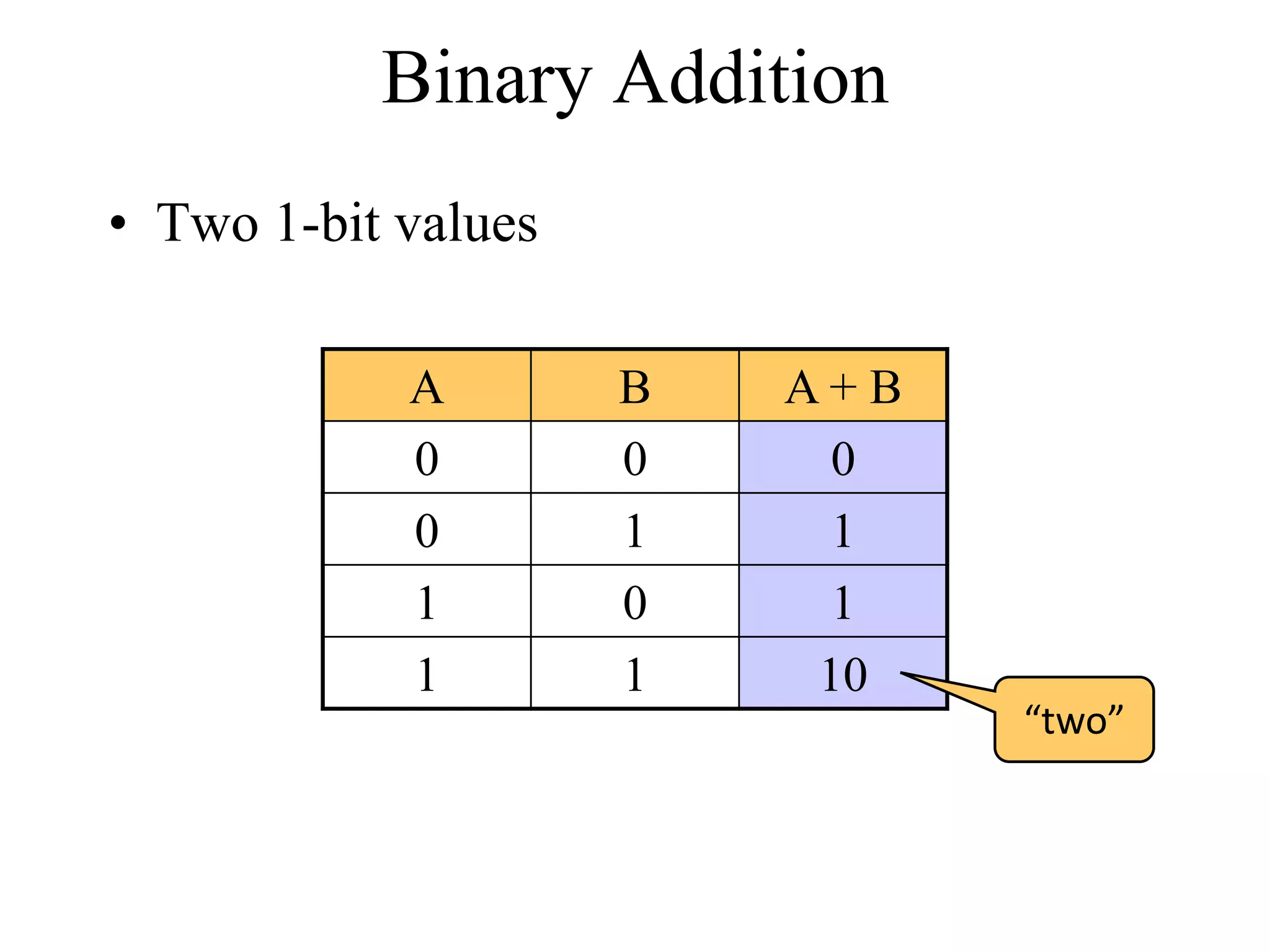
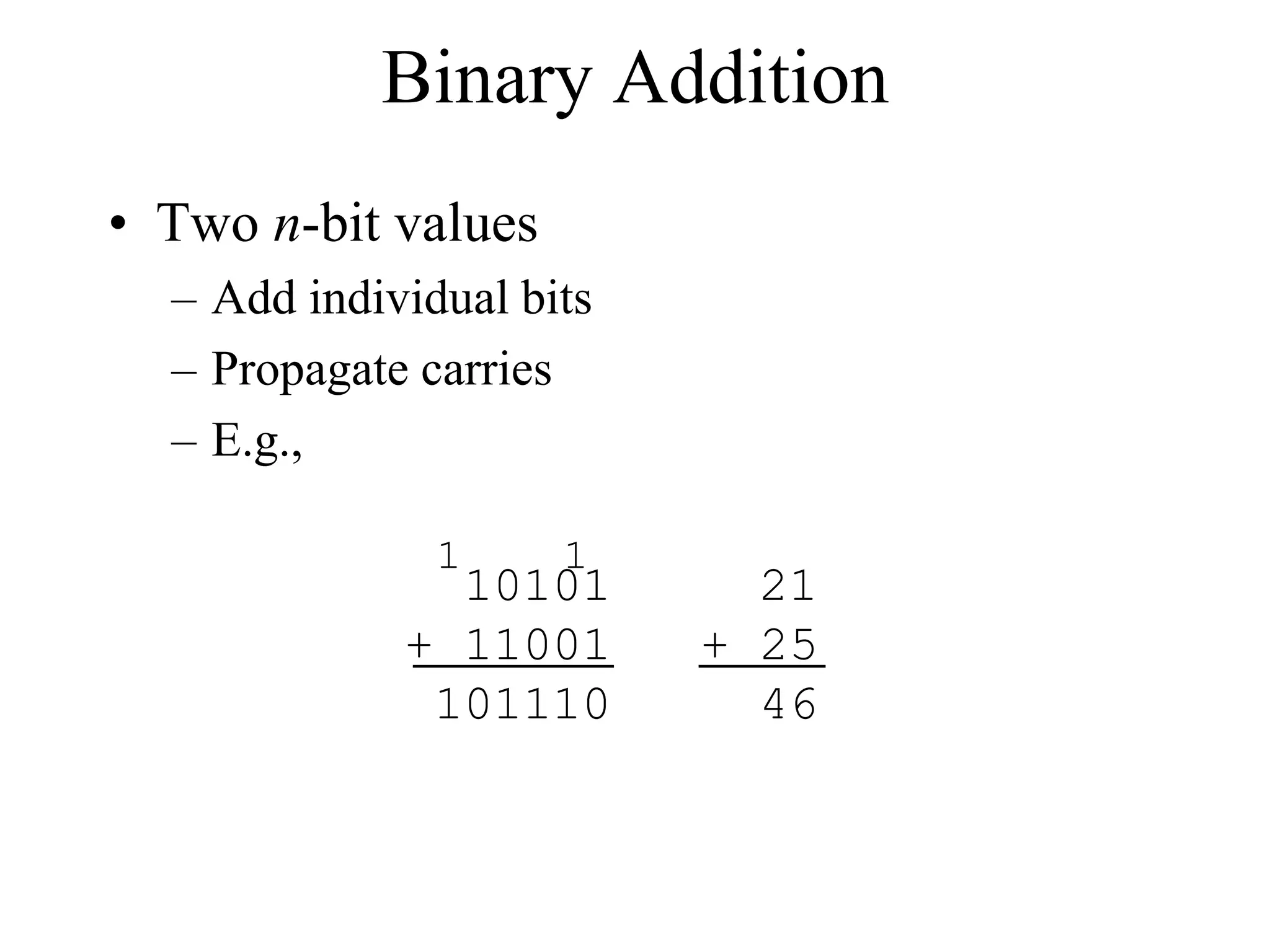
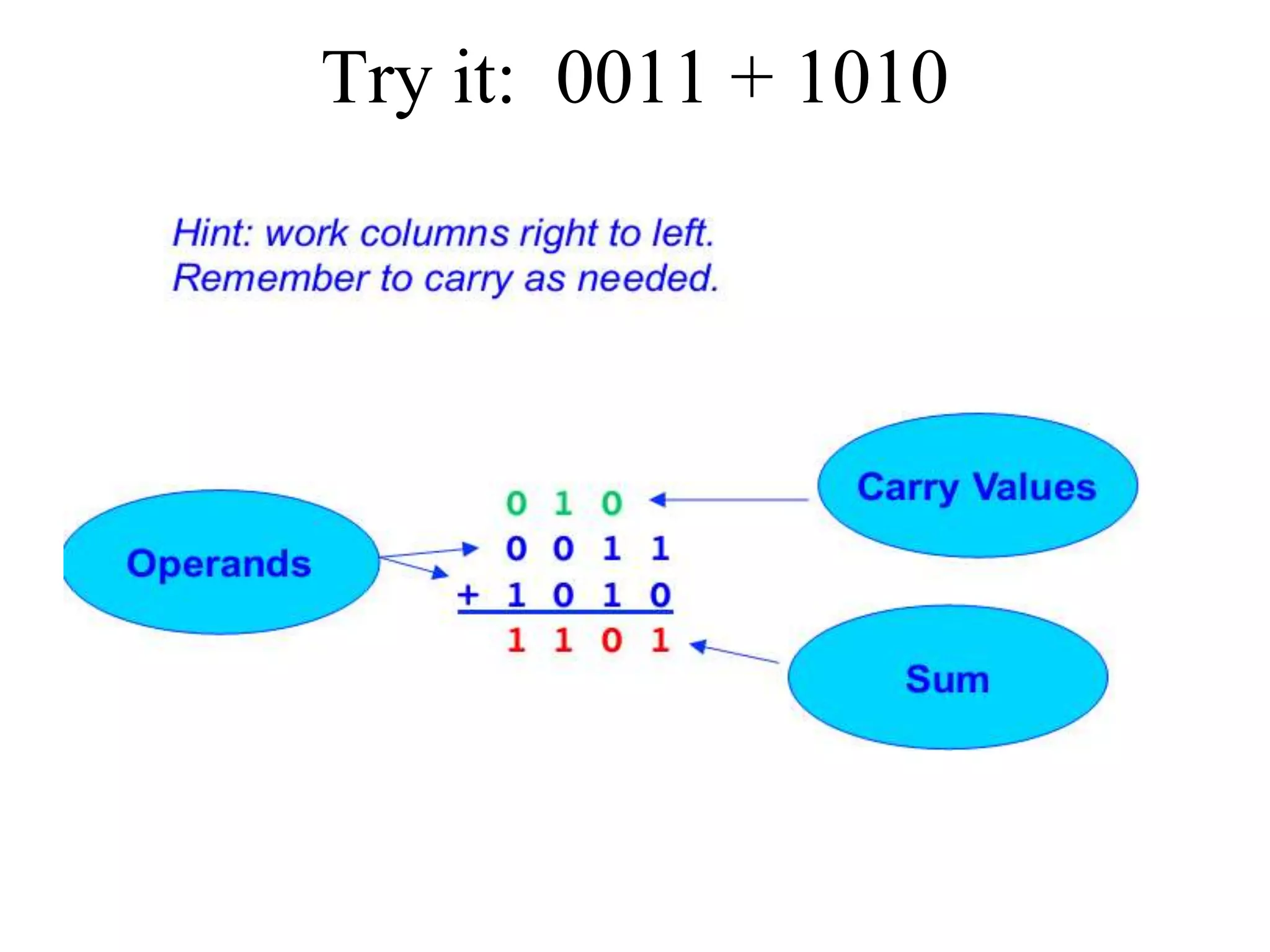
