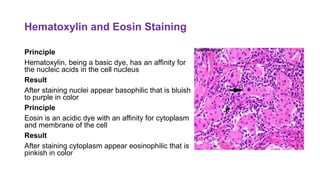
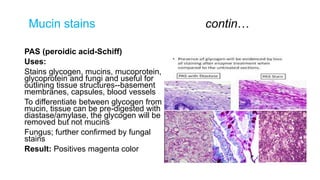
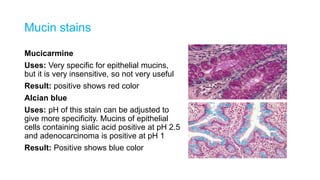
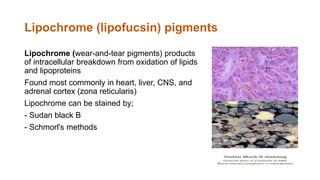
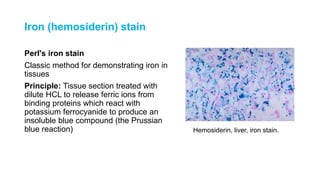
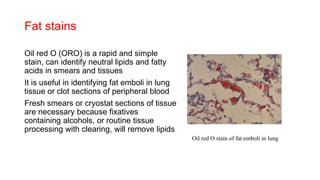
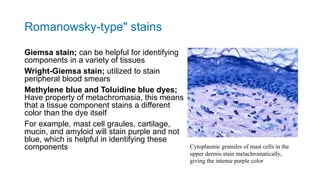
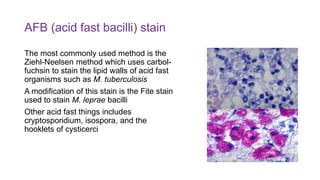
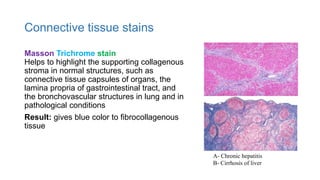
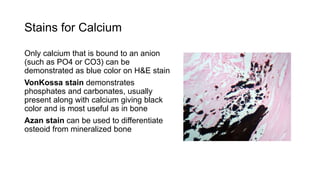
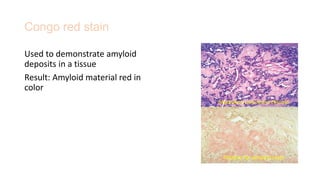
This document discusses various special stains used in pathology and their principles and results. It describes hematoxylin and eosin staining which stains cell nuclei purple and cytoplasm pink. It also discusses mucin stains like PAS, mucicarmine and Alcian blue; melanin, lipochrome, iron, fat, AFB, fungal and connective tissue stains. It provides examples of stained tissues and conditions and includes an assignment with questions.