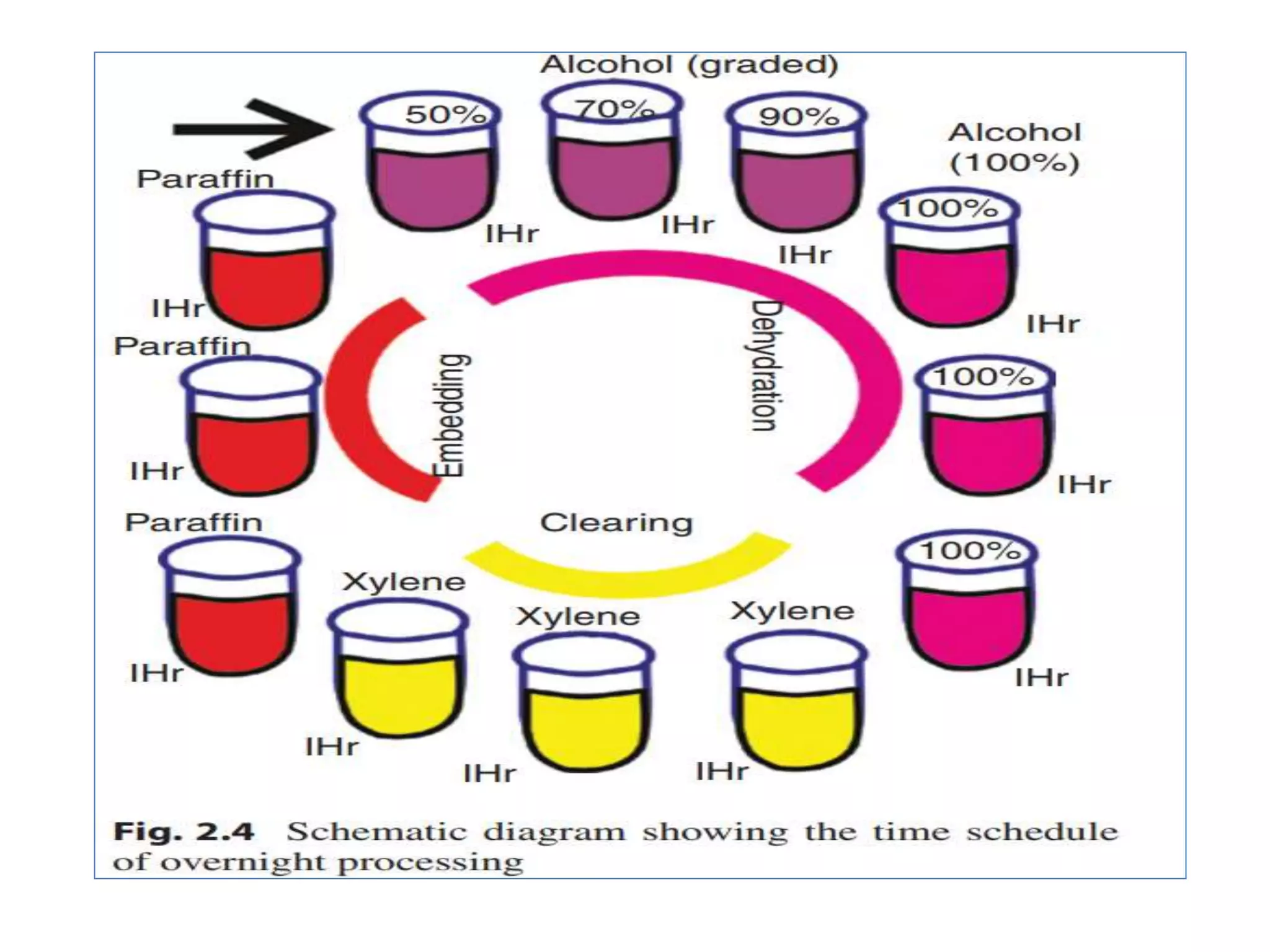
Tissue processing involves removing water from tissue and replacing it with paraffin wax to provide rigidity for microscopic examination. The main steps are fixation, dehydration using increasing concentrations of alcohol, clearing with xylene to remove alcohol, and impregnation with molten paraffin wax. Automated tissue processors complete this process overnight using different stations for each step. Factors like tissue size, agitation, heat, and vacuum pressure influence effective processing. Ethyl alcohol is most commonly used for dehydration, while xylene is used for clearing prior to paraffin wax impregnation and embedding.