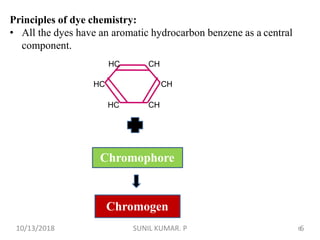
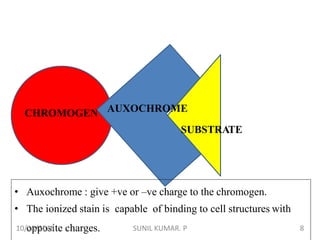
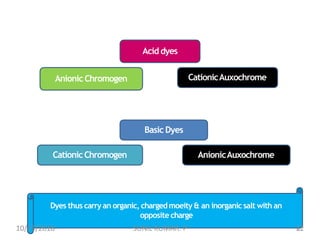
This document discusses hematoxylin and eosin stains. It provides details on:
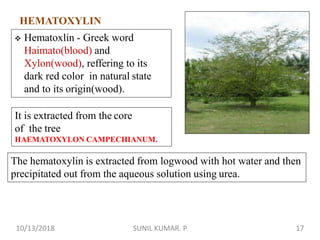
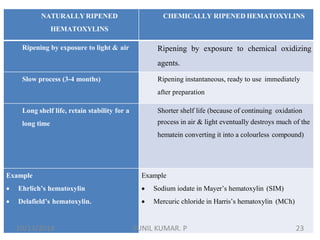
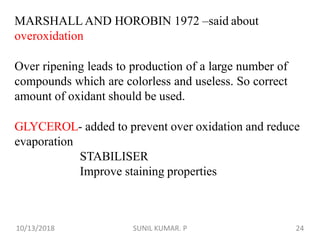
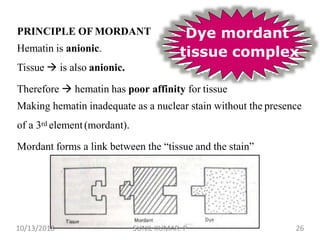
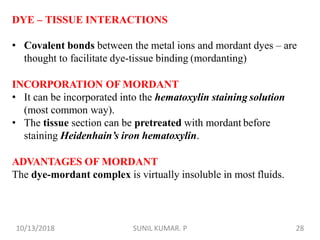
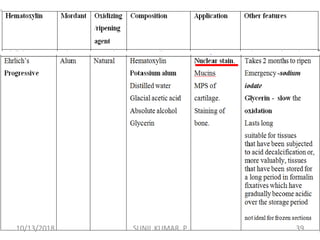
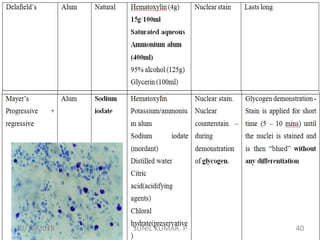
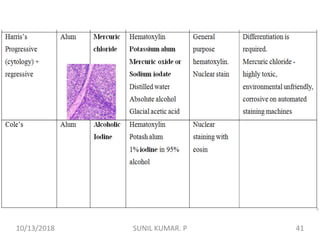
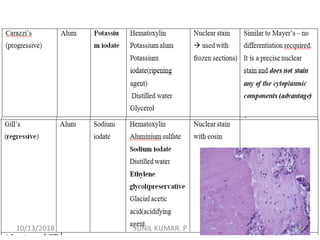
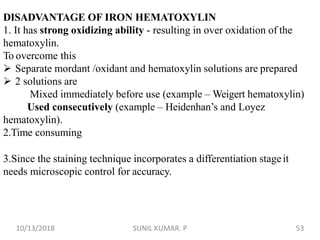
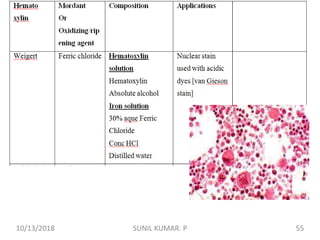
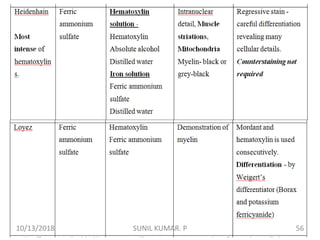
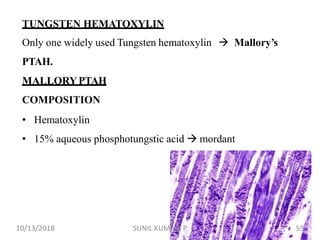
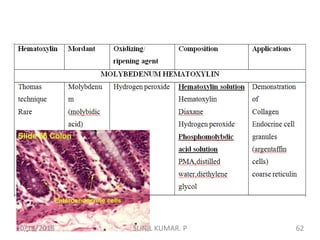
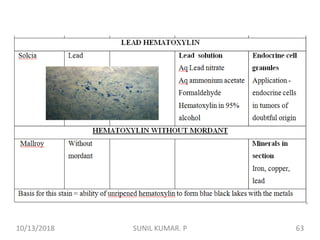
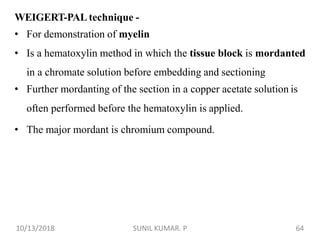
1) Hematoxylin is extracted from logwood and oxidized to hematin, which is responsible for staining properties. It requires a mordant like aluminum or iron salts to bind to tissues.
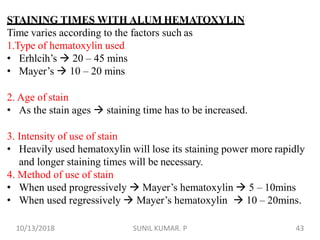
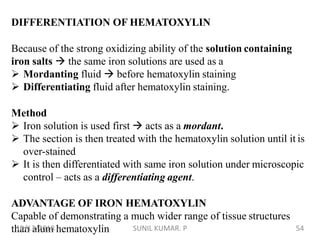
2) Alum hematoxylin is commonly used, with potassium or ammonium alum as the mordant. Sections can be overstained and differentiated, or stained for a predetermined time.
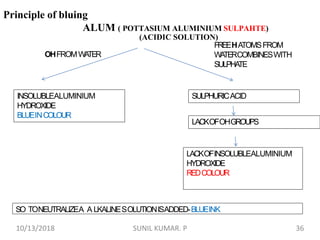
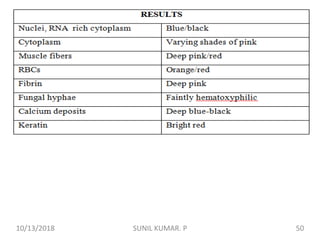
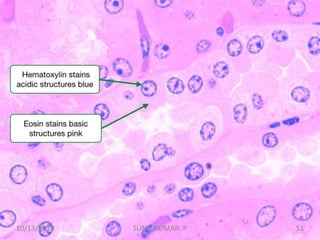
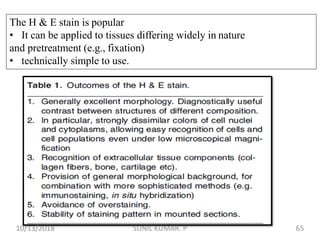
3) After differentiation, sections are "blued" in a weak alkaline solution to convert the hematin stain from red to blue-black in the cell nuclei.