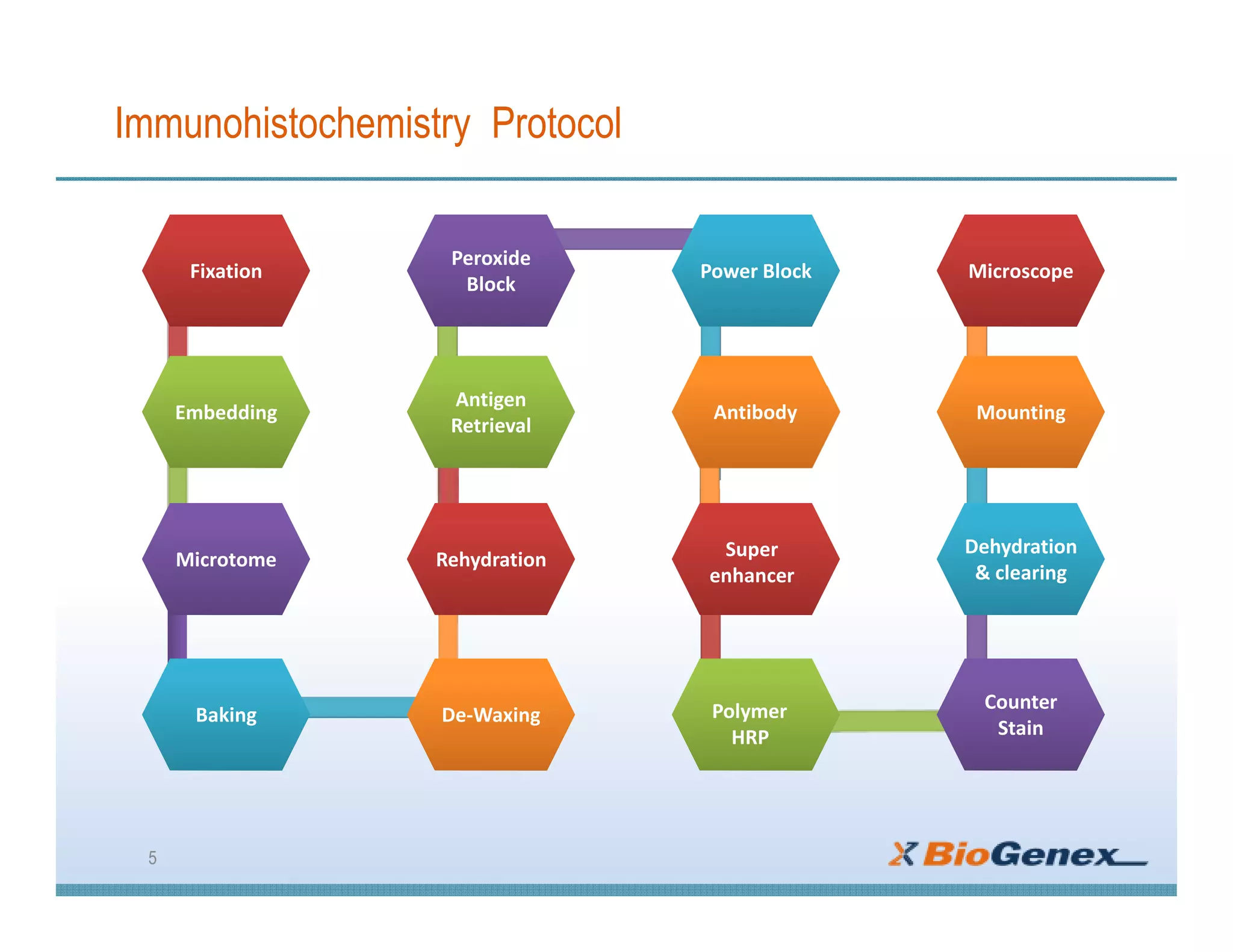
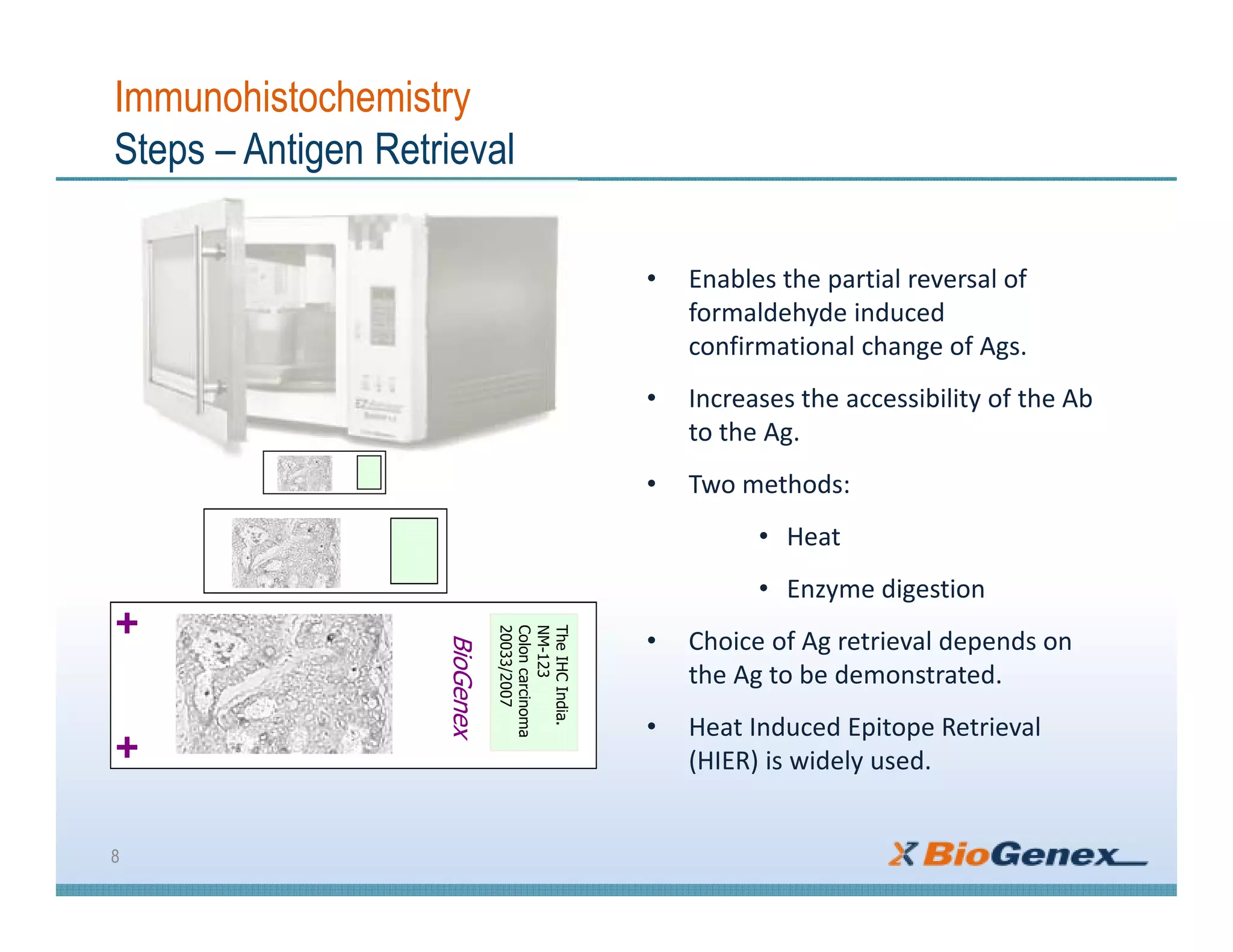
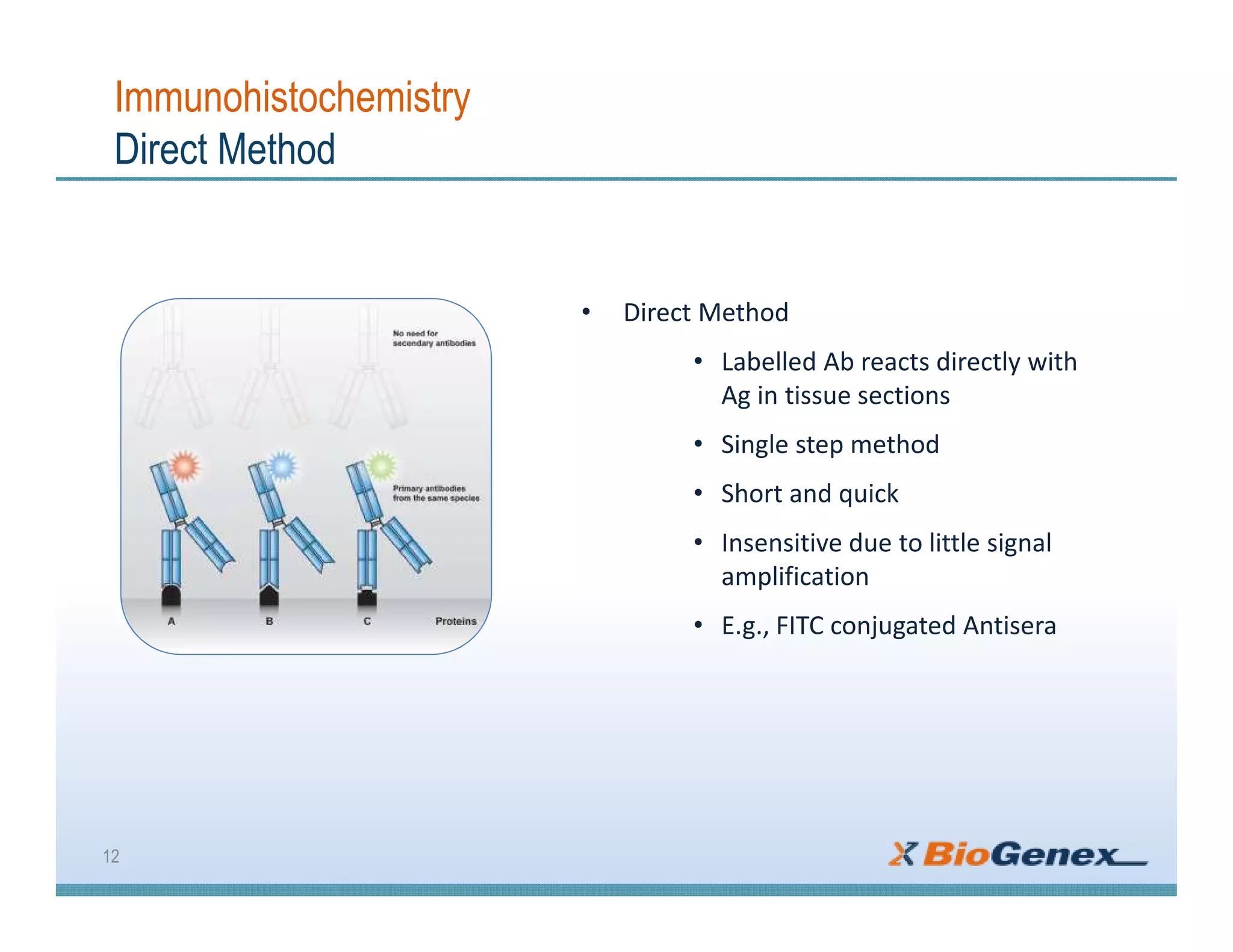
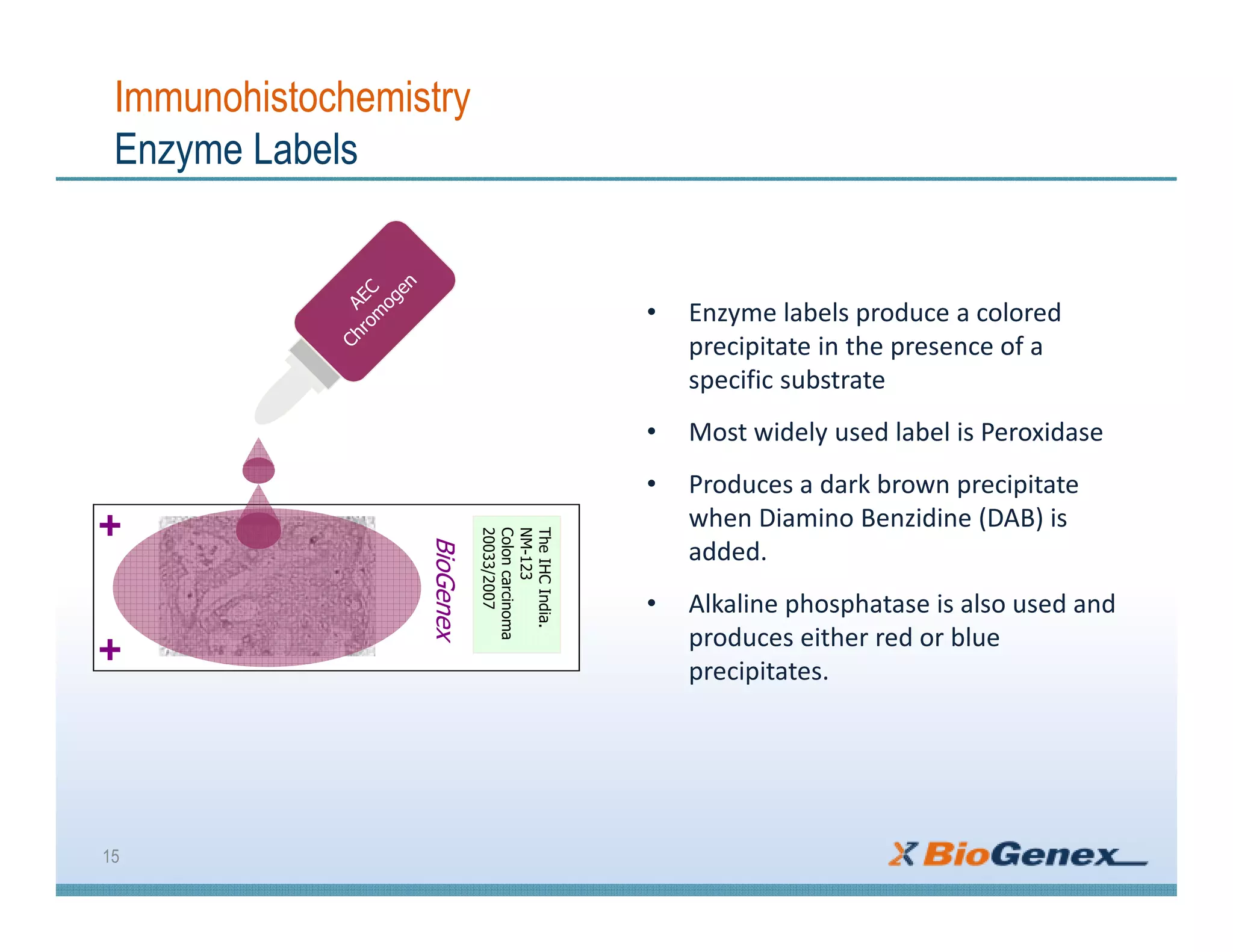
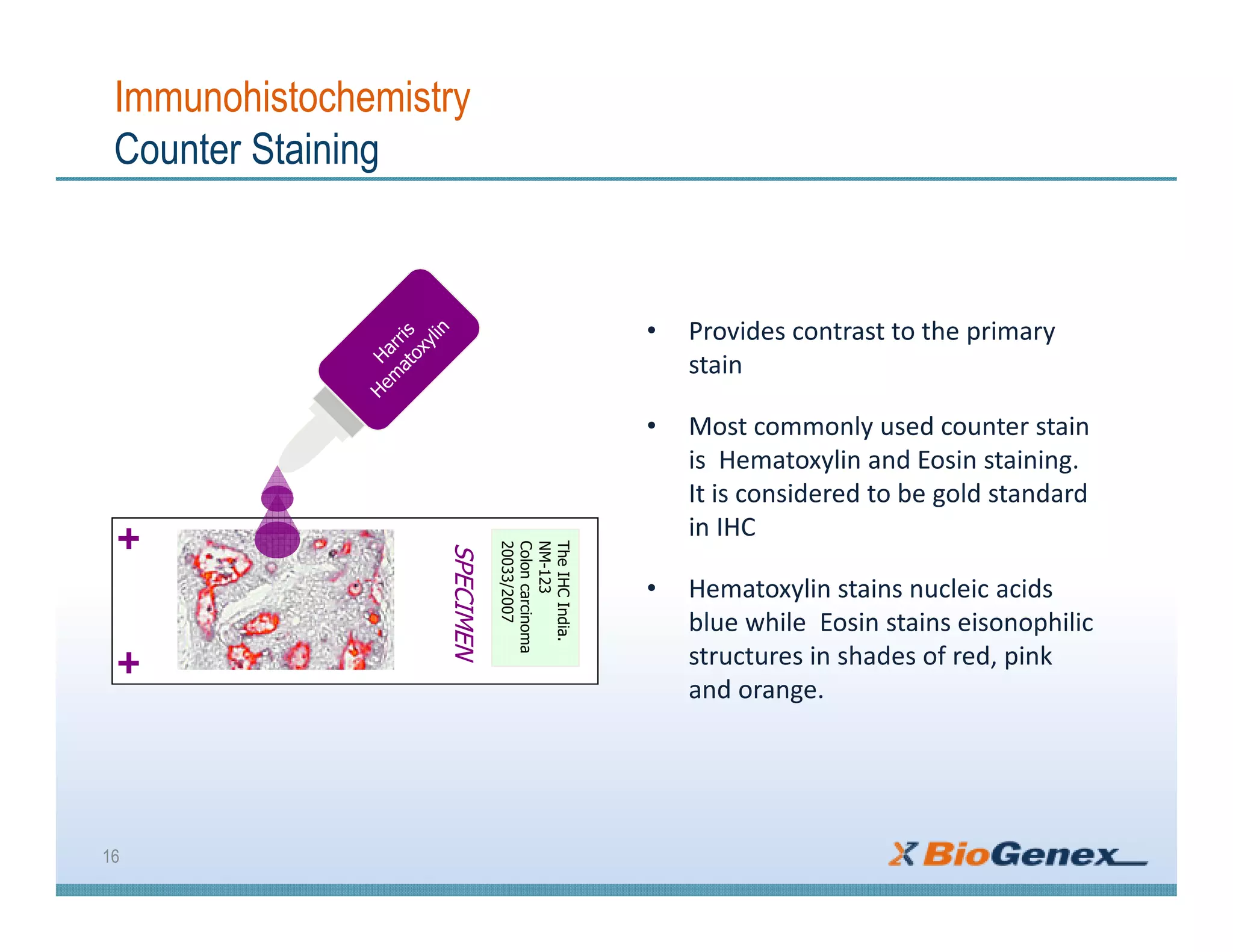
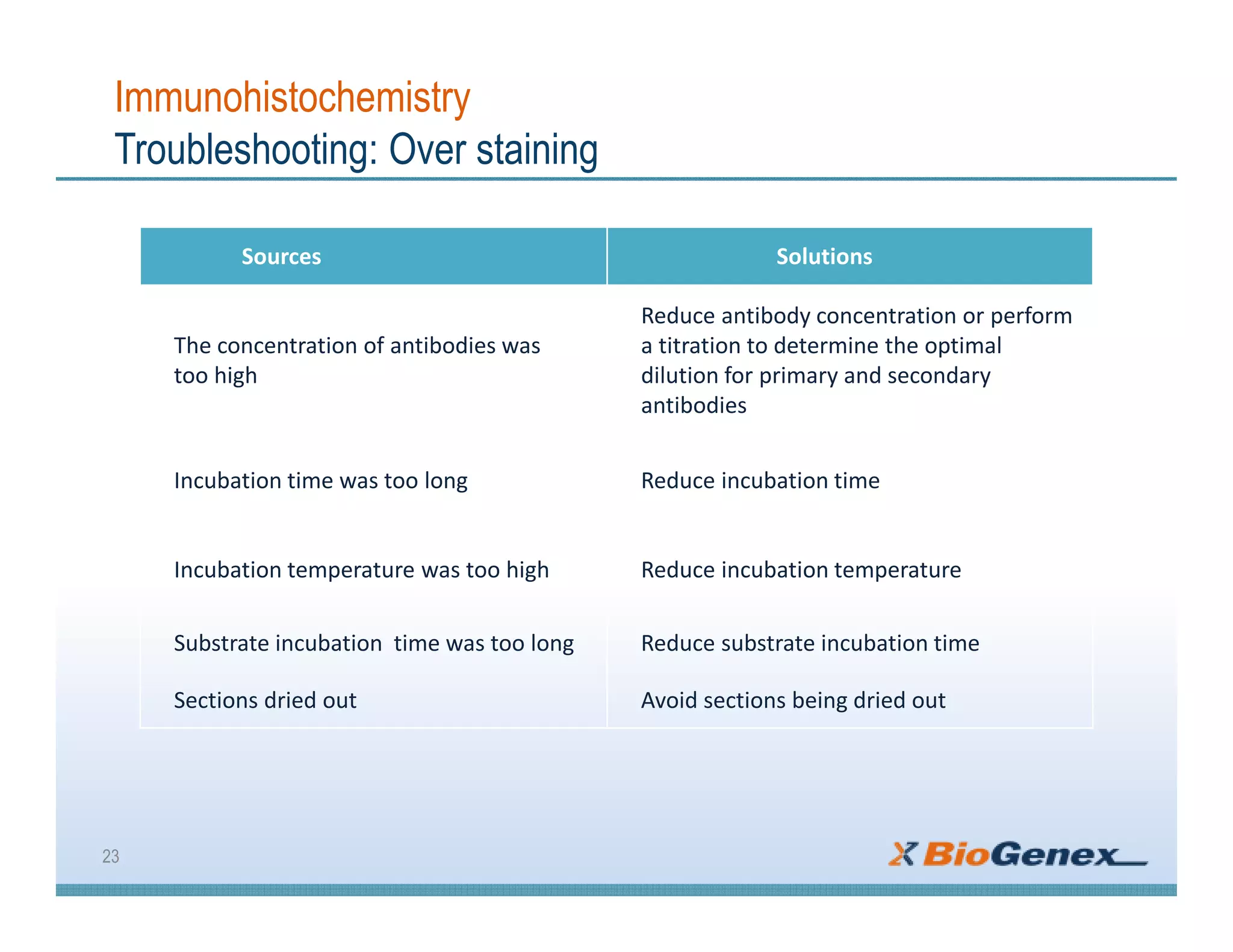
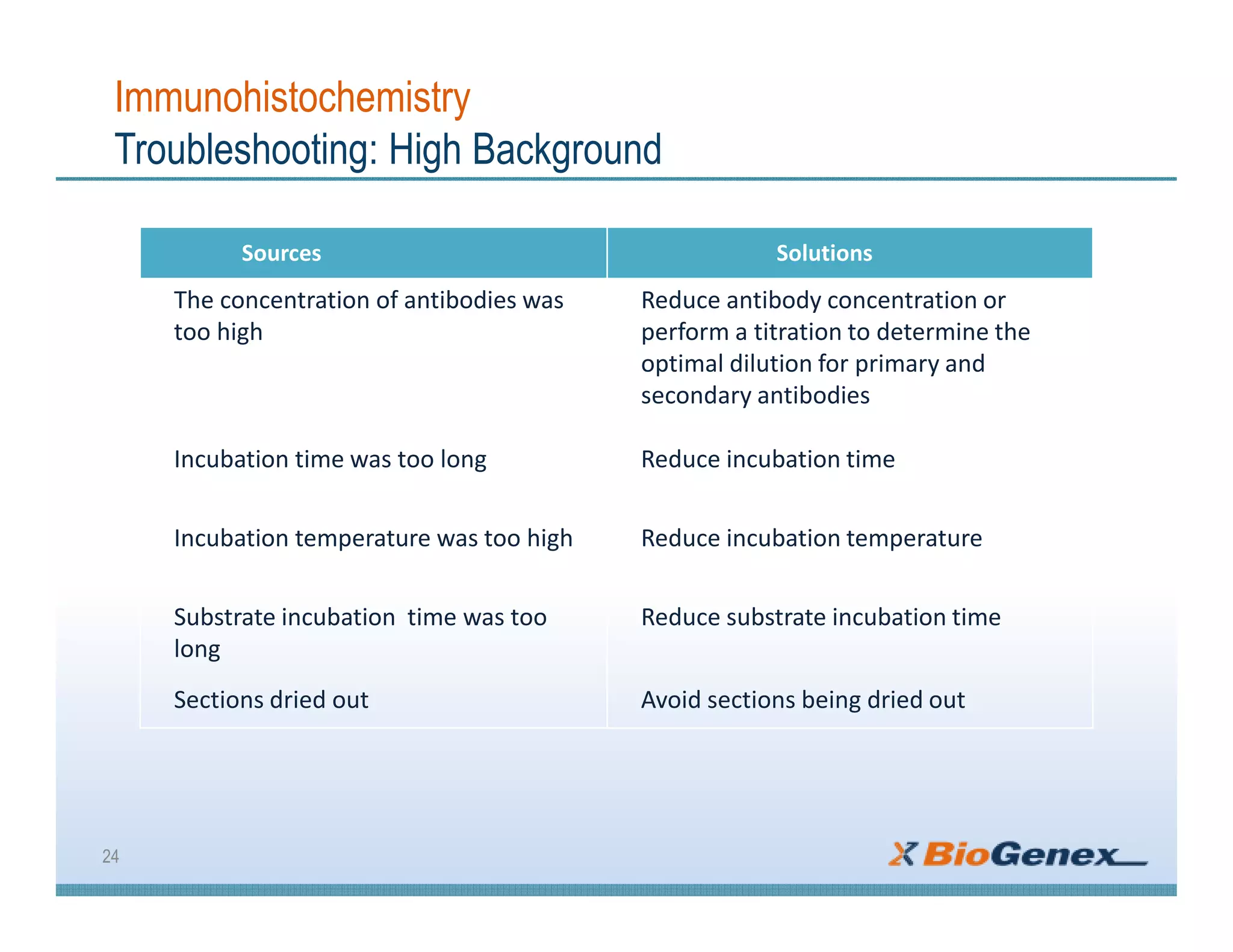
The document provides a comprehensive overview of immunohistochemistry (IHC), detailing its integration of immunology and histochemistry to localize antigens in tissues using antibodies. It outlines the steps involved in IHC, including fixation, slide preparation, antigen retrieval, and staining techniques, while also addressing troubleshooting and automation in IHC procedures. Applications of IHC span various fields such as tumor pathology and neurodegenerative diseases, emphasizing its significance in diagnosing and classifying diseases.