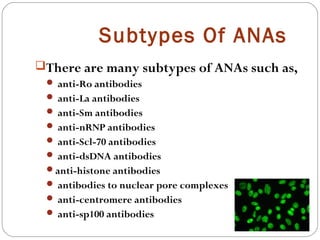
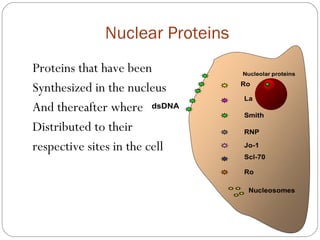
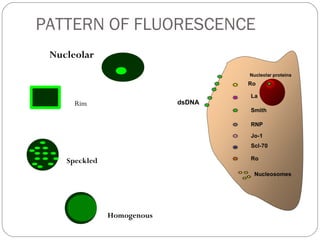
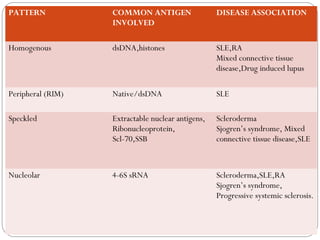
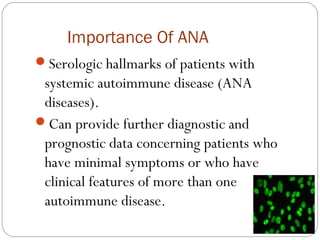
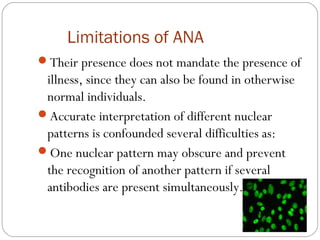
This document discusses antinuclear antibodies (ANAs), which are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. There are many subtypes of ANAs that bind to different nuclear proteins. Indirect immunofluorescence is the reference method for detecting ANAs using three tissues and viewing under fluorescence microscopy, where positive samples show apple-green fluorescence in distinctive patterns associated with particular antigens and diseases. ANA testing is important for diagnosing and managing autoimmune conditions but can also be present in normal individuals so results need accurate interpretation.