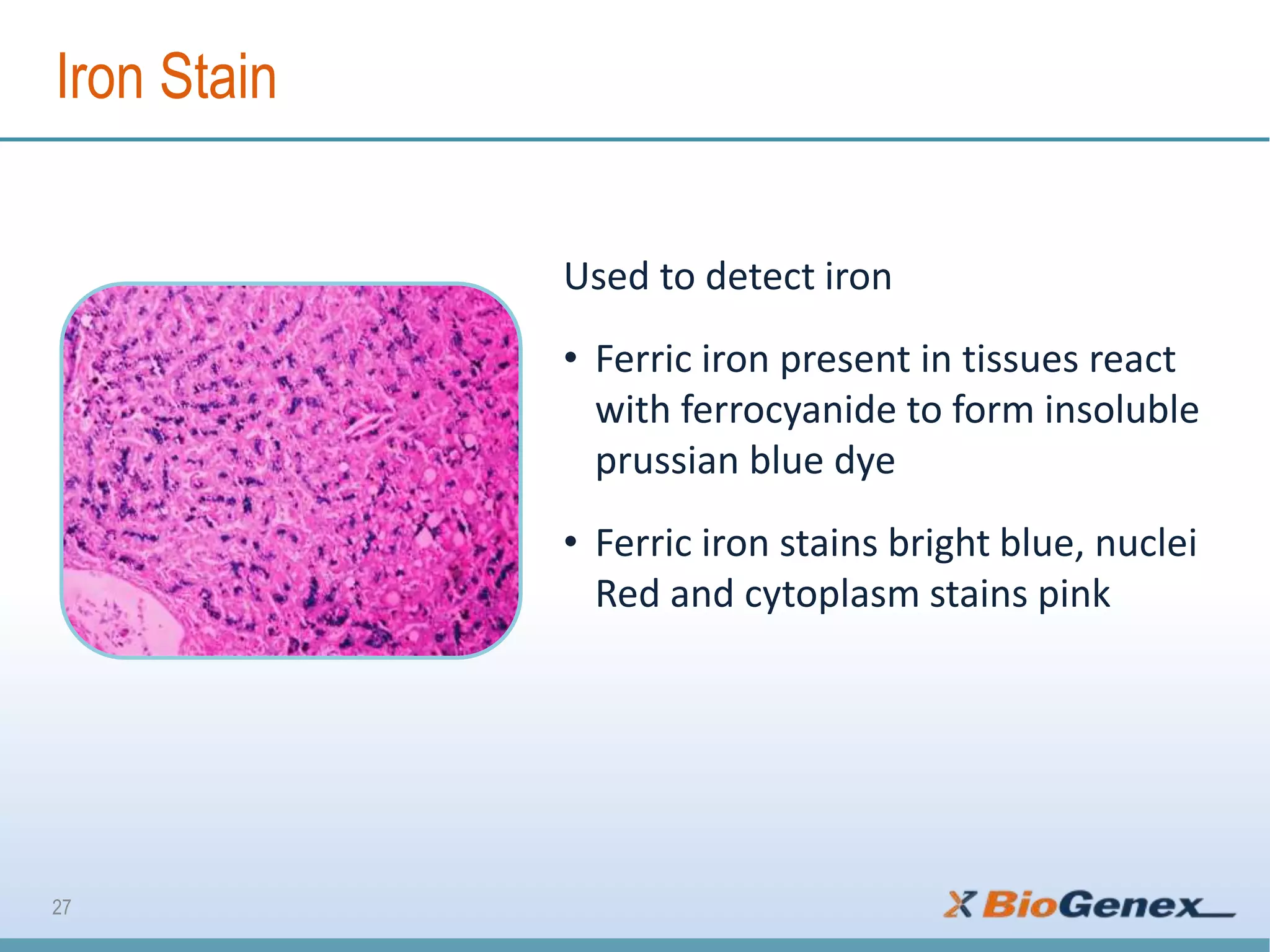
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various special stains used in histology for the detection of different biological components such as microorganisms, connective tissues, carbohydrates, and minerals. It describes the specific staining techniques, their target substances, and the colors associated with each stain, highlighting their diagnostic significance. Additionally, it mentions the availability of more than 30 different special stains offered by a specific provider.