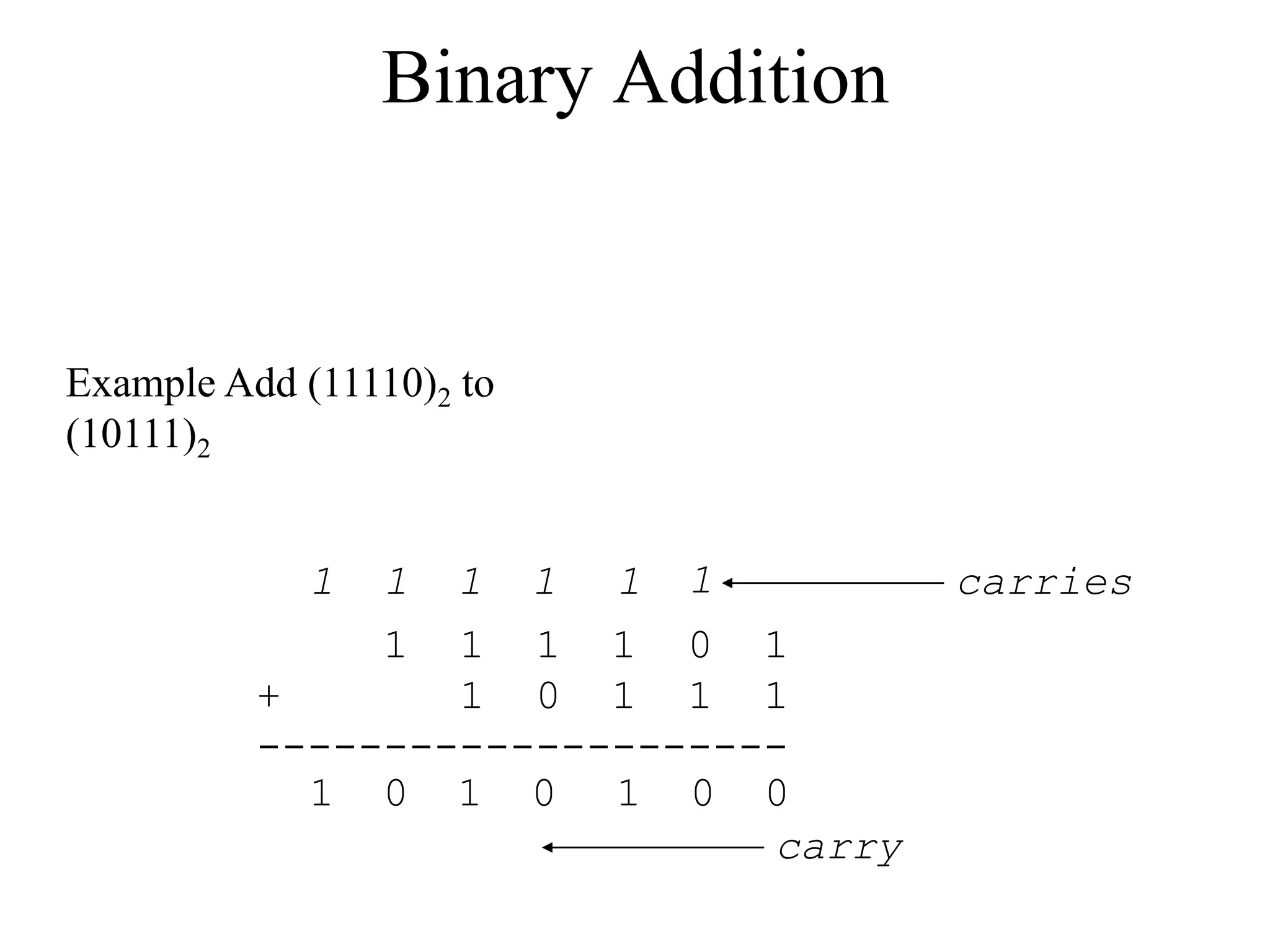
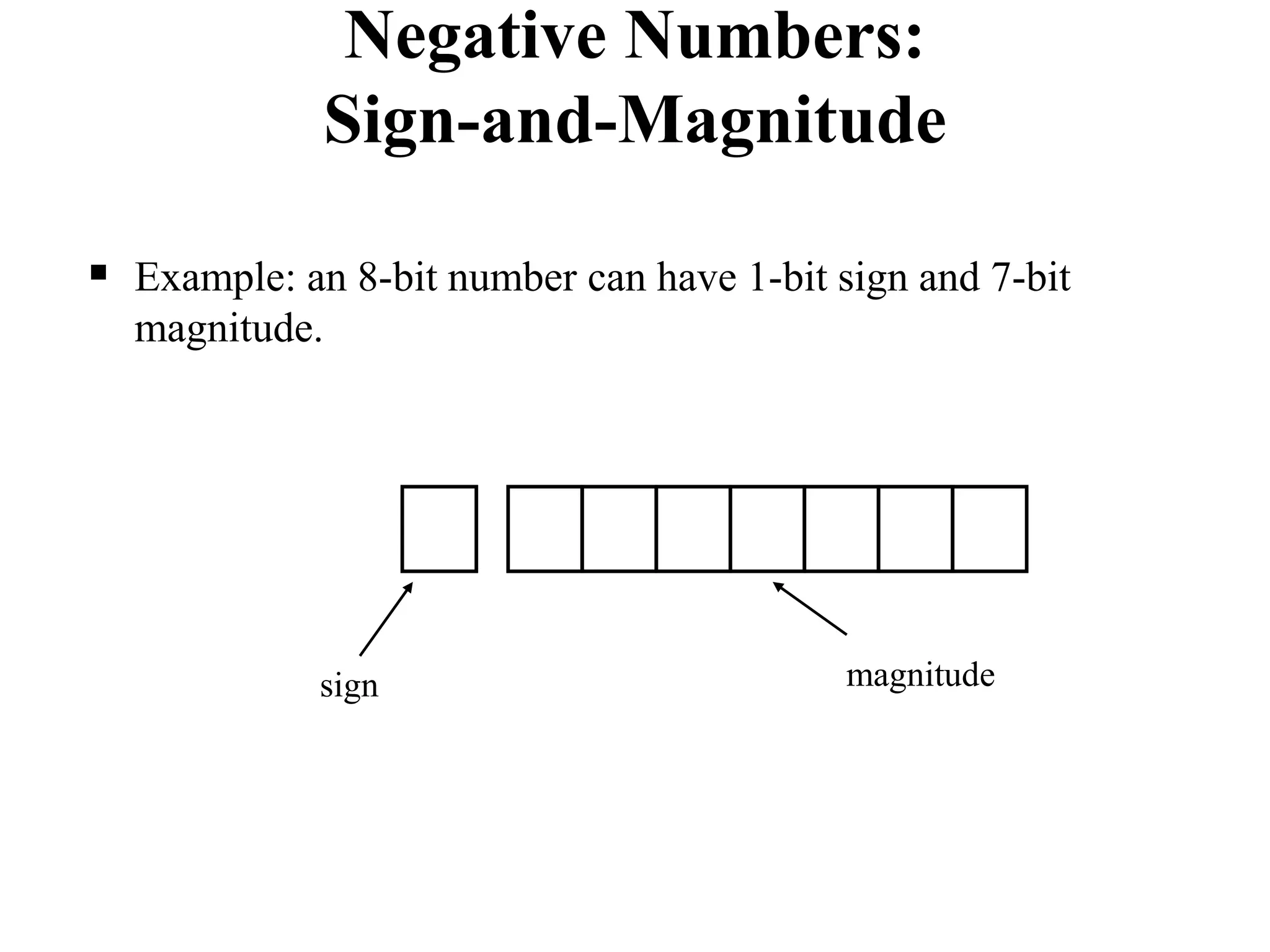
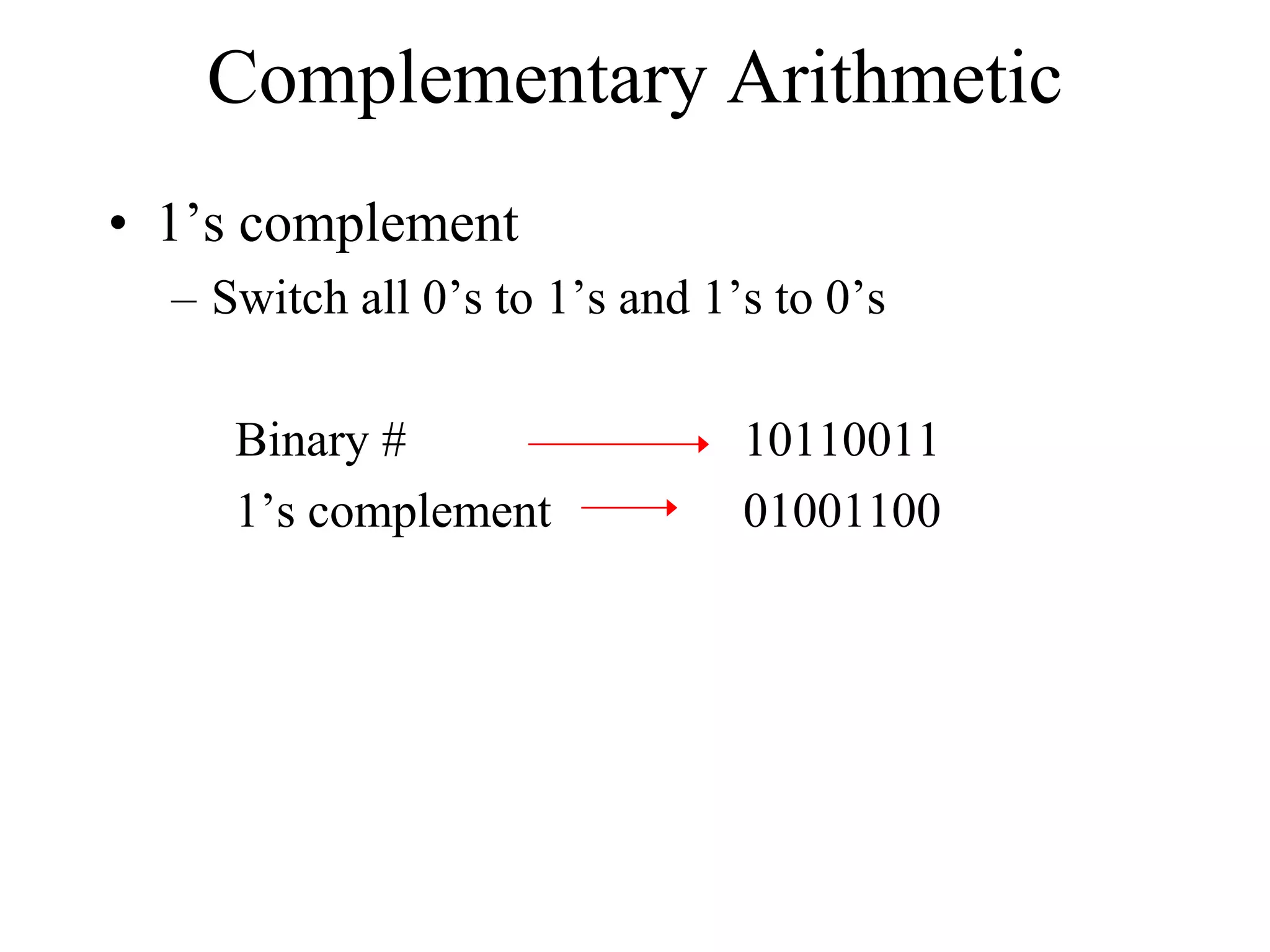
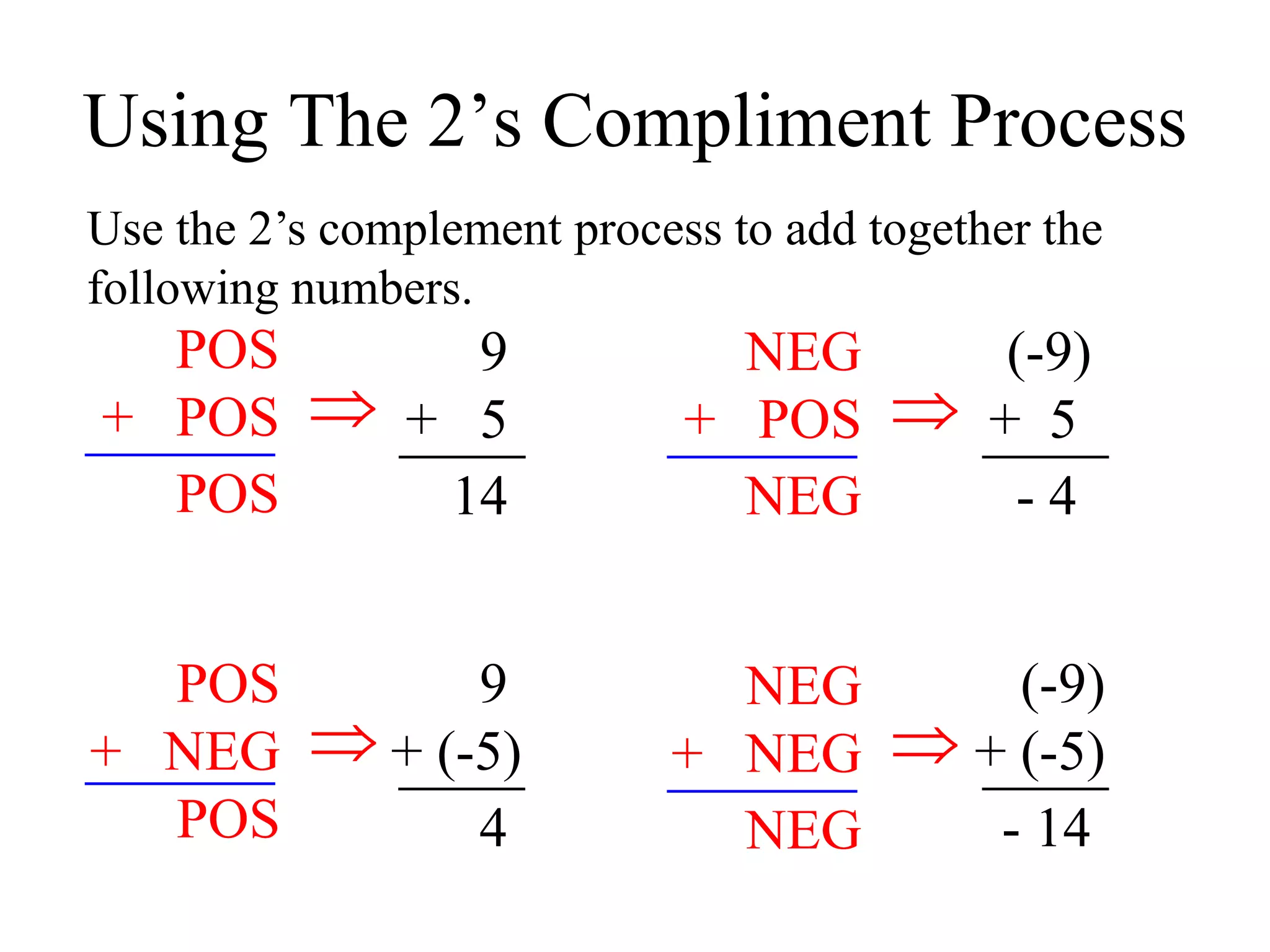
This document discusses computer arithmetic, focusing on binary addition and the representation of both unsigned and signed numbers. It explains the methods of representing signed numbers, including sign-and-magnitude, 1's complement, and 2's complement, along with examples of complementary arithmetic and its application in subtraction. The document also illustrates how to perform addition with both positive and negative numbers using 2's complement.











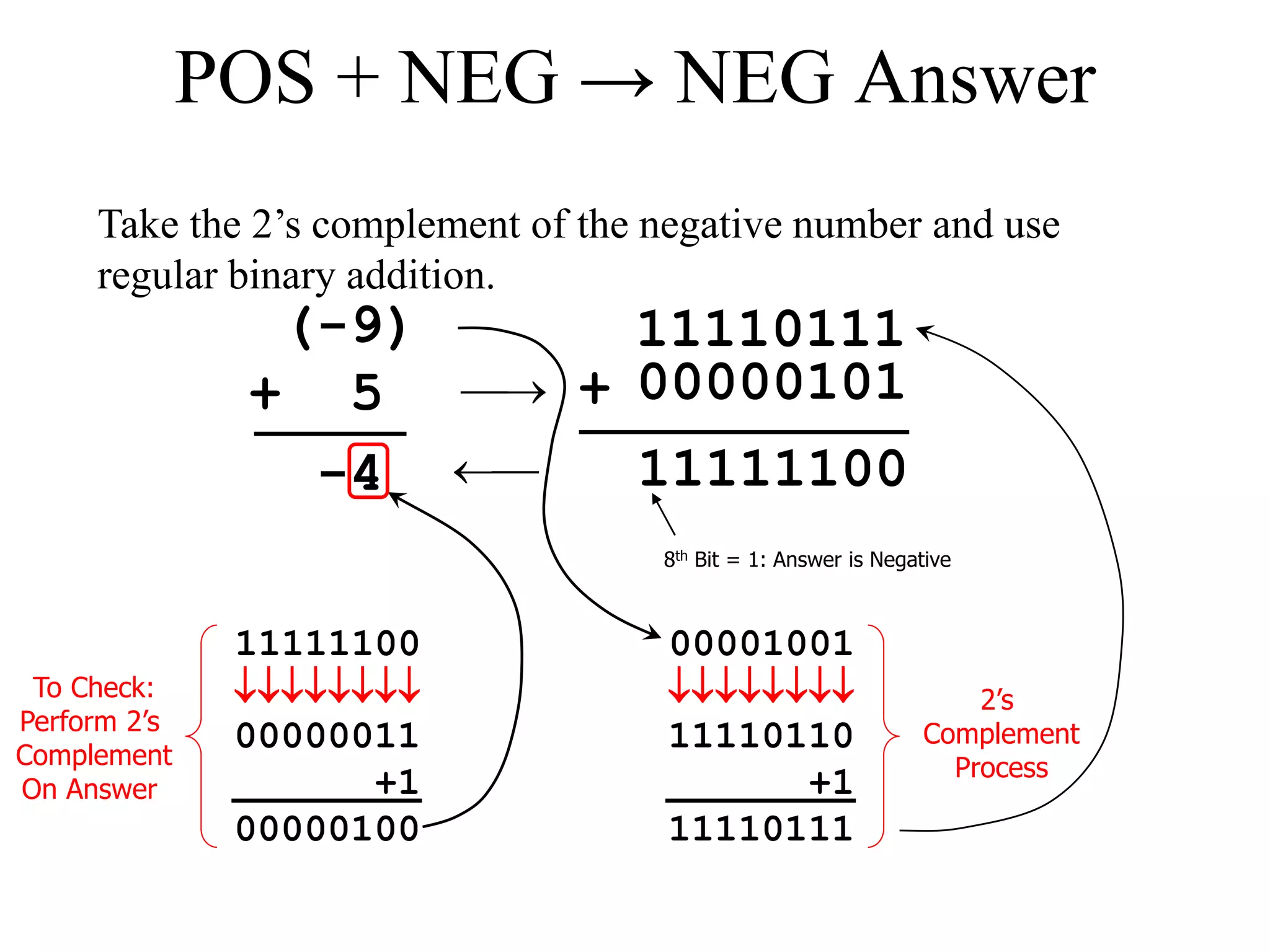
![POS + NEG → POS Answer
Take the 2’s complement of the negative number and use
regular binary addition.
000010019
+ (-5)
4
11111011+
00000101
11111010
+1
11111011
2’s
Complement
Process
1]00000100
8th Bit = 0: Answer is Positive
Disregard 9th Bit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture06computerarithmatic-200416101331/75/Lecture-06-computer-arithmatic-19-2048.jpg)
![NEG + NEG → NEG Answer
Take the 2’s complement of both negative numbers and use
regular binary addition.
11110111(-9)
+ (-5)
-14
11111011 +
2’s Complement
Numbers, See
Conversion Process
In Previous Slides
1]11110010
8th Bit = 1: Answer is Negative
Disregard 9th Bit
11110010
00001101
+1
00001110
To Check:
Perform 2’s
Complement
On Answer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture06computerarithmatic-200416101331/75/Lecture-06-computer-arithmatic-21-2048.jpg)